Updated July 25, 2023

Differences Between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease
A lease is a contractual agreement between the lessor (owner of the asset) and the lessee (rents the asset). In this contract, the lessor gives the right to use a property for a particular period, and in return, the lessee gives a series of lease payments. Two types of lease are mainly involved: capital lease and operating lease. A capital lease is also called a finance lease. Lessor can be any entity, company, independent body, bank, or institution. A lessee can be anything from transportation, Real Estate, Agriculture, Construction, etc.
For a lease to be classified as a capital lease in U.S. GAAP, any of the four conditions must be satisfied:
- The present value of the lease payment must be equal to or greater than the asset’s fair market value. i.e., Whatever payments we were supposed to make in the tenure, if we compare its present value with the market value, if P.V (lease)> or = M.V of asset, classify it as a capital lease. Suppose the property’s Market Value is 100 and the payments are made for 25 years, getting P. V of all the payments is 110. Here it is greater so classified as a capital lease.
- The lease term is greater than or equal to 75%of the useful life asset. In our example, tenure is 25 years, and suppose the useful life of the property is 20 years. So, 75% (20) = 15 years, which satisfies the condition classified as a capital lease.
- A transfer of ownership at the end of the tenure.
- An option to purchase the asset at a discounted price at the end of the tenure. For IFRS, there is one more criterion to evaluate it as a capital lease.
- Only the lessee can utilize the asset without any major changes in the lease assets.
Before starting with the differences, just think of a capital lease as owning property and an operating lease as just renting the property. Let us understand the difference between the two leases with the same example.
Head To Head Comparison Between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease (Infographics)
Below is the Top 7 difference between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease:
Key Differences Between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between Capital Lease and Operating Lease:
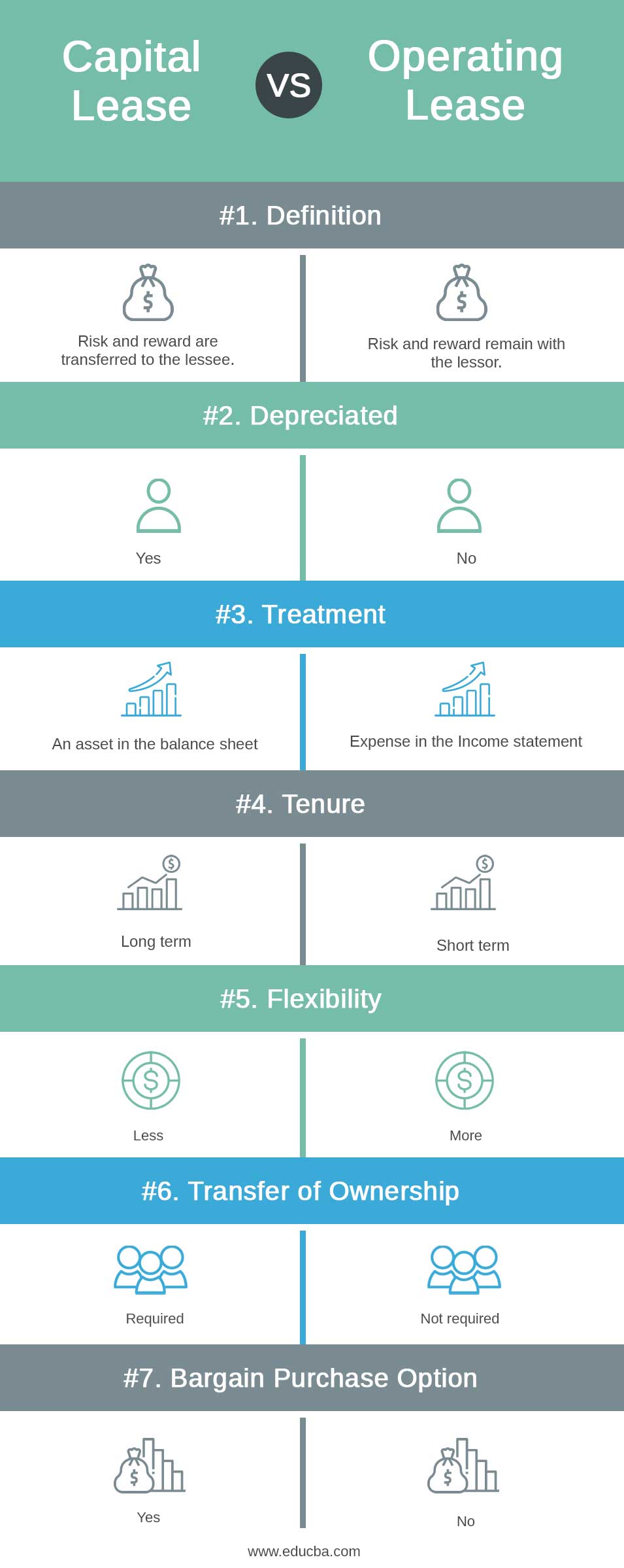
- Risk and returns related to the asset ownership are transferred to the lessee in a capital lease. In an operating lease, the risk and rewards related to the asset ownership remain with the lessor.
- While taking the same example as above, we depreciate the asset in our balance sheet, i.e., the property we own is depreciated over time. Due to the depreciation of the capital lease, the taxable income reduces. However, renting a property is not depreciated over the period.
- Accounting treatment for both types of lease varies from to lessee or lessor. The Operating lease is treated as an expense in the income statement. An asset is not transferred and lent to the lessee. There is no balance sheet entry in the case of an operating lease. No depreciation for the asset. In a capital lease, there is a transfer of ownership of an asset to the lessee’s account. The lease Is thus treated as a loan and the payments (Interest amount) as expenses in the income statement. An asset is recorded in the Balance Sheet. The present value of an asset is taken in the balance sheet and is depreciated over the period.
- The tenure of the capital lease is long-term, whereas it is short-term for the operating lease. So, transfer of ownership is required in the capital lease and not in the operating lease. E.g. Owing a property for a long-time duration, one needs to transfer the ownership rights. In the case of renting, it is for a very short period, and transfer of ownership is not mandatory. The transfer of ownership in an operating lease stays with the lessor for the entire lease period. In the case of the capital lease, the ownership transfer is optional at the end of the tenure period. The title may or may not be transferred to the lessee.
- A capital lease doesn’t have flexibility compared to an operating lease. As the accounting treatment is very easy in the operating lease, one can change the asset regularly and update it. In our current example, we have considered renting a property as an operating lease. If we need to change the rental property, the process is easy as the only expense is involved. In the case of a capital lease, when we own the property, the flexibility of changing the asset decreases drastically.
- Transfer of ownership is required in the capital lease and not in the operating lease. E.g. Owing a property for a long-time duration, one needs to transfer the ownership rights. In the case of renting, it is for a very short period, and transfer of ownership is not mandatory. Due to this, the capital lease has a high risk of obsolescence. There is no risk of obsolescence involved in the operating lease.
- The bargain purchase option is available in the case of the capital lease. In the operating lease, there is no bargain purchase option available.
Comparison Table of Capital Lease vs Operating Lease
Below is the topmost comparison between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease.
| Basis of Comparison |
Capital Lease |
Operating Lease |
| Definition | Risk and reward are transferred to the lessee. | Risk and reward remain with the lessor. |
| Depreciated | Yes | No |
| Treatment | An asset in the balance sheet | Expenses in the Income statement |
| Tenure | Long term | Short term |
| Flexibility | Less | More |
| Transfer of Ownership | Required | Not required |
| Bargain Purchase Option | Yes | No |
Examples of Capital Lease and Operating Lease
An example of a Capital and Operating Lease is
Operating Lease
A company enters into an agreement of 4 years to rent the building. There is no cancellation and renewal policy. The landlord carries out the maintenance. Thus, this lease is classified as an operating lease.
Capital Lease
ABC Ltd leased out construction equipment from XYZ’s real estate company. The lease period is of 6 years. Considering 10 percent as the rate converting the rate to the Present value. The present value factor for 6 years at 10 percent is 4.355. The payment of leased payment is 3 lakhs. The Present Value of the minimum lease payment is 4.355*3=13.065 lakhs.
Conclusion
Before concluding and deciding the type of lease, one must gain proper knowledge of the accounting and tax treatment done. Both capital and operating lease have their advantages. Based on the company’s needs and the present tax scenario, decide on one or even a combination of both types of a lease for different company assets.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to the Difference between Capital Lease vs Operating Lease. Here we also discuss the Capital Lease vs Operating Lease key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-