Updated September 22, 2023
What is a Budget Surplus?
A budget surplus is when the revenue the government collects from taxes is more than its expenditure in a specific fiscal year. Governments can run into surpluses when they increase taxes or reduce government expenditure. This usually happens during an economic boom.
A budget surplus indicates that the government is managing its finances effectively. Thus, the government can spend the extra funds on public welfare, infrastructure development, paying off debt, or investing for future generations. However, it is essential to use this fund wisely, or it can hurt the economy.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- A budget surplus occurs when the government earns more tax revenue or reduces expenditure.
- To calculate it, subtract the government’s spending and transfer payments from its tax revenue.
- It can lead to economic growth, lower interest rates, and lesser government debt.
- If the government does not spend the surplus funds correctly, it can lead to deflation and economic slow-down.
Formula
Calculating a budget surplus is quite simple. Following is the formula:
Where:
- Tax Revenue: Total income from various forms of taxation, such as income tax, sales tax, corporate tax, and more.
- Government Spending: Money the government uses for purchasing goods and services, infrastructure projects, operational expenses, etc.
- Transfer Payments: Capital the government spent on social security payments, unemployment benefits, and welfare payments.
Interpretation:
- A positive government savings amount indicates a budget surplus
- A negative government savings value signifies a budget deficit.
Example
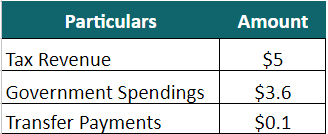
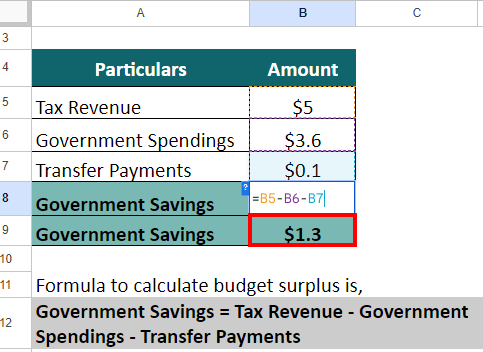
Suppose, in the fiscal year 2022, the government of a small nation received $5 trillion in tax revenue and spent $3.6 trillion on healthcare, education, infrastructure, and so on. The transfer payments for the year were $0.1 trillion. Now, calculate the Government Savings.
Given:
Solution:
Let us use the formula,
= $5 trillion – $3.6 trillion – $0.1 trillion = $1.3 trillion
As we can see from the above image, as the savings are positive, the government had a budget surplus of $1.3 trillion for the year 2022.
Real-World Examples
Following are some of the instances where governments ran into a budget surplus.
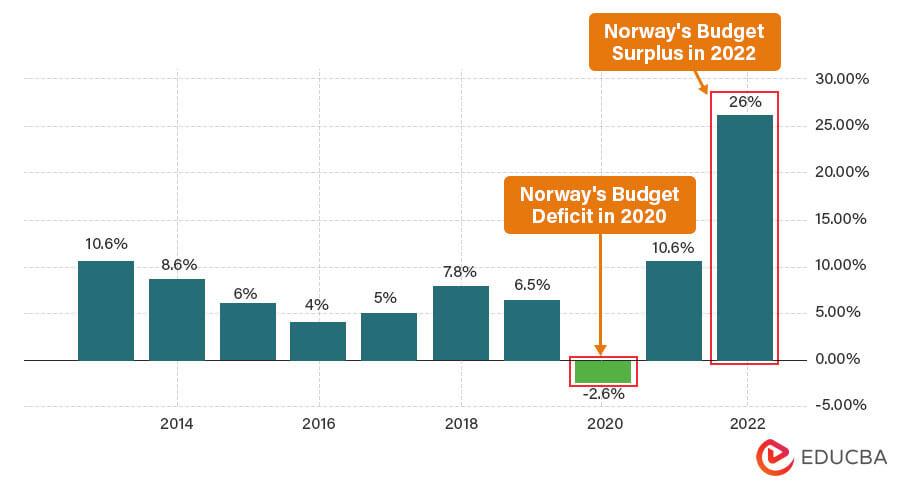
Example #1: Norway
In 2022, Norway saw the highest budget surplus among all world countries. It had a surplus of 26% of GDP. It is almost more than double its 2021 surplus of 10.6%. However, among several years of consistent surplus, Norway did have a budget deficit in 2020 (-2.6%).
(Data Source: Trading Economics)
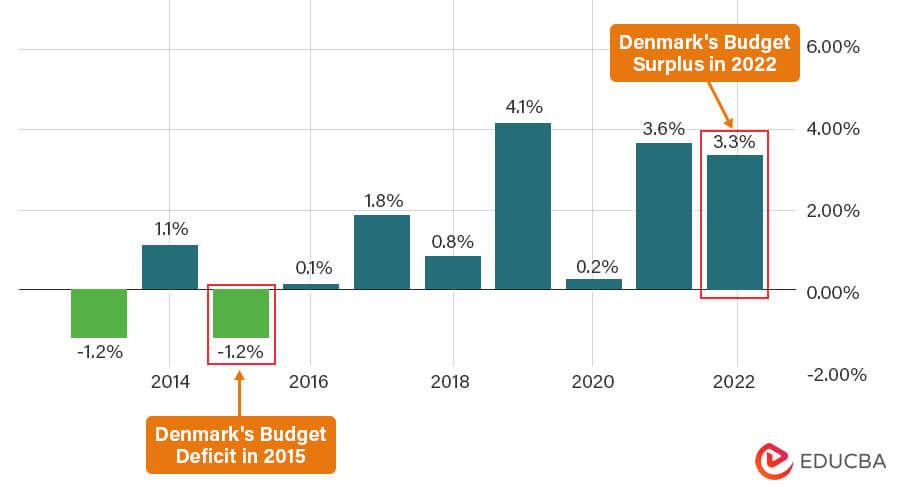
Example #2: Denmark
Denmark had a budget surplus of 3.3% of GDP in 2022. The country has continued to show a surplus for several years since 2016. Its surplus for 2021 was 3.6% of GDP. The country announced that this number may fall further as they are starting to invest in development projects.
(Data Source: Trading Economics)
Example #3: Australia
Australia has seen several budget surpluses during the late 90s and early 2000s. However, it recently posted its first-ever surplus in 15 years. Australia posted a budget surplus of AU$4.2 billion for the first quarter of 2023. The surplus has been largely attributed to increasing commodity prices and is said to be short-lived. The government believes that it will be back in a budget deficit due to increased spending on healthcare, eldercare, and defense.
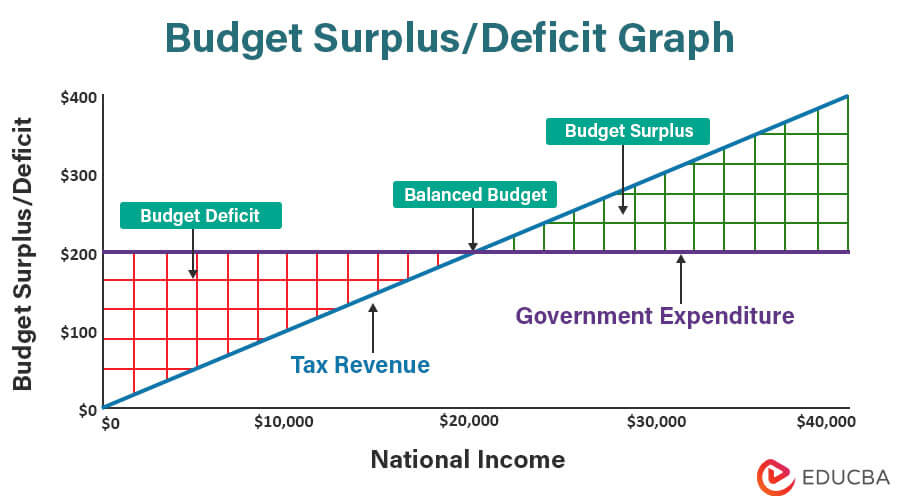
Budget Surplus/Deficit Graph
What is it?
There is a single budget surplus/deficit graph that explains how budget deficit or surplus occurs. This graph helps economists analyze a nation’s financial health and fiscal responsibility over a specified period. Thus, it can help policymakers, economists, and the public understand the nation’s financial position.
Diagram:
Given below is the budget surplus diagram.
Where,
- The x-axis shows the national income
- The y-axis shows the budget surplus, balance, or deficit.
Example:
Let us understand the above budget surplus diagram with the help of an example.
Let’s say Country A’s government has the following revenue and expenditure for the respective national income.
| National Income | Revenue | Expenditure |
| $0 | $0 | $200 |
| $10,000 | $100 | $200 |
| $20,000 | $200 | $200 |
| $30,000 | $300 | $200 |
| $40,000 | $400 | $200 |
Here are the observations from the above data and diagram,
- Tax Revenue:
The tax revenue increases with increasing national income. It is because, with higher income, individuals pay higher taxes. Thus, we can see that the tax revenue line has an upward slope on the graph.
- Expenditure:
The government expenses stay constant because even if the government has no income or the national income is $40,000, it must spend a necessary amount for the nation. Thus, the expenditure stays constant for a longer period unless there is a sudden requirement. Therefore, we can see that the expenditure line on the graph stays horizontal.
- Balanced Budget:
If, at any point, the revenue from the taxes and the government expenses are equal, it is called a balanced budget. We can see this point on the graph where both the tax revenue and the expenditure lines meet.
- Budget Deficit:
Now, from the graph, we can find the budget deficit. It is the area before the budget balance, below the expenditure line. It occurs when government spending is higher than tax revenue. In our graph, we can see this when the national income is less than $20,000.
- Budget Surplus:
Again, from the graph, we can identify if there is a budget surplus. It is the area after the budget balance above the expenditure line. It happens when the government spending is lower than tax revenue. In our graph, we can see this when the national income is more than $20,000.
Effects of Budget Surplus
A budget surplus can have the following good and bad impacts:
1. Economic Growth
The government can spend the surplus funds on the public and create more employment opportunities. This can reduce unemployment, improve infrastructure, and lead to a stable economy.
2. Reducing Government Debt
A government can use its surplus to lessen its debt. For instance, countries like Italy, Greece, and Portugal have accumulated unmaintainable debt levels. Greece solely depends on the EU and IMF to thrive. In such cases, if the countries run into a surplus, they can use the funds to pay off their debt.
3. Decrease in Interest Rates
When a government uses its surplus to overcome debts, it leads to lower interest rates. This can be beneficial to both consumers and companies. This is because lower interest rates encourage more consumption, borrowing, and investment, helping the economy to grow.
4. Deflation
The switch from a budget deficit to a surplus can create deflation. It happens when the government spends less on the broader economy, reducing demand and causing deflation. The other possibility is that since taxes generate surplus, consumers and businesses have less money to invest and spend, again causing deflation.
5. Lower Quality Public Services
A budget surplus often means that the government hasn’t been spending adequately. This can manifest as a lesser investment in welfare, education, health, salary caps for government departments, etc. All of this can negatively impact the quality of service given to the general public.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of a budget surplus:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| A budget surplus can give the government the required flexibility to spend the money on more important things. | A budget surplus can mean higher taxation, thus decreasing the disposable income of consumers and firms. |
| It can help reduce inflation by decreasing the circulation of money in the economy. It can thus drive down prices of goods and services. | When there’s less money to spend, it can cause a decrease in morale and investments. |
Final Thoughts
A budget surplus is not always good, and neither is a budget deficit. Spending a lot more or a lot less than the revenue impacts the economy adversely. Hence, governments should aim for a balanced budget. It’s a situation where the total revenue equals the total expenditure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a budget surplus and a budget deficit?
Answer: In simple terms, when a government or a business has more money than it needs, it’s called a surplus, and when it needs more money than it has, that’s a budget deficit.
Q2. When is the right time for a Budget surplus?
Answer: Although a budget surplus indicates financial stability, it’s not necessary for a healthy economy. Today, most nations do not achieve a budget surplus but choose a policy for expansion complementing a budget deficit. According to OECD data, most of the European economies have a budget deficit. The world’s leading economies, like the US, rarely see a budget surplus and often run into a budget deficit.
However, it doesn’t mean that a budget surplus is always bad. It can be appropriate when the economy is in the growth or boom phase. During the growth phase, the government can increase its tax revenue and later utilize these funds for the betterment of the country.
Q3. What causes a budget surplus?
Answer: A budget surplus can occur due to the following reasons:
- Increase in Tax Revenue: When a government starts collecting more taxes due to increased economic activity, increased corporate profits, or tax reforms, it can result in a surplus.
- Decrease in Government Spending: When a government starts spending less on education, healthcare, infrastructure, jobs, and other expenses, it can lead to cost savings, resulting in a surplus.
Recommended Articles
The above EDUCBA article is a guide to Budget Surplus. To learn more about other economics-related topics, please read the following articles,