Introduction
Is your Ubuntu system failing to boot? Staring at a frustrating blank screen or a missing GRUB menu can leave you feeling helpless. But before you resign yourself to reinstalling the entire operating system, there’s a hero waiting in the wings: Boot Repair. Boot Repair is a free and user-friendly tool designed explicitly for Ubuntu to tackle common bootloader issues. Whether you’ve recently installed Windows alongside Ubuntu, experienced an upgrade gone wrong, or accidentally messed with your system partitions, Boot Repair can diagnose and fix the problem, getting your system back up and running in no time.
Table of Contents
What is Boot Repair Ubuntu?
Boot Repair for Ubuntu is a free graphical application that helps diagnose and fix bootloader issues on Ubuntu systems and other Linux distributions. It simplifies the often complex task of bootloader repair, making it accessible even to users who aren’t familiar with the technical details. It offers various functions, such as reinstalling GRUB, resolving boot loops, repairing boot entries, and restoring the boot sector.
Think of it as a mechanic for your computer’s startup process. The bootloader is a crucial program that tells your computer which operating system to load when it starts up. If this program gets corrupted or misconfigured, your system might not boot properly. Boot Repair acts as a troubleshooter, identifying the problem and applying fixes to get your Ubuntu system booting again.
Installing Boot Repair Ubuntu
To install Boot Repair on your system, you need to have Ubuntu installed. Refer to this detailed, step-by-step guide on installing the Ubuntu link.
To install Boot Repair on Ubuntu, follow these steps:
- Open a Terminal: To open a terminal window, press Ctrl+Alt+T.
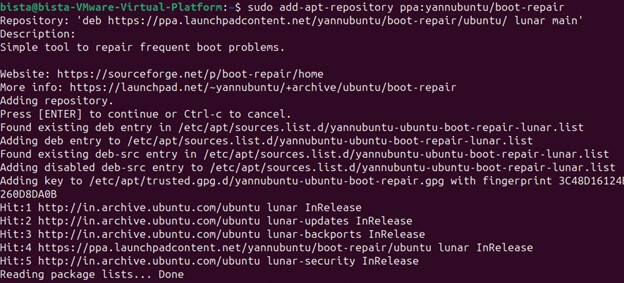
- Add the Boot Repair PPA: Enter the following commands to add the Boot Repair PPA (Personal Package Archive) to your system:
“sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair”
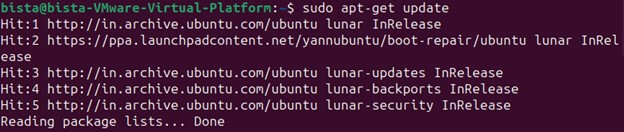
“sudo apt-get update”
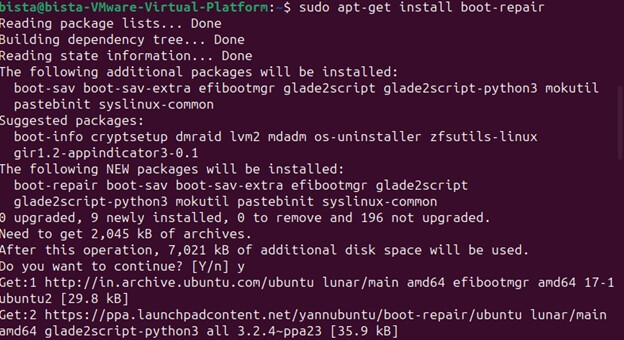
- Install Boot Repair: Once you have added the repository, you can install Boot Repair by simply running the following command:
“sudo apt-get install boot-repair”
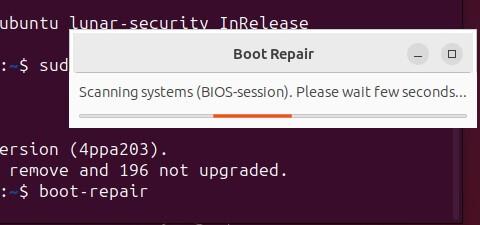
- Launch Boot Repair: After completing the installation, start Boot Repair by entering the following command:
“boot-repair”
- Use Boot Repair: The Boot Repair application has a user-friendly interface. To identify and resolve any boot-related problems on your system, adhere to the instructions shown on the screen.
After following these steps, Boot Repair will be installed and ready to fix boot problems on your Ubuntu system.
Getting to Know Boot Repair Ubuntu
Boot Repair is a powerful utility designed to help you diagnose and fix boot-related issues on Ubuntu and other Debian-based Linux distributions. Here’s how to get to know Boot Repair:
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): Boot Repair provides a user-friendly GUI, making it accessible even to users who are uncomfortable with command-line tools.
- Bootloader Repair: It specializes in repairing issues related to the bootloader, such as GRUB. It includes fixing bootloader corruption, reinstalling GRUB, or configuring it to boot multiple operating systems.
- Automatic Detection: Boot Repair simplifies troubleshooting by automatically detecting bootloader, partition table, and boot configuration issues.
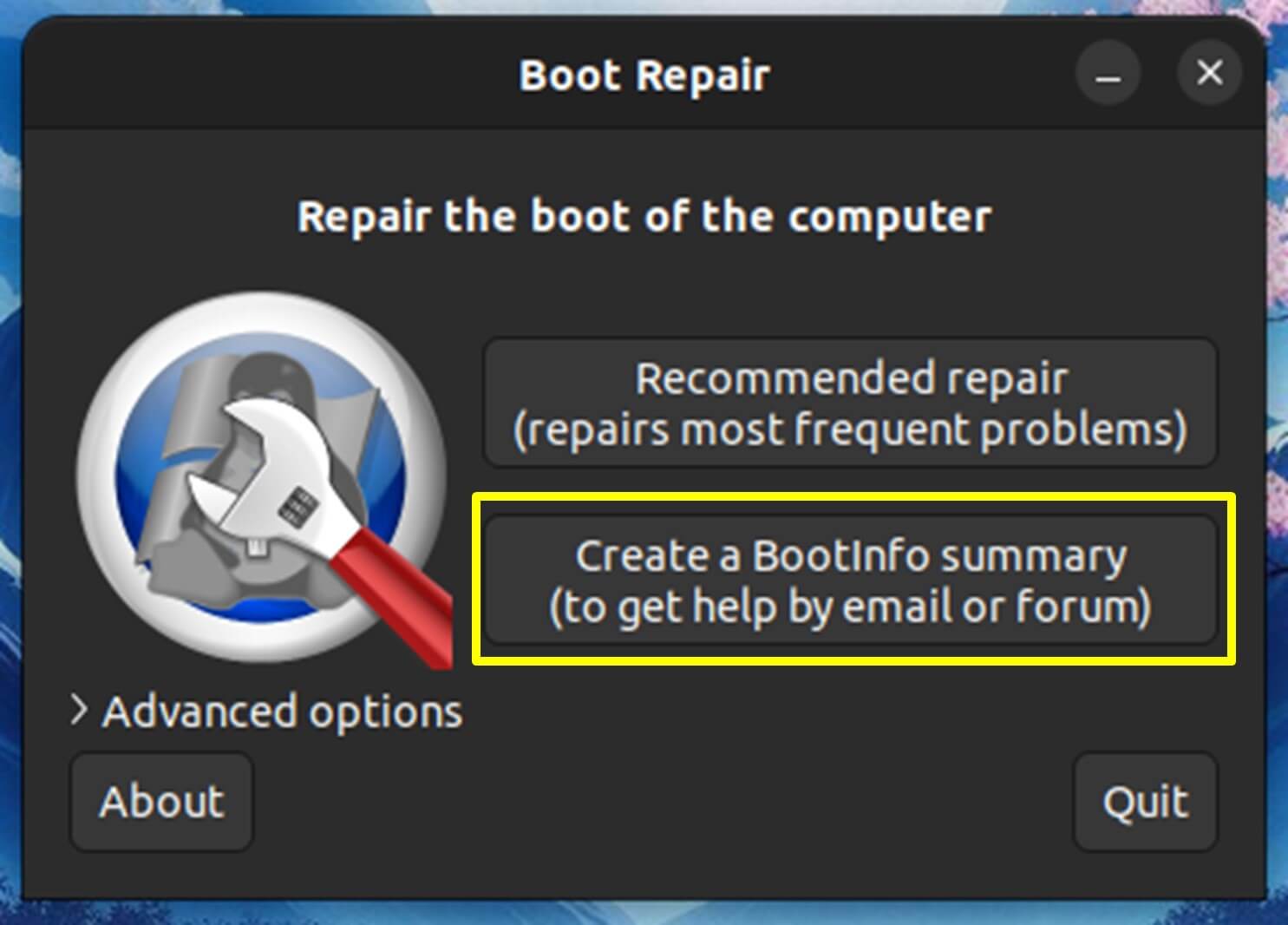
- Boot Information: The tool provides a “Create BootInfo” feature that generates a report on your system’s boot configuration. This report can help you diagnose issues and seek help on forums.
- Recommended Repairs: After analyzing your system, Boot Repair may suggest repairs or allow you to choose from various repair options, which may be helpful for less experienced users.
- Advanced Options: For more experienced users, Boot Repair provides advanced settings and options to customize the repair process and address specific issues.
- Live USB/CD Compatibility: You can use Boot Repair on a live Ubuntu USB or CD to help restore your system when it doesn’t boot.
- Community Support: Boot Repair is widely recognized within the Ubuntu community and is a valuable tool for resolving boot problems or helping others troubleshoot their systems.
Boot Repair can resolve boot-related issues more easily and efficiently, ensuring your Ubuntu system starts up reliably.
Common Boot Issues Solved by Boot Repair Ubuntu
Boot Repair for Ubuntu may help with a variety of common boot issues, including as
- Corrupted Bootloader (GRUB): Boot Repair can repair or reinstall the GRUB bootloader, which is crucial for the boot process. It is particularly helpful when GRUB is corrupted or missing.
- Dual Boot Problems: If you have a dual-boot system with Ubuntu and another operating system (such as Windows), Boot Repair can resolve issues where one OS fails to display properly in the boot menu or boot.
- Boot Partition Errors: When the boot partition is misconfigured, damaged, or not set appropriately, Boot Repair can help you reconfigure it and ensure proper booting
- Missing or Invalid Boot Entries: It can detect and repair missing or incorrect entries in the bootloader configuration, allowing you to boot into all installed operating systems.
- Booting to a Grub Rescue Prompt: If you encounter the “grub rescue” prompt, Boot Repair can help you recover and restore normal booting.
- Partition Resizing and Relocation: Changing the size or location of your partitions can lead to boot issues. Boot Repair can reconfigure the bootloader to accommodate these changes.
- UEFI/BIOS Compatibility: Boot Repair can help configure the bootloader for compatibility and proper booting on UEFI and BIOS systems.
- Boot Timeout and Default OS: It can set the default OS and boot timeout settings, allowing you to customize the boot menu behavior.
- Boot Information Report: Boot Repair can generate a “BootInfo” report with detailed information about your system’s boot configuration. This report can be helpful when seeking support forums.
- Network-Enabled Repairs: Boot Repair can establish an internet connection to update bootloader components and enhance the repair process.
How to Use Boot Repair Ubuntu?
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Boot Repair in Ubuntu to fix common boot-related issues:
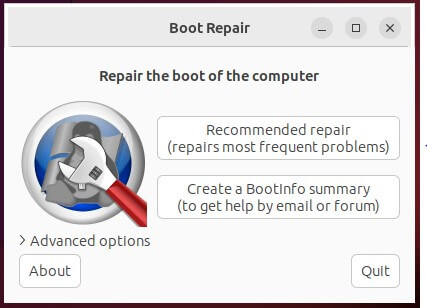
- Running the “Recommended Repair”:
- When you launch Boot Repair, it will automatically scan your system to detect any issues related to booting.
- After the analysis is finished, it will offer suggestions for any necessary repairs.
- To execute the “Recommended Repair,” click the relevant button in the Boot Repair interface.
- Boot Repair will apply recommended fixes, such as reinstalling GRUB, updating settings, and adjusting as needed.
- Reviewing the Repair Report
- After the recommended repair process is complete, Boot Repair will generate a detailed report.
- This report includes details of the repairs carried out and may contain diagnostic information.
- Reviewing this report is crucial as it can help you understand any changes and address potential issues.
- You can save this report for reference or when seeking help from others on support forums.
- Rebooting Your System
- Once the recommended repair has been executed, you can reboot your system.
- Use the following command in the terminal to reboot your system:
sudo reboot
- After the reboot, your system should ideally start without previous boot-related issues.
Boot Repair simplifies the process of repairing common boot problems in Ubuntu, making it a valuable tool for ensuring a reliable and functional boot process.
Advanced Boot Repair Options
Boot Repair offers advanced options for users who want more control over the repair process or need to address specific boot-related issues. Here’s a breakdown of these advanced options:
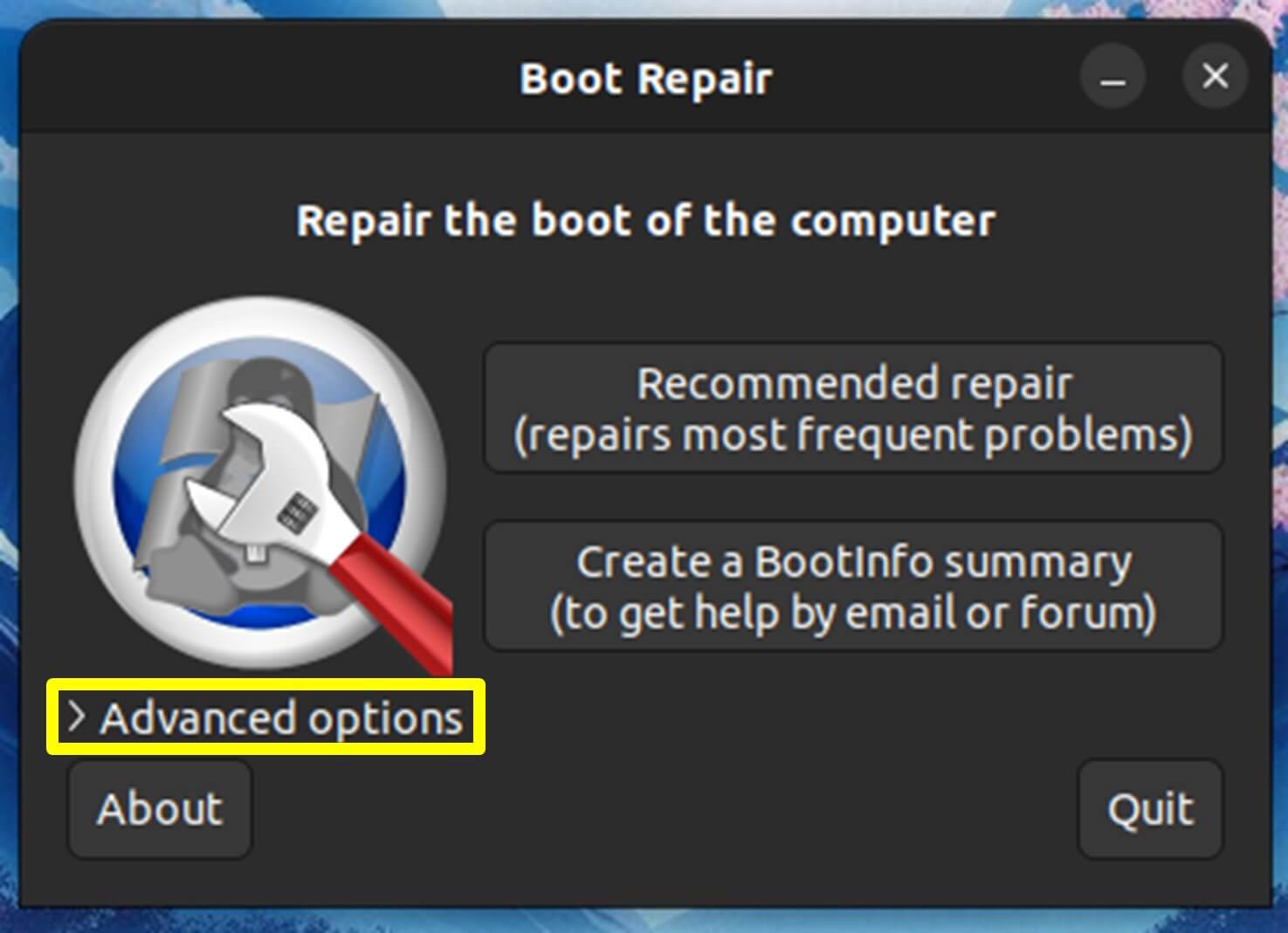
- Accessing Advanced Options
Once you initiate Boot Repair in Ubuntu, the advanced options become accessible by selecting the “Advanced options” tab or menu found within the Boot Repair interface.
- Choosing Specific Repair Options
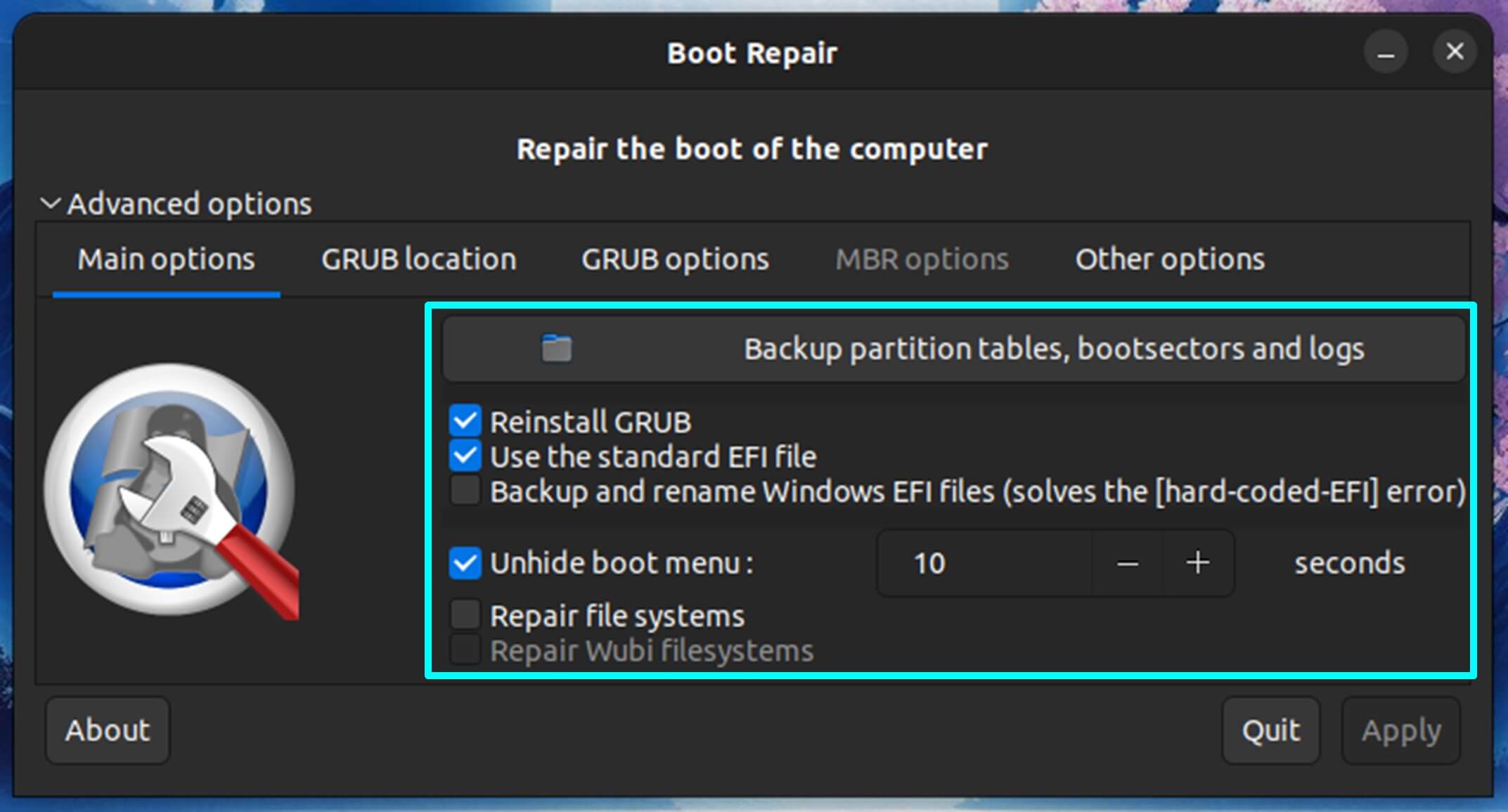
You can select specific repair options tailored to your issue within the advanced options. Some common advanced repair options include:
- Reinstall GRUB: This option allows you to reinstall the GRUB bootloader explicitly, which is essential when the issue is related to GRUB.
- Restore MBR (Master Boot Record): Use this option to repair a corrupted Master Boot Record common in BIOS systems.
- Purge GRUB: This option might be helpful if you need to delete and reinstall GRUB.
- Restore Boot Sector: When the boot sector of a specific partition is damaged or missing, this might be handy.
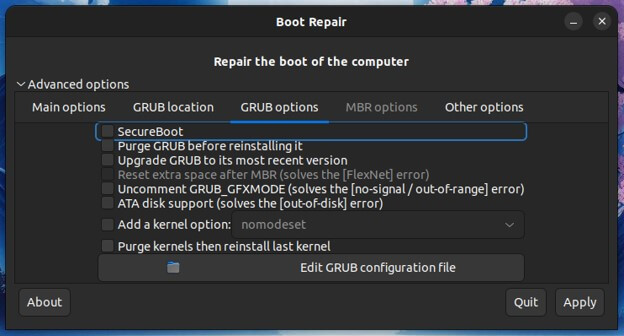
- Tweaking Grub Settings
- Boot Repair allows advanced users to fine-tune GRUB settings, customize options, configure timeout values, and set the default operating system to boot.
- You can access the GRUB configuration file and make manual changes if needed, though this should be done cautiously.
- Performing Custom Boot Repairs
- If the recommended and advanced repair options don’t solve your boot issue, you can try custom boot repairs for more specific problems.
- Custom repairs allow you to configure and repair your bootloader settings manually. This is typically for experienced users who understand the intricacies of bootloaders and partition configurations.
Boot Repair offers advanced options that give users greater flexibility and control over the repair process when they better understand their boot problems. However, it’s crucial to be cautious when using these advanced options, particularly when manually modifying the bootloader configuration. Any incorrect settings can lead to additional issues, so it’s essential to exercise caution.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
When using Boot Repair on Ubuntu, follow these safety precautions and best practices:
- Backup Data: Before making any changes, it is essential to back up your important data to prevent any loss in case something goes wrong.
- Understand the Process: Familiarize yourself with Boot Repair’s features and options to make informed decisions during the repair process.
- Use Default Settings: In most cases, stick to Boot Repair’s default settings unless you have a specific reason to change them.
- Internet Connection: During the repair process, Boot Repair may require package downloads. Please make sure that you are connected to the internet.
- Keep a Record: Take note of any changes made by Boot Repair, such as partition modifications or configuration updates.
- Read Documentation: Consult official documentation or community resources for guidance and troubleshooting tips.
- Avoid Forceful Actions: Don’t force any actions unless you’re certain it’s necessary, as it could worsen the situation.
- System Updates: Ensure your system is up-to-date with Ubuntu updates before using Boot Repair.
- Reboot Gracefully: Reboot your system gently after repair and verify that the boot issue is resolved.
Conclusion
When it comes to troubleshooting and fixing boot-related issues on Linux systems, Boot Repair for Ubuntu is an essential tool. It offers a user-friendly interface that automatically detects and resolves problems that can prevent your system from starting. Users can effectively and safely recover their system’s boot functionality by following safety precautions, understanding the process, and keeping data backups. Boot Repair simplifies the often complex task of managing bootloaders, making it a valuable utility for ensuring Ubuntu’s smooth and reliable operation and other Linux distributions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Boot Repair Ubuntu” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,