Difference Between Book Value vs Market Value
Companies record an asset’s price as book value in the Balance sheet, excluding depreciation. Whereas Market value is the price (lower or higher than the book value) that can be brought when selling off that asset class, or it is the price that the customer offers during the sale of the assets.
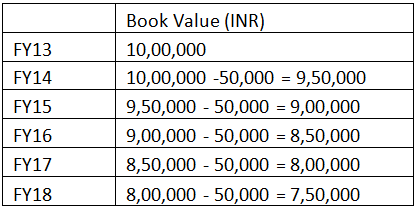
For example, ABC Co. Ltd purchased Machinery for INR I,00,0000 during FY13. With a straight-line depreciation of INR 50,000 per year, the Book value for the next four years would be as follows:
Thus, during the end of FY18, the calculated book value of the machine, excluding depreciation, was INR 7,50,000. The original cost of the machinery during FY13 stood at INR 10,00,000. A depreciation of INR 50,000 per year was charged due to the erosion caused by the wear and tear of the machine or the cost of its functioning. The market scenario (Buyer sentiment) may not be the same during the Machine’s selling. Suppose the Market price for the same machinery depends upon the Machinery and Demand and supply conditions.
For example, the list of buyers may quote a price ranging from INR 7 00,000 to INR 7,30,000, which is less than the book value by INR (20,000 to 50,000). If the Demand for second-hand machinery is high and the market is willing to pay INR 8, 00,000 then the Difference between Book Value and Market value is positive. There is a scope of profitability in the second instance.
Financial markets decide a particular stock price depending on the company’s fundamentals and the business’s earning potential in the coming years. The price is called the ‘Market Value’ of the stock. Whereas, Book value, on the other hand, is the theoretical representation of an asset class that is recorded in the financial statement. In case of liquidation of the business, the excess Assets left over after paying all the liabilities is the Book value or the value the shareholders would receive in the full and final settlement.
Book Value vs Market Value (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 difference between Book Value vs Market Value
Key Differences Between Book Value vs Market Value
Both Book Value vs Market Value are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences:
- Companies record the price of an asset class as book value, while buyers or investors discount a particular asset class as market value.
- The amount the Investors will get (All assets minus all liabilities) during liquidation is termed the Book value. The Market price whereas decided by the class of investors or the traders who control the financial markets as a whole and value an asset class based on the fundamentals of that particular asset class.
- The fluctuation in prices is very common in the case of the Market Value, whereas in the case of Book value, the price tends to move during each quarter as per the accounting treatment done by the Accountants.
- The Financial Market plays an important role in determining the Market value, whereas only the fundamentals of the particular Asset class play an important role during the calculation of Book value.
- Depreciation is integral to the Book value, whereas depreciation hardly plays any part in market value. Only the investor’s sentiment primarily drives the price movement.
Head To Head Comparison Between Book Value vs Market Value
Below is the topmost comparison between Book Value vs Market Value:
| The Basis of Comparison | Market Value | Book value |
| Related to | Related to the current price a buyer is willing to pay. The value prevalent in the Financial market, or is the price of the Stock as valued by the group of investors or traders. | Related to the Purchase price, less depreciation is recorded on the Balance sheet. The price which the Share-holders will get during the liquidation of the Business |
| Meaning | The price is decided after the demand and supply constraints, and the price movement is cyclical; it purely depends upon the psychology of the buyer and seller and the sentiment of the Financial markets. Sometimes, the buyer is ready to pay higher than the book value when the demands are more or the class of investors thinks the Fundamentals are robust. The Business would deliver higher profitability in the coming years. For example, in the Indian stock market, the market price of a Private Banking stock with good growth and good management (HDFC Bank) usually trades more than 4.8 to 5 times the book value. | The price shown in the Financial statement i.e. the Cost price less any Depreciation or Amortization, is known as book value. Fixed assets are subject to depreciation charges, while intangible assets such as goodwill are subject to amortization charges. In other words, the financial statements theoretically show the price. |
| Depreciation | Market Value depreciation is not accountable in most cases, but the buyer and seller decide the valuation, and it is dependent on demand and supply. | Depreciation is considered when the value of the assets is put into the records. This provides an estimation of the price of the assets that the company would be showing to the Investor’s group, the suppliers, and the other related parties with which the business deals. |
| Calculations | Market price = Average Price Earnings multiple of the Sector * Earning Per Share (approximately) | Book value = Cost price of the Assets less Depreciation and Amortization.
Or (Assets – Liability )/ Number of shares outstanding |
| Financial Market | The Market value is entirely dependent on the Financial market. | Does not have any relation to the Financial markets. |
Conclusion
The Book value vs market value is are prime driver in determining the value of an asset class. However, considering a higher market value over the book value is considered good for a particular asset class, and vice versa.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top 9 differences between Book Value and Market Value. Here, we take the difference between Book Value vs Market Value with examples, infographics, and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –