Updated July 13, 2023
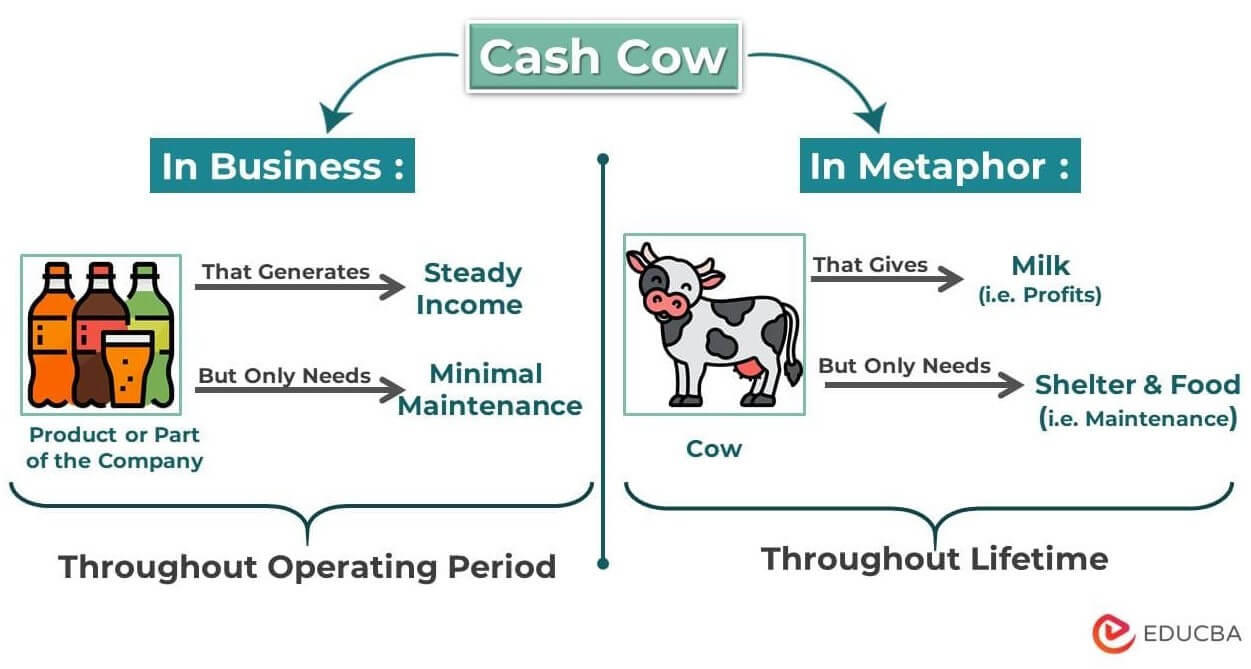
Cash Cow Meaning
Suppose you have a business that keeps generating a good amount of profits from the day it starts till you close it down. Also, it took significantly less money to purchase or open this business. In the business world, we use the term “Cash Cow” to explain this type of business.
The word “Cash Cow” symbolizes cows that produce milk throughout life, giving their owner a good income. And the cow requires only basic shelter and food, not heavy maintenance. Thus, it costs very less but brings in significantly more money.
This term is from the Boston Consulting Group’s Growth-Share Matrix, which organizes products or parts of a company into different categories: cash cows, stars, question marks, and dogs. Cash cow is one of the best categories to be in.
They make so much money because they have a lot of customers and a small amount of competition. With a cash cow, you can make a lot of money without spending much and use that money to invest in other businesses that need more attention.
To understand this concept, let’s consider a travel company named Travelers Gateway.
Travelers Gateway is a tour company that specializes in organizing trips to Switzerland. One of their most popular tour packages is “Swiss Village Tours.”
In Swiss Village Tours, travelers can walk through the beautiful streets of Swiss villages and experience the simple Swiss culture. People who love the charm of Swiss villages book this tour.
It brings in a lot of money for Travelers Gateway and does not cost much, making “Swiss Village Tours” a cash cow for the company.
The profits from Swiss Village Tours help Travelers Gateway offer more tours in Switzerland. This growth allows more people to have wonderful experiences in Switzerland and gives the company new opportunities.
Real-World Cash Cow Examples
Here are a few real examples of cash cows:
1. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola is a globally recognized beverage that has become a cash cow example due to its successful establishment as a strong brand for itself throughout its history. For the following reasons, Coca-Cola is an absolute cash cow.
| Coca-Cola | Reasons for Cash Cow |
| Strong brand recognition and customer loyalty | Global recognition and a loyal customer base that enjoys its signature cola. |
| Extensive distribution network | The distribution network ensures its products are available worldwide, contributing to continuous sales and profitability. |
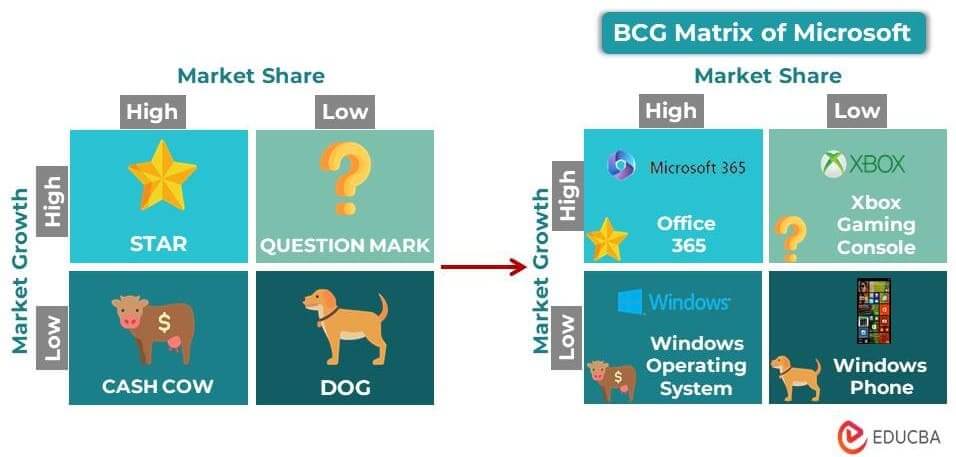
2. Microsoft Windows
Both individuals and businesses have preferred Microsoft Windows as the primary choice for personal computer operating systems for a long time. Microsoft releases new updates and features with each new version, attracting more customers and reinforcing its dominance in the market. Other reasons are as follows:
| Microsoft Windows | Reasons for Cash Cow |
| User-friendly interface | The operating system’s interface is very easy-to-use. |
| Industry-wide adoption | Many businesses use it for their day-to-day operations. It contributes to a steady stream of revenue through licensing and support services. |
3. Visa
Visa dominates the global payment processing industry. As more and more people prefer using cards instead of cash, Visa makes money by charging fees on each transaction. Other reasons are as follows:
| Visa | Reasons for Cash Cow |
| Dominance in global payment processing | Visa is a leader in the global payment processing industry, enjoying a significant market share. |
| Wide acceptance and usability | Visa cards are widely accepted, making them the primary choice for international travelers and global commerce. |
Revenue Contribution
The table below presents well-known products (cash cows) and their revenue contribution in 2022.
| Cash Cow | Total Revenue Contribution in 2022 |
| Apple iPhone | 52.11% |
| Google AdWords | 58.1% |
| Amazon Prime | 6.85% |
(Revenue Source: 2022 Annual Reports of respective firms)
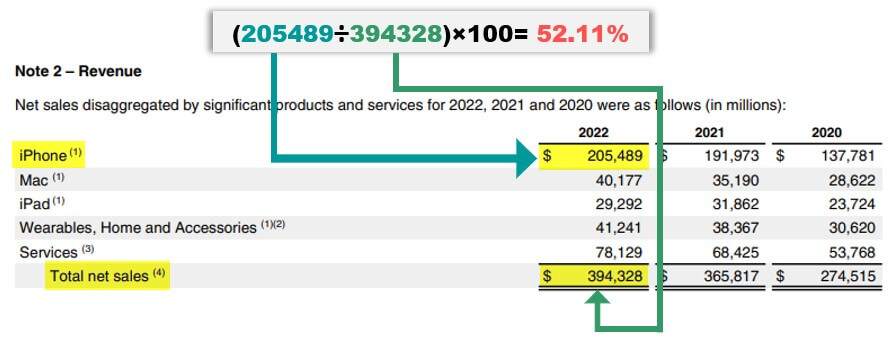
Note: Here is how you can find the contribution margin for iPhone.
- Divide the sales generated by iPhone in 2022 by the total net sales.
- Then multiply the resulting value by 100.
The image below shows the calculation for iPhone’s revenue contribution. The image source is Apple’s 10K Report for the year 2022.
(Image Source: Apple 10K Report- 2022)
Case Study: Gillette
Let us look at Gillette and analyze how the company has introduced several product lines that act as a cash cow over the years.
1. Market Identification (1901):
Procter & Gamble (P&G) found a promising market for shaving and grooming products for men who want a convenient and safe shaving experience. It allowed them to establish Gillette, a personal care company, as a leading brand in the industry.
2. Brand Building (1901-1920):
Using their market identification, the company introduced the safety razor offering men a convenient and safe shaving experience. It soon became their cash cow product, making Gillette a shaving and grooming product leader.
3. Expansion (1921-1950):
Gillette then expanded its product line to include various razor models, shaving creams, and aftershaves, building a range of products that became its cash cow.
4. Continuous Innovation (1951-2000):
Through continuous innovation, the company introduced new products like adjustable razors, twin-blade razors, and razors with pivoting heads. They kept adding more products to their cash cow status.
5. Marketing Success (2001-Present):
Gillette’s ongoing success as a cash cow brand is because of its wide range of products, effective marketing campaigns, and popular advertisements.
6. Cash Cow Status (2010-Present):
Gillette’s diverse lineup of shaving and grooming products, including razors, creams, and aftershaves, has solidified its cash cow status in the market.
Cash Cow Matrix
The Cash Cow Matrix is a Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Growth-Share Matrix. This strategic management tool helps companies understand which products or services are making a lot of money and have high market growth and market share.
It has four quadrants:
| Quadrant | Definition | Description | Example |
| 1. Question Mark | A business is still figuring out if it will be successful or not. It needs more time and money. |
|
Apple TV |
| 2. Star | A successful business that grows fast but needs much attention and investment. |
|
Apple’s iPhone, Coca-Cola’s Kinley |
| 3. Cash Cow | A business that makes a lot of money without needing much money to run. |
|
Apple’s MacBook |
| 4. Dog | A business that is neither popular nor makes a lot of money. |
|
Landline Telephones |
BCG Matrix Example
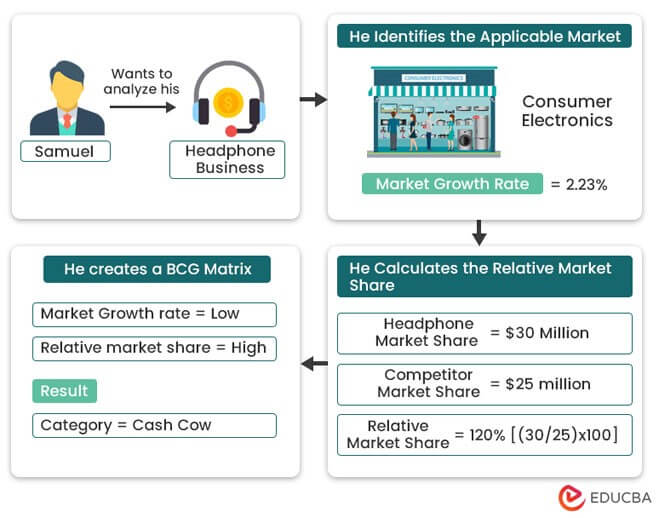
Step 1: Begin by identifying the specific entity to analyze, e.g., product, business unit, firm, or brand.
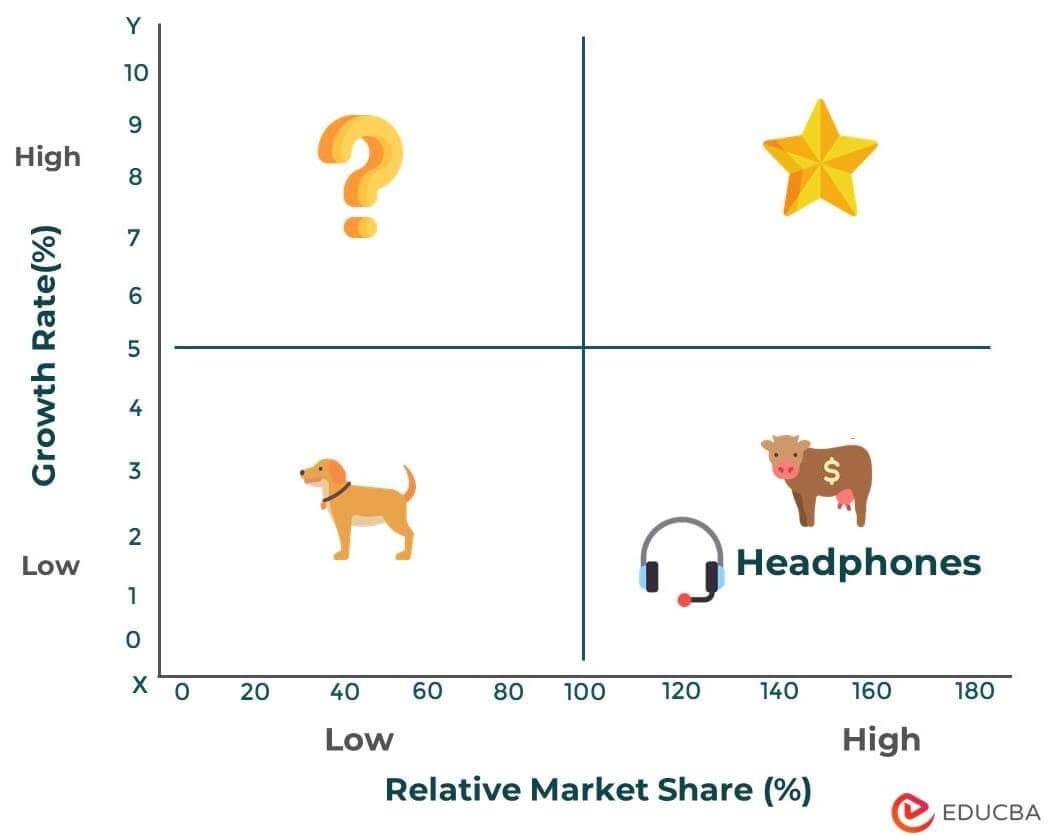
Example: Samuel wants to analyze a specific product, the headphones from his business, TuneBeats Ltd.
Step 2: Determine the applicable market for the entity identified in Step 1.
Example: The applicable market for the headphones will be consumer electronics.
Step 3: Calculate the relative market share of the entity. One must divide the market share of the target product by the market share of the strongest competitor in the same market. The answer comes in the form of a percentage.
Example: As per the business, the headphone market share of TuneBeats Ltd. is $30 million. Moreover, the market share for the biggest competitor in the industry is $25 million. The relative market share will be $30 million/ $25 million = 120%.
Step 4: Find out the estimated growth rate of the overall market. Its base factors include industry research, market analysis, or historical data.
Example: The estimated growth rate for this market is 2.32% per year.
Step 5: Plot the calculated figures on the matrix. The X-axis represents the estimated growth rate of the overall market, while the Y-axis represents the relative market share.
Example: As per the below matrix, the product (headphones) is a cash cow for the TuneBeats business. Here is a representation of the product on the matrix:
Strategies
There are various strategies to solidify the cash cow status of products:
1. Market Expansion
By expanding into new geographical regions and targeting new customer segments, the company can increase a product’s usage among customers. It will further cement the cash cow’s market position and build success in untapped markets.
Example: McDonald’s
McDonald’s Strategy:
McDonald’s expanded its market by entering new countries. It targeted new customer segments and adapted its menu to local tastes and preferences.
2. Cost Efficiency
Optimize the cash cow’s profitability by focusing on operational efficiency and cost control. It could include streamlining processes, renegotiating supplier contracts, or implementing lean practices to cut costs.
Example: Walmart
Walmart’s Strategy:
Walmart’s cost-efficiency strategy included extensive everyday offers, streamlined operations, and advanced technology utilization to drive profitability. Walmart also benefits from economies of scale due to its global presence, extensive store network, and distribution channels.
3. Strategic Alliances
Strategic partnerships and collaborations with complementary businesses to create additional value and revenue sources can help solidify the cash cow position of a company. Cross-selling or bundling products/services can help utilize the cash cow’s customer base.
Example: Apple
Apple’s Strategy:
Apple formed strategic alliances and partnerships with various companies, such as iTunes, partnering with record labels and app developers to create additional value and revenue sources.
4. Product Innovation
To attract fresh customers or maintain existing ones, one must constantly develop and improve the cash cow product. Consumer satisfaction requires adding novel features, expanding product lines, or introducing supplementary services.
Example: Amazon
Amazon’s Strategy:
Amazon constantly added new benefits and services to its cash cow product – Amazon Prime membership.
Challenges to Cash Cow
There are various challenges to the functioning of cash cows:
1. Technology: Technological developments can disturb the workings of industries when a company’s technology becomes outdated and needs replacement. Staying ahead of the curve can always work in favor of the industries.
2. Saturation: Cash cows operate in mature markets where customer demand has reached saturation. In such a situation, maintaining sales growth can become very challenging. Competitors may also try to gain market share, increasing competitive pressures and potentially eroding profits.
3. Shifting Customer Preferences: Customer requirements and preferences change over time. Cash cows must adapt to these changes to remain relevant in the market. A cash cow must adapt to changing client expectations to maintain market share with competitors or see revenues decline.
4. External Factors: Shifts in economic conditions, consumer behavior, or changes in government regulations are some external factors that can impact cash cows. The company needs to stay relevant and adaptable to these developments to prevent undue risks while benefiting from emerging opportunities.
Advantages
- Steady Growth: The company or business unit under the cash cow category grows steadily, providing consistent cash flows to the company.
- Increased Cash Reserves: The cash reserves of the company increases. As a result, it provides the company with an extra cushion for capital spending in the future.
- Enhanced Market Share: An increase in market share represents an increase in the customers’ confidence.
- Lower Investment Requirements: Cash cows typically require lower investment levels than other categories, such as stars or question marks.
- Reduced Competition: The competition is already less when the business unit converts from a star category to a cash cow.
Disadvantages
- Slower Profit Growth: The profits will grow at a slower rate as compared to companies/products in the star category.
- Risk of becoming Outdated: In case the product of the cash cow unit becomes outdated or off-market, the business unit will start losing its market share and profits, thereby moving to the dog category.
- Market Share Maintenance: The company must maintain quality and delivery annually to retain consistent market share.
- Limited Sales Growth: Cash cows operate in mature markets with limited sales growth opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the characteristics of a cash cow business?
Answer: A cash cow business has the following characteristics:
- Large and loyal customer base
- Established market dominance
- Minimal competition
- Low investment requirements
- Consistent profitability
Q2. How can a company identify its cash cow products?
Answer: Companies can identify their cash cow products by analyzing their financial data, such as:
- Revenue and profit margins
- Market share
- Growth rates
Products or business units with high market shares and consistent profitability over an extended period will likely be cash cows.
Q3. How can a cash cow business sustain its profitability over the long term?
Answer: A cash cow business can sustain its profitability over the long term by implementing the following strategies:
- Continuously meeting the needs of its customers
- Maintaining its market share through effective marketing
- Implementing customer retention strategies
- Adapting to changing market conditions
The business needs to monitor industry trends, innovate when necessary, and invest in maintaining the quality and relevance of its products or services.
Q4. Can a cash cow business transition to a different category in the BCG Matrix over time?
Answer: Yes, a cash cow business can transition to a different category in the BCG Matrix. Over time market conditions may change over time, reflecting a change in the business’s growth rate or market share. Thus, If the market’s growth rate declines, the company moves from the cash cow category to a different category.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Cash Cow. Here we also discuss the definition, examples, and matrix, along with the advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –