Updated November 6, 2023
Difference Between Bull Market vs Bear Market
A bull market is defined as a continuous period where prices rise — generally for months, quarters, or years. Like the stock market, other asset classes can also have bull markets, such as commodities, real estate, or foreign currencies. Investing can be risky even for the most seasoned investors during bear market periods. A bear market can be defined as a period in which investor confidence is extremely low, along with falling stock prices.
Bull Market
A 20% rise in stock prices, following a previous 20% decline followed by another 20% decline, is one commonly accepted definition of a bull market for stocks. Accompanying a bull market are several things, to mention a few; bull markets generally happen when the economy is strengthening or strong. There will likely be strong GDP growth, and companies’ financial performance will be on the rise along with other better economic data.
Investor confidence remains another strong indicator of a bull market. There is a strong overall demand for stocks during a bull market, and the overall tone of market commentary bends to be positive. IPO activities in bull markets are higher as investors are ready to put in more money for better value.
Bear Market
During a bear or falling market, many investors opt out to sell off their stocks for fear of further losses, thus giving rise to a vicious cycle of negativity. Typically, over at least two months, bear markets are marked by a 20% downturn or more in stock prices, although the financial implications of bear markets can vary.
Bear markets typically begin following a period of more favorable stock prices when investor confidence begins to fade. To avoid losing money from the falling stock prices that investors anticipate, they tend to sell off their investments as they grow increasingly pessimistic about the market.
Investors might capitalize on low stock prices by reinvesting in the stock market at some point during a bear market. This behavior can ripple and cause widespread panic, making stock prices plunge and impacting the relative companies’ dividend yields. A bear market can eventually transition to a bull market as trading activity rises and investor confidence grows.
Head To Head Comparison Between Bull Market vs Bear Market (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between Bull Market vs Bear Market.
Key Differences Between Bull Market vs Bear Market
Let us discuss some of the major differences between a Bull Market and vs Bear Market:
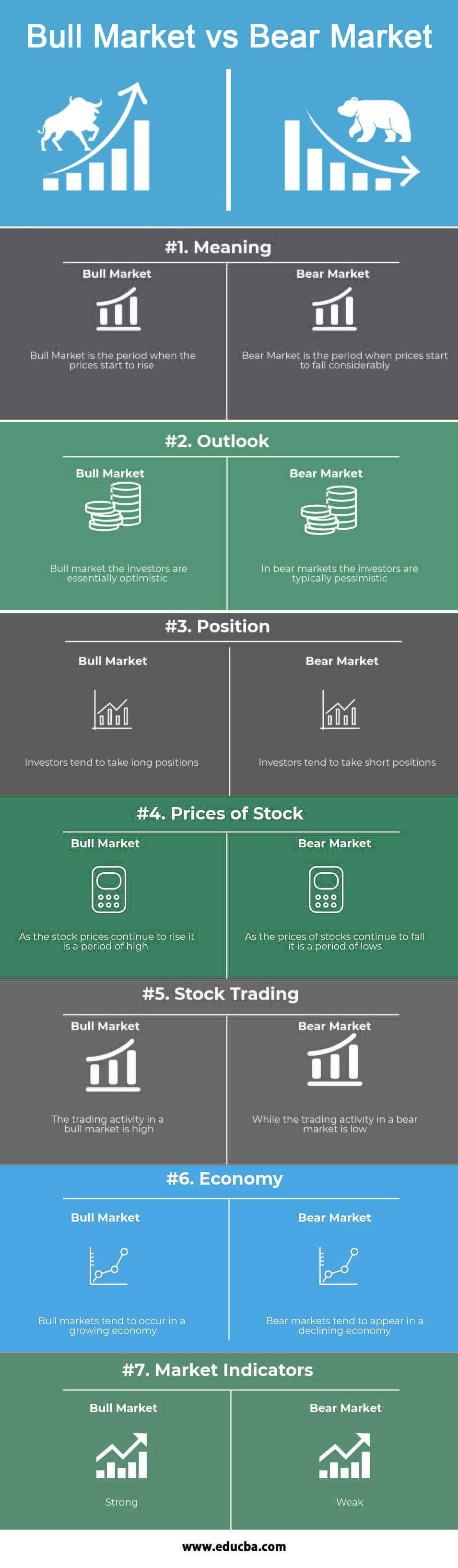
- Bull Market is considered when there is a rise in the total performance of the market. Bear Market is when the market undergoes a huge decline in market performance.
- In a Bull market, the investors are essentially optimistic; in a bear market, the investors are typically pessimistic.
- Investors tend to take long positions in the bull market, i.e., buying shares to book profits if the prices increase. While in the bear market, the investors take a short position, i.e., they sell the stocks to make a profit when prices go down further.
- As the market continues to rise, it is a period of high stock prices when it is a bull market. It is a period of lows as the markets continue to decline, and stock prices do as well.
- As the demand increases, the investor’s response toward the bull market becomes positive, attracting more investors. On the other hand, due to the continuous fall, investors’ response is negative, and investors tend to pull out of the market.
- There are strong market indicators when we talk about bull markets. One can find weak market indicators in a bear market.
Comparison Table of Bull Market vs Bear Market
Let’s look at the top comparison between Bull Market and Bear Market below.
| Basis of Comparison | Bull Market | Bear Market |
| Meaning | Bull Market is the period when the prices start to rise | Bear Market is the period when prices start to fall considerably |
| Outlook | Bull market, the investors are essentially optimistic | In bear markets, the investors are typically pessimistic |
| Position | Investors tend to take long positions | Investors tend to take short positions |
| Prices of Stock | As the stock prices continue to rise, it is a period of high | As the prices of stocks continue to fall, it is a period of lows |
| Stock Trading | The trading activity in a bull market is high | While the trading activity in a bear market is low |
| Economy | Bull markets tend to occur in a growing economy | Bear markets tend to appear in a declining economy |
| Market Indicators | Strong | Weak |
Conclusion
Bull Market vs Bear Market are both important on their terms. The bull and Bear markets help determine the stock price movements and investor confidence. Investors use both Bull Market and Bear Market to switch through various buying and selling modes.
They are primarily different in terms of the nature of price movement. When the price movements are on the upside, the markets are said to be in a bull market with strong economic conditions. When the movements are downward, the markets are said to be in a bear market with weaker economic data or financial performance.
In the Bear Market, trading activities are lower due to weak investor confidence. In Bull Market, trading activities increase substantially as investors’ confidence rises and they are attracted to the market.
The most simplistic understanding of these differences is with their names when they charge: bulls tend to raise their horns while attacking, and bears tend to attack downwards with their paws, i.e., swiping down.
Can an investor use both Bull Market vs Bear Market to their advantage? The answer is yes; both Bull Market vs. Bear Market have been discussed with their respective meanings and usage, along with the difference between Bull Market and Bear Market in the article.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bull Market vs Bear Market. Here, we discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles –