Updated March 30, 2023
Introduction on Bus topology advantages and disadvantages
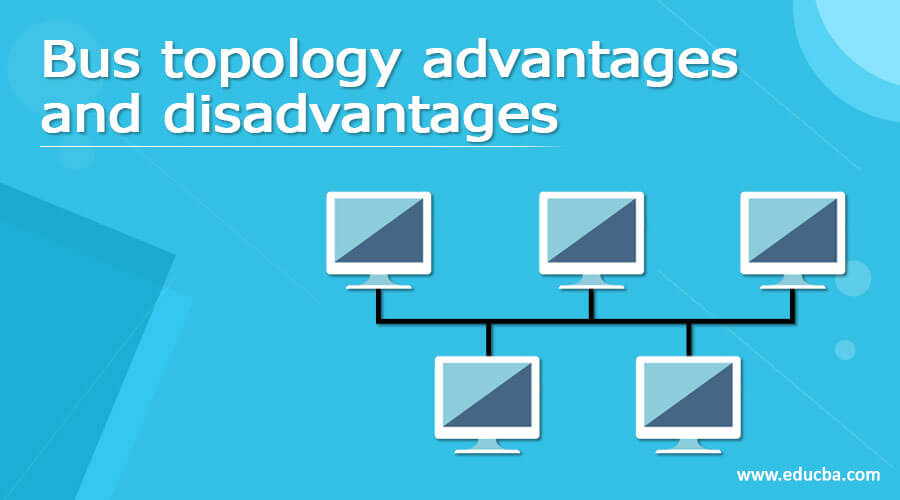
The bus topology is implied on a local area network connected to all the nodes via a single cable. The cable where all the nodes are linked is called the backbone, and if it is broken, the whole topology fails. On the other hand, bus topology can be easily installed and doesn’t involve much cabling when compared to other topologies. The best example of bus topology is the Ethernet network, where one computer behaves as a server in the network whereas the other computers act like clients. Hence the data is transferred between computers and clients. In this topic, we will look at Bus topology advantages and disadvantages in detail.
Advantages and disadvantages of bus topology
The advantages and disadvantages of bus topology are briefly discussed in this article.
Advantages
Different advantages are mentioned below:
1. Easy configuration
If the peripheral has an exact connection mechanism, it can be easily deployed in the network. If the user connects any new device, immediately it becomes a part of the network and starts to work. A temporary connection network can also be easily configured. If few users need common access to printer or hardware components, the demand meets the requirement immediately.
2. Affordable
When compared to other topologies like a star, ring, and hybrid networks, bus topology is easy to implement as it requires minimum cable lengths. Though the terminator is needed at both ends of the cable to ensure the network functionality, it is still cheap and affordable.
3. Reliability
If one component of the peripheral fails in a bus topology, the rest of the network remains connected and operating. So the linear nature of bus topology doesn’t affect the performance of the system as it provides uninterrupted communication.
4. No additional components
The linear configuration of bus topology enables free data flow through the network. Instead of hubs and switches, the central file server is installed which implies only a few points of possible potential failure occurs, which is manageabIn addition, it. It creates a localized network that can operate effectively with other terminals when connected.
5. Possible extensions
The scope and size of the bus topology are constrained. But it can be extended when required with an additional cable. The additional peripherals or repeater or connector or hardware component can be joined to the network using cables. It maximizes the occurrence of packet collision, but it can be controlled easily. It is a simple configuration that holds people together to work quickly for a lower cost.
6. Scalability
The point-to-point topology is another option for a small network. Bus topology has an advantage as it supports many nodes instead of only two nodes. This is how the original Ethernet network was built. Thinnet uses bus topology to form a local area network which is used to build working groups and departments. The data devices, printers, routers can be linked to the existing systems in addition to terminals or computers. It increases productivity speed as it sends commands directly to the required peripheral instead of giving commands to a centralized network. The users can stay local and enhances the production speed by keeping the workers more dynamic over time.
7. Power requirements
The terminators are the passive devices that are deployed in bus topology. It is made of capacitors and resistors, which implies that it doesn’t require any power source. It is easy to deploy a modest LAN at virtual in any location where networking is helpful to a working group or department.
Disadvantages
Different disadvantages are mentioned below:
1. Security
The adding of devices to the existing network affects the reliability and performance of the system. The backbone connects every peripheral and computer so the additional components will slow down the whole network as it involves only one cable. If that single wire is damaged, the entire network goes down or it results in a split of dual networks. As it is connected to a single wire, it is possible to view the data transaction that occurs through the entire network and every terminal can access the other terminals too. It means that the security features are difficult to set up as everyone can peek into other activities.
2. Size
The length of the bus topology is defined and only the maximum number of components can be added to the network. This limitation in size and backbone length maximizes the risk of collision in the network as the communication space is at a premium. It is cheap and easy to install but the maintenance cost is higher when it comes to the long run. It may be affordable for simple and short-term networks. It is not suitable for those who require growth in their network
3. Tolerance of faults
As the size of this network is limited, a single break collapses the entire network. It is not possible to restore complete communication without replacing the single cable. Therefore, it. It is not used as a stand-alone fix. A breakage can cause the connected components to lose communication with other devices at another end of the network. When it is set up in a large network, speed and data quality issues may also occur. Here the data packets are colliding with one another, and the outcome will be data loss. Maximizing the data nodes that exist in the network has an uninterrupted impact on the communication quality that occurs and so the network size is limited naturally.
4. Network issues
The communication issues in bus topology occur when it is prone to improper termination. It requires two terminators by ISO 11898 at two extreme network ends which act as a controlled node and the other is the node placed away from the controller. If these terminations are not used properly, the baud rates can be useful in port-to-port communication which consumes more time and process to identify the network issue. Bus topology doesn’t have effective communication; instead, it shares the data among the network. They don’t have proper coordination which means a lot of transmissions occurs at the same time and that creates heavy network traffic and leads to high potential data loss.
Conclusion
Hence these are the few advantages and disadvantages of bus topology, and it can be installed according to the user requirements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bus topology advantages and disadvantages. Here we discuss the few advantages and disadvantages of bus topology. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

