Updated July 11, 2023
What is Break-Even Point in Accounting?
In accounting, the term “break-even point” refers to the level of production or sales at which a particular company neither incurs any loss nor generates any profit. In other words, a company generates just enough revenue to meet all its expenses, so it doesn’t earn any profit. Mostly it is expressed in terms of the number of units.
Explanation of B.E.P in Accounting
Accounting is primarily used for determining the level of production or sales which should be achieved to avoid any losses due to core business operations. The break-even analysis is very important from the perspective of the start of planned capacity expansion or the launch of a new product line. The analysis indicates what production level is necessary to justify the capacity expansion or new product line.
How to Calculate Break-Even Points in Accounting?
Accounting can calculate by dividing the total fixed production costs by the difference in the selling price and variable cost for each unit. Mathematically it is represented as,
Examples of B.E.P in Accounting
Following examples are given below:
Example #1
Let us take the example of ASD Inc. to illustrate the computation of the B.E.P in accounting. It is an office stationery manufacturing company, and it is currently setting up a new unit for the manufacturing card holder. The annual fixed cost is expected to be $160,000, while the variable cost per unit will be $0.90, which includes raw material costs and direct labor expenses. Determine at what production level the cardholder manufacturing unit will start booking profit if the selling price of each cardholder is$2.50.
Solution:
- Given, Selling price = $2.50
- Variable cost = $0.90
- Total fixed costs= $160,000
Accounting Break-Even Point calculates as
Accounting Break-Even Point = Total Fixed Costs / (Selling Price – Variable Cost)
- Accounting Break-Even Point = $160,000 / ($2.50 – $0.90)
- Accounting Break-Even Point = 100,000
Therefore, ASD Inc.’s new unit must produce a minimum of 100,000 cardholders to avoid operational losses. Any increase in production from this level will result in profit.
Example #2
Let us take another example to explain how to calculate accounting. SDF Inc. is a pizza manufacturing company that started a brand new store two months back. The new unit has yet to start booking any profit, and the store manager intends to ascertain the new unit. Help the store manager determine the break-even concept based on the given information:
- The average selling price of each pizza: $17
- The average variable cost of each pizza: $7
- Total fixed costs: $10 million
Solution:
- Given, Selling price = $17
- Variable cost = $7
- Total fixed costs= $10,000,000
Accounting Break-Even Point calculates as
Accounting Break-Even Point = Total Fixed Costs / (Selling Price – Variable Cost)
- Accounting Break-Even Point = $10,000,000 / ($17 – $7)
- Accounting Break-Even Point = 1,000,000
Therefore, the new store has to achieve sales of 1,000,000 pizzas before its starts booking profit.
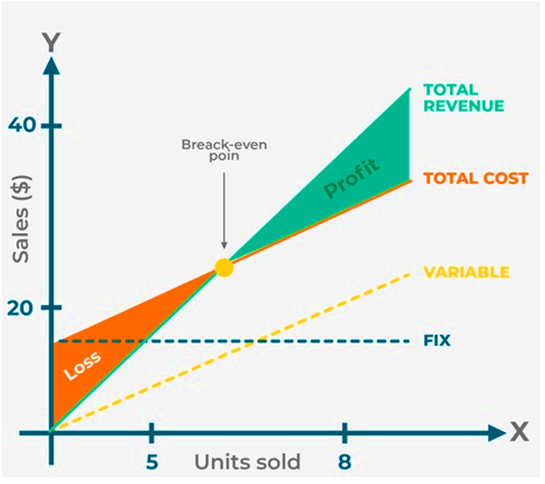
Break-Even Point in Accounting with Graph
In the above graph, green represents the total revenue. In contrast, the orange line represents total cost, which combines fixed costs (blue dotted line) and variable costs (yellow dotted line). Now, it can be seen that the line for total cost remains above the total revenue before the break-even point, and as such, it is the loss zone. However, after the break-even point, the line for total revenue goes above the total cost, which is the profit zone.
How to Reduce Break-Even Points in Accounting?
As can be seen from the formula, the break-even point can be reduced by:
- Decreasing fixed costs of production
- Increasing the selling price per unit
- Decreasing variable costs of production per unit
Difference Between Accounting Break-Even Point and Financial Break-Even Point
Some of the major differences between the accounting break-even point and the financial break-even point are as follows:
- The accounting B.EP determines the level of output required to cover all costs, while the financial break-even point ascertains the earnings level at which EPS is zero.
- An accounting B.EP calculates zero operating margins, while the financial break-even point is based on zero net income.
- The financial B.EP applies to personal purposes, while the accounting B.EP primarily applies to companies and organizations.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of B.E.P in accounting are as follows:
- This helps measure the profit and losses made at different sales or production levels.
- It also facilitates forecasting the probable impact of changes in the selling price of an item.
- It helps in understanding the relationship between fixed costs and variable costs.
- This can be used to ascertain the effect of change in cost and efficiency on overall profitability.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages of B.E.P in accounting are as follows:
- This is based on an unrealistic assumption that the selling price remains constant at all output levels.
- It assumes that sales and production remain at the same level, again impractical.
- It takes a significant amount to prepare a break-even chart.
- This concept only applies to a single product or mix of products.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that a seasoned businessman can use the concept of accounting break-even points and charts to determine profitability at any given level of production. However, it has its own limitations in terms of impractical assumptions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Break-Even Points in Accounting. Here we also discuss the introduction, how to calculate the B.E.P in accounting, and advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –