Updated June 21, 2023

What is Bull Spread?
The term “bull spread” refers to the options strategy designed to earn profit from a moderate increase in the underlying security price. This strategy involves the simultaneous purchase and sale of either call or put options with the same underlying asset and expiry date but at different strike prices. The seller constructs the opportunity with a higher strike price and purchases the one with a lower strike price, whether using call or put options.
Explanation
The bull spread strategy actively aims to profit from a slight increase in the underlying security price, as indicated by its name. By utilizing call options or put options and applying the concept of put-call parity, it becomes possible to construct a bull spread strategy.
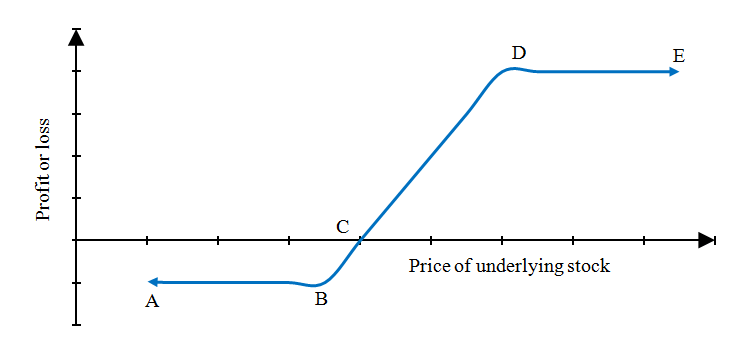
Graphical Representation of Bull Spread
Diagram represents the payoff of the bull spread strategy are:
The above diagram represents the payoff of the bull spread strategy. Line AB represents the payoff during the worst-case scenario, i.e., when the underlying security price decreases contrary to the bullish expectation of the trader. Point C represents the breakeven point when the underlying security price is adequate to cover the spread credit. From point A to point C, the strategy is loss-making but limited. From point C onwards, the process becomes profitable. It goes up to line DE, the maximum profit when the underlying security price moves in line with the trader’s expectation and exceeds the strike price.
Examples of Bull Spread
Example #1
Let us take the example of a trader who built a bull call spread, believing a particular stock will increase moderately before the options expiration. Let us assume that the underlying stock was trading at $110, and the trader purchased a call option with a strike price of $115 at $2 and sold another call option with a strike price of $120 at $1. The premium received on the sale offsets the cost (premium) of the purchase, and the net premium paid for the spread comes to be $1. Determine the maximum profit and maximum loss of the bull call spread.
Solution:
In the best-case scenario, the underlying stock’s market price will be $120 or above the trader’s book maximum profit. In this case, the trader can buy the underlying stock at $115 and sell at $120and hence the payoff can be calculated as,
Payoff maximum profit= Call spread – Net premium paid
- Payoff maximum profit = ($120 – $115) – ($2 – $1)
- Payoff maximum profit= $4
In the worst-case scenario, the underlying stock’s market price will finishbelow$115, and hence both the call options will expire out of the money. In this case, the trader incurs a maximum loss, and the payoff can be calculated as,
Payoff maximum loss= – Net premium paid
- Payoff maximum loss = – ($2 – $1)
- Payoff maximum loss = – $1
Therefore, the spread’s maximum profit and maximum losses are $4 and $1, respectively.
Example #2
Let us take the example of the trader employing a bull put spread. In this case, the trader purchased a put option with a strike price of $115 at$3 and sold another put option with a strike price of $120 at $7. The premium paid on the purchase and received on the sale results in a spread credit of $4. First, determine the bull put spread’s maximum profit and maximum loss.
Solution:
In the best-case scenario, the underlying stock’s market price will be $120 or above the trader’s book maximum profit. In this case, both options will expire unexercised, resulting in the net credit spread as shown below.
Payoff maximum profit= Net credit spread
- Payoff maximum profit = ($7 – $3)
- Payoff maximum profit = $4
In the worst-case scenario, the underlying stock’s market price will finishbelow$115. In this case, the trader will have to purchase the underlying stock at $120, and he can sell it at $115 and hence incur the maximum loss that can be calculated as,
Payoff maximum loss= Net Premium Paid – Put Spread
- Payoff maximum loss = ($7 – $3) – ($115 – $120)
- Payoff maximum loss = -$1
Therefore, the maximum profit and maximum losses are $4 and $1, respectively, in this case, too, due to call-put parity.
Types of Bull Spread
- Bull call spread: The construction involves purchasing and selling call options for the same underlying asset with the same expiration. The buyer purchases at a lower strike price, while the seller sells at a higher strike price. Sometimes, the buyer purchases an at-the-money call option while selling an out-of-the-money call option.
- Bull put spread: The investor constructs it by purchasing and selling put options for the same underlying asset with the same expiration. The investor buys the put option at a lower strike price while selling it at a higher strike price. Sometimes, the investor purchases an out-of-the-money put option while selling an in-the-money put option.
Bull Spread Futures
The essential features of any bull spread (either constructed with a call or put options) are as follows:
- The trader believes the market will go up moderately but is less confident with the bullish expectation.
- It is constructed by buying two simultaneous calls or put options.
- Both the options have different strike prices.
- Both the options have the same underlying security.
- Both the options expire on the same date.
- The trader earns a maximum profit when the underlying stock price finishes above the shorted strike price at the time of the option’s expiry.
- The strategy fixes both the maximum upside and downside.
Advantages of Bull Spread
Some of the significant advantages are as follows:
- In case of an adverse price, it limits the losses to a pre-determined level.
- This strategy results in a higher return on capital blocked as the net margin requirement is lower than that of the naked option.
Disadvantages of Bull Spread
Some of the major disadvantages are as follows:
- The strategy results in limited upside, even in the case of a bull run.
- The ratio of risk and reward is slightly skewed towards risk.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that the objective of the bull spread strategy is to earn profit from the gradual price rise in the underlying stock but at a lower cost. Also, given the lower risk, this strategy limits the scope of potential gains. But the strategy is built for this – lower price and limited profit and loss range.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bull Spread. Here we also discuss the definition and types of a bull spread, its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –