Updated April 4, 2023

Introduction to CDMA vs GSM
Landlines connected People across geography through voice calls over a wired network till the 1980s. Pointed wireless connections like microwave networks facilitated long-distance calls, TV telecasting, etc. Cellular technology using radio frequency wave enabled wireless last-mile connectivity to the users and kept them connected even when they moved from one place to another. Cellular network, being wireless, saves costs on physical media like Cable and its cumbersome maintenance. Data transfer facility over and above voice connectivity enabled people to share data on the move. Mobile technology spread its wings to connect moving entities like automobiles, ships, and airplanes to monitor their location and track their performance as well. This technology paved the way for quicker adoption of new digital technologies like IoT and opened up many new business opportunities. CDMA and GSM are the most popular standards for mobile communication, and many of the latest generations of mobile technologies were built on the fundamentals provided by GSM and CDMA.
In this article, we will analyze the features of GSM, CDMA and compare them.
Head to Head Comparison between CDMA vs GSM (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 comparisons between CDMA vs GSM:
Key differences between CDMA vs GSM
Let us discuss some key differences between CDMA vs GSM in the following points:
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) and GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) belong to the second generation of digital mobile standards (2G), and they replaced first-generation (1G) Analog standards. 2G technology reigned in the 1990-2010 time period, and it could not cater to the data requirements of new digital applications. 3G/4G technologies replaced GSM/CDMA, but the basic concepts of GSM/CDMA were used in building the new standards, and it is only a virtual extension of old technologies.
1. Technology of CDMA and GSM
GSM
- Developed by Europeans in the 1980s as Groupe Special Mobile standard, adopted by Asia,
- This digital, Circuit-switched mobile technology widely embraced by all over the world, and it enjoyed 80% global market share at its peak.
- Used in Voice as well as data services (SMS and MMS).
- It uses Time Division Multiple Access methods for transmitting a signal in an 850 MHz – 1900 MHz frequency band. The communication channel, narrow bandwidth of 200 kHz carved out in frequency space, is divided into eight-time slots called a frame. Each user is allotted a frame, and the signals are transmitted over that frame on a rotational basis. At any point, the time signal of one user will only be transferred, but all the users will feel the entire band is servicing.
- Components in GSM are mobile station, base transceiver station (Tower), Base station controller, Mobile switch center and operations.
CDMA
- Multiple signals or data streams are sent over a communication channel as one complex signal. It results in effective utilization of the available.
- The spread spectrum technique is followed in CDMA, which allows many users to share the frequency band simultaneously, and each user’s signal is tagged with a unique sequence number (Code).
- The frequency band of 800 MHz to 1900 MHz is used.
- The entire channel bandwidth is available to all the users for all the time, and the codes are used to distinguish signals of
2. SIM Cards
- The Subscriber identity module (SIM) card is mandatory in GSM instruments, and it contains International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI), password protection, and activation/deactivation facilities. SIM cards are provided by the service provider and activated once.
- There is an inbuilt SIM in CDMA instruments, and it has an Electronic serial number, and the caller number should be assigned/activated by the service provider.
3. Flexibility
- In GSM, SIM cards can be freely moved from one instrument to another without the service provider’s intervention. The caller number can be ported from one service provider to another service provider.
- In CDMA, Changing the instrument is not easy for a consumer, as the carrier will have to be involved in invoking the new instrument.
4. Security
CDMA has more security features inbuilt into it than GSM technology, and some of them are
- CDMA has an encryption facility
- 64-bit authentication key and Electronic Serial Number of the device strengthens security aspects of
- Unique codes attached to signals of the users in the communication channel provides security cover in CDMA. By virtue of its design, breaking of CDMA data is not
- In GSM, user’s signals are transmitted in the time slots of a frequency channel on a round-robin basis as it is
- Since the Signals in GSM are packed in narrow bands in a concentrated manner, they can be traced easily, leaving security concerns. Whereas CDMA transmits the information in the entire channel and they have little security
- CDMA-IS-41 security protocols are one among the best in Mobile communication standards
5. Radiation
GSM phones are more vulnerable to radiation risks as they generate wave pulses continuously and more exposure to electromagnetic fields. Radiation levels of GSM phones are 28 times higher and more biological reactivity than that of CDMA.
6. Global Usage
GSM has 80% market share globally, and it is present in more than 200 countries. A globe trotter with a GSM phone will have the least roaming issues as he travels through the world.
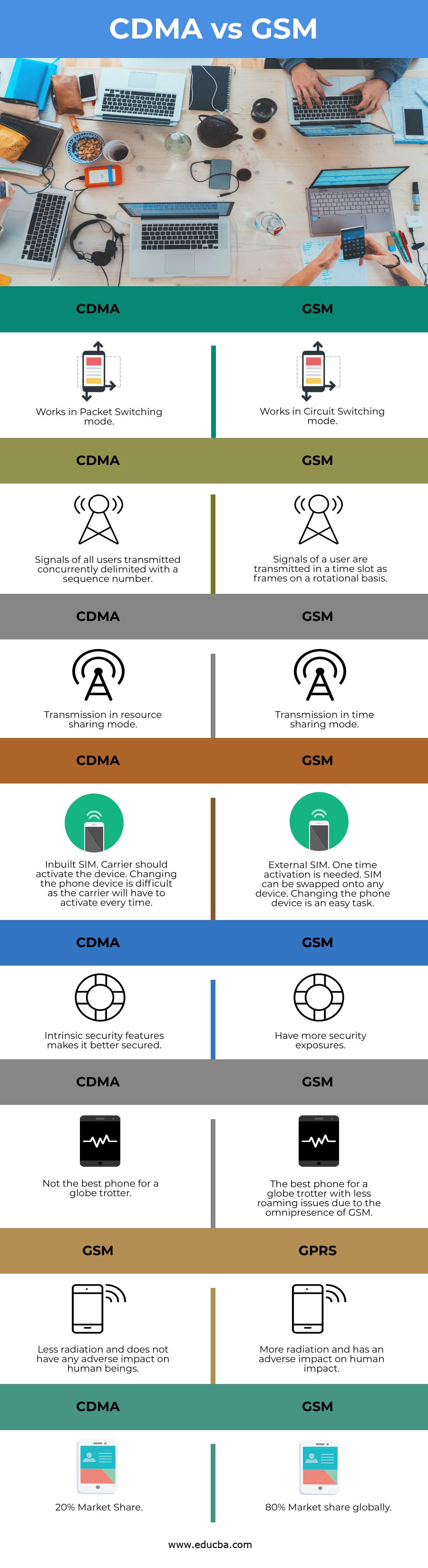
Comparison Table of CDMA vs GSM
The table below summarizes the comparisons between CDMA vs GSM:
|
CDMA |
GSM |
| Works in Packet Switching mode. | Works in Circuit Switching mode. |
| Signals of all users transmitted concurrently delimited with a sequence number. | Signals of a user are transmitted in a time slot as frames on a rotational basis. |
| Transmission in resource sharing mode. | Transmission in time sharing mode |
| Inbuilt SIM. A carrier should activate the device. Changing the phone device is difficult as the carrier will have to activate every time. | External SIM. One time activation is needed. SIM can be swapped onto any device. Changing the phone device is an easy task. |
| Intrinsic security features makes it better secured. | Have more security exposures. |
| Not the best phone for a globe trotter. | The best phone for a globe trotter with less roaming issues due to the omnipresence of GSM. |
| Less radiation and does not have any adverse impact on human beings. | More radiation and has an adverse impact on human impact. |
| 20% Market Share. | 80% Market share globally. |
Conclusion
The performance of the phone does not depend on whether it uses GSM or CDMA standards, but it depends on the back end infrastructure of the network and software controlling it. GSM and CDMA technologies are fundamentally robust and reigned the mobile market for quite a long time period, and the later technologies were built over these two technologies.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top differences between CDMA vs GSM. Here we discuss the CDMA vs GSM top key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –