Business Expenses Definition
Business expenses are the costs incurred by a company to operate and generate revenue. They can be classified as either fixed or variable.
Fixed expenses, like rent or salaries, remain constant and independent of the company’s business activity. In contrast, variable expenses, such as advertising, change in proportion to the level of business activity.
Effective management of business expenses is essential for a company’s financial health. By controlling expenses, a business can increase its profits, reduce its tax bill, and improve its cash flow.
Business Expenses List
Here are a few standard costs that are part of any business regardless of industry or size:
- Raw materials and supplies: The cost of the materials needed to produce a product or provide a service.
- Labor costs: Wages, salaries, and benefits paid to employees.
- Operating expenses: The day-to-day expenses of running the business, such as rent, utilities, office supplies, and insurance, are the operating expenses.
- Marketing and advertising: The cost of promoting the business and attracting new customers.
- Research and development: The cost of developing new products or improving existing ones.
- Depreciation: Depreciation means the gradual reduction in the value of an asset over time, such as a building or equipment.
- Interest on loans: The cost of borrowing money to finance the business.
- Taxes: Taxes include the various taxes that a business must pay, such as income tax, sales tax, and property tax. Managing these taxes can become easier with FreshBooks taxes, which helps small business owners efficiently track and file taxes, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance.
How do Business Expenses Work?
Business expenses allow businesses to operate by incurring recurring costs such as rent, salaries, advertising, etc.
For instance, a company rents a 1,000-square-foot office space for $1,500 per month and pays the landlord monthly for the right to use the area for its operations. Rent expense is crucial as it is the money businesses pay to use physical space, like an office, retail store, warehouse, etc., for their business.
Further, as the business starts making money, it pays for salaries, utilities, and advertising to keep the business running and growing. The company records these payments as business expenses on its income statement. In this case, the rent, salaries, utilities, and advertising are recurring costs that the company will incur to operate the business.
At the end of every fiscal year, the company subtracts these costs from its income to determine whether it made a net profit or loss. Keeping track of these costs can help a business understand its financial performance and make better decisions about how to run and invest in the future.
Real-World Examples
#1 Amazon
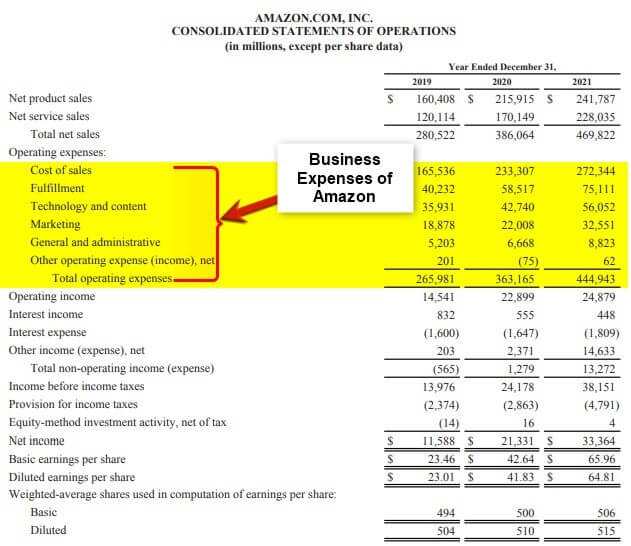
Amazon, one of the largest e-commerce companies in the world, incurred a total of $444.9 billion in operating expenses in 2021, according to its 2021 annual report.
(Image Source: Amazon Annual Report 2021)
This figure includes costs for sales & marketing, technology & content, fulfillment, and others. Amazon spent $56.05 billion on technology and content, $32.55 billion on marketing, and $75.11 billion on fulfillment.
#2 Coca-Cola
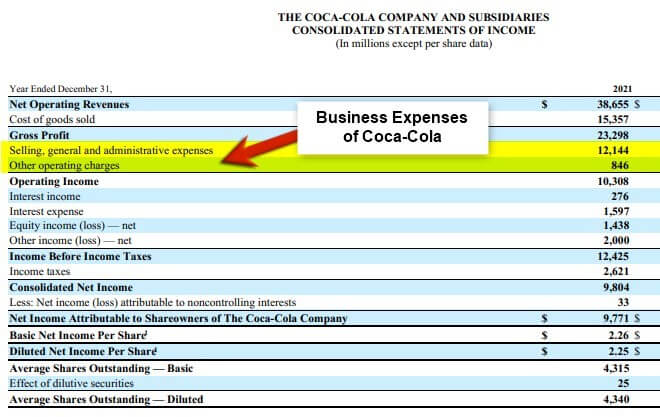
According to Coca-Cola’s 2021 annual report, it incurred a total cost of $12.99 billion in operating expenses in 2021.
(Image Source: Coca-Cola Annual Report 2021)
This figure includes advertising, distribution, stock-based compensation costs, and more. The company spent $2.5 billion on selling and distributing, $4 billion on marketing, etc.
Steps for Tracking Business Expenses
Keeping track of business expenses is essential for financial management and tax purposes. Here are some steps to follow to keep track of such expenses:
Keep receipts
- Save receipts for all business-related expense, such as supplies, equipment, travel, and meals.
- Keep track of the date, amount, and purpose of the expenditure on the receipt.
Use accounting software
- Use accounting software as well as an automated expense management tool to keep track of your expenses automatically
- It will help you to categorize your expenses, generate reports, and streamline your financial record-keeping.
Maintain a spreadsheet
- Use a spreadsheet to keep a record of your expenses manually.
- It can help you to keep track of your expenses in real-time and to organize them into categories.
Set a budget
- Create a budget for your business expense to help you stay on track and avoid overspending.
- It will also help you to plan for future costs and make informed financial decisions.
Business Expenses Trackers
Business expense trackers are online tools or software that help businesses track their operating expenses. Following are a few examples of expense trackers:
Mint
- This mobile application is an excellent tool for small businesses, side hustles, or freelancers.
- It supports a wide range of lenders, and the app is available on Android and iOS.
Expensify
- It is a cloud-based Business Expense Tracker that helps businesses manage their expenses and keep track of their spending.
- This tool takes many of the manual steps needed to keep track of expenses, like scanning receipts, putting costs into categories, and making reports.
- Receipts from Airbnb, Uber, and more get automatically imported into Expensify. It is available in iOS, Android, and Desktop versions.
Zoho Expense
- It is arguably one of the best android expense tracker apps. This application is handy for mid-sized businesses.
- It offers benefits like receipt management, approvals, travel management, reimbursements, etc.
SAP Concur
- SAP and Concur have established this mobile application for small and mid-sized businesses.
- One advantage of using SAP Concur is that it offers services tailored to individual companies’ needs. One can add functionalities later as required.
FreshBooks
- A cloud-based accounting platform, FreshBooks is available for a single user and up to five clients.
- It is a good option for entrepreneurs and is available in iOS, Android, and Desktop versions.
Tax Deductible Business Expense
Tax-deductible business expenses are expenses that a business can deduct from its taxable income, reducing the tax it has to pay. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides guidelines for what qualifies as a tax-deductible business expense. Here are some examples:
Office rent and utilities: Rent paid for your office space, as well as expenses for utilities such as electricity, gas, and water, are deductible expenses.
Employee salaries and benefits: Wages, salaries, bonuses, and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans are tax deductible.
Business travel expenses: Expenses related to business travel, such as airfare, car rental, accommodation, and meals, are deductible.
Marketing and advertising expenses: Expenses incurred for advertising and marketing purposes, such as website development, social media advertising, and print ads, are deductible.
Equipment and supplies: Purchases of business equipment, such as furniture, laptop/computers, office supplies, software, etc., are deductible.
Professional services: Expenses for professional services such as legal and accounting services are deductible.
Business insurance: Insurance premiums paid for business liability, property, and workers’ compensation insurance are deductible.
Depreciation and amortization: The cost of assets used in the business, such as equipment and property, can be deducted over time through depreciation or amortization.
Charity or donations: Any capital contribution to charitable trusts, donations to relief funds, etc., are deductible under the IRS.
How to Write Off Business Expenses?
To write off business expenses, you must claim them as deductions on your business tax return. Here are the steps to follow:
Keep accurate records
- Keep accurate and detailed records of all your business expenses.
- It includes receipts, invoices, bills, and other documents showing the cost and the date incurred.
Determine if the expense is deductible
- Check if the cost is deductible under the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) guidelines.
- Generally, an expense that is ordinary and necessary for the operation of your business are deductible.
Categorize the expenses
- Organize your expenses into categories such as travel, office supplies, equipment, etc.
- It will help you claim deductions more quickly and provide valuable insights into your spending patterns.
Determine the deduction method
- The IRS allows two methods for deducting expenses: the standard deduction or itemized deduction.
- The standard deduction is a fixed amount determined by the IRS, while itemized deductions allow you to deduct the expenses you incurred.
File your tax return
- Include the total amount of your business’s expenses in your tax return.
- If one uses the standard deduction method, one can deduct the fixed amount determined by the IRS.
- If one uses the itemized deduction method, one will need to provide documentation to support your expenses.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. An individual uses an OTT subscription for movies or web series. Does that come under personnel expense or business expense?
Answer: Whether an individual’s OTT subscription for movies or web series is considered a personal or a business expense depends on the circumstances in which it is used.
- If the individual uses the subscription purely for personal, non-business-related purposes, such as entertainment or relaxation, it is considered a personal expense. Personal expenses are not tax-deductible, so the individual could not claim this expense as a deduction on their tax return.
- However, if the individual uses the subscription for business purposes, such as research for a work project or professional development, it may be considered a business expense. A business expense is tax-deductible so that the individual can claim this expense as a deduction on their tax return, subject to the guidelines and limitations set by the relevant tax authorities.
Q2. Does bribing a client or customer come under business expenses?
Answer: No, bribing a client or customer does not come under business expenses. Bribing is illegal and unethical and is not considered a legitimate business expense.
Bribing a client or customer is against the law and can have severe consequences for the person and the business. These consequences can include fines, legal penalties, and damage to reputation.
Q3. Can freelancers practice writing off business expenses?
Answer: Yes, freelancers can practice writing off business expenses as tax deductions. In general, freelancers are considered self-employed individuals and are therefore eligible to claim business expenses related to their freelance work on their tax returns.
Freelancers can write off various expenses related to their work, including equipment and supplies, office expenses, home office expenses, and transportation expenses. However, it’s important for freelancers to keep accurate records of their expenses and to ensure that they only claim expenses that are directly related to their freelance work.
Q4. Do contributions to political parties come under tax deductions for business?
Answer: The United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) says that donations to political campaigns and parties are “political campaign contributions,” which are not usually tax-deductible as charitable donations. Thus, no contributions to political parties are tax-deductible in the US. However, the laws regarding political contributions and tax deductions vary by country and change over time.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Business Expenses” was beneficial to you. For further guidance on business-related topics, EDUCBA recommends these articles: