Updated April 15, 2023
Introduction to CentOS Set Timezone
The following article provides an outline for CentOS Set Timezone. The timezone is very important in terms of the synchronization that comes into the picture. While installing the CentOS operating system, we are configuring the timezone in it. But in certain circumstances, if we need to do the changes in timezone configuration, we can also do that. In the CentOS environment, the time zone is nothing but a region of the globe. It will follow the informality of the time. It will also help to maintain constitutional, national, and commercial purposes. There is one more term in the timezone, i.e., the short time zone. The short time zone will help to represent the local time of the country. As per the requirement, we can easily change the timezone of the CentOS environment.
Syntax of timedatectl Command
timedatectl [ OPTIONS ... ] [ COMMAND ]1. timedatectl: The timedatectl is nothing but a utility. It will help to get the details about the timezone in the CentOS Environment. We can use the timedatectl keyword in the syntax or command. It will accept arguments like different options, commands, etc. The timedatectl command will help to deal with the system timezone in the CentOS environment.
2. OPTIONS: We can provide the different flags as the option that is compatible with the timedatectl command.
3. COMMAND: As per the requirement, we can use a different command or the combination of the command with the timedatectl.
How does CentOS set timezone Command Works?
As we have discussed, the timezone is very important in terms of the application, job scheduling, etc. It will also play an important role while the CentOS system is in cluster mode. In a single cluster, there are multiple machines. All the machines are in sync with each other. If the system timezone is not in sync, then it will also impact the authentication mechanism also (when the machines having Kerberos configuration, etc.)
Note: Once we have disabled the firewall, then the firewall will stop permanently. Once the machine reboots still, the firewall will be in a stop state only.
Below are the lists of options that are compatible with the firewalld option.
- –no-ask-password: It will ask for the authentication while the user is triggering the query.
- –adjust-system-clock: If we are passing the “–adjust-system-clock” when the set-local-rtc is invoked. The system clock will synchronize from the RTC again then it will take the new setting into the environment or account. If this thing does not happen then, the RTC will synchronize from the system clock.
- -H, –host: It will help to execute the operation remotely. This option will use the SSH communication channel to talk with the remote manager machine. The container name will be enumerated with the machinectl, i.e., the “-H, –host.”
- -M, –machine: It will help to execute the operation on the local container. It will also specify the container name to connect to.
- -h, –help: It will display short information on the screens. The output will be in text format. It will exit automatically.
- –version: It will display the short version information. The output will be in string format. It will exit automatically.
- –no-pager: It will help to do not pipe output into a pager.
- status: It will help to display the current settings of the system clock. It will print the information of RTC also.
- set-time [TIME]: It will help to set the system clock to the specified time. It will also update the RTC time accordingly. It will specify the time format, i.e., “2012-10-30 18:17:16”.
- set-timezone [TIMEZONE]: It will help to set the system time zone to the specified value. We can also list out the available timezones. If we have configured the RTC in terms of the local time, it will also update the RTC time.
- list-timezones: It will help to list out the available time zones. It will display the output of one per line.
Examples to understand CentOS set timezone Command
Here are the following examples mention below
1. CentOS set timezone: Get the status of the timezone
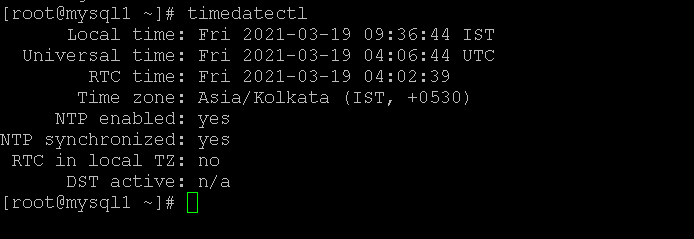
In the CentOS environment, we are able to get the status of the current timezone. In the below command, we are checking with the timedatectl. We have different commands or utility also to check it.
Command:
timedatectlExplanation:
As per the below command, we are able to get the current timezone status of the CentOS environment. The current timezone is IST hrs.
Output:
2. CentOS set timezone: List the timezone
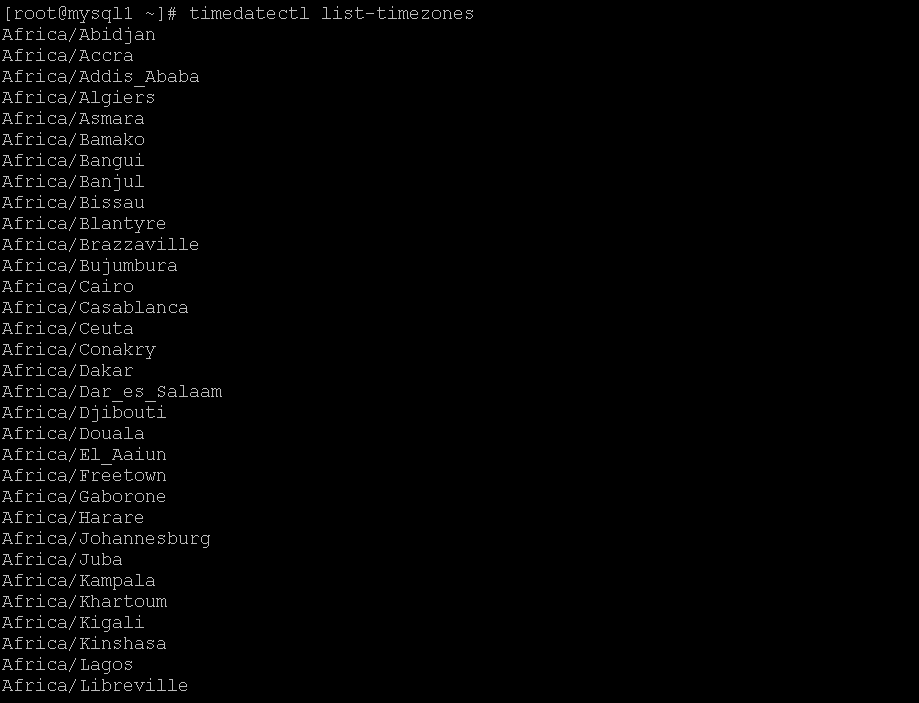
In the CentOS environment, we have the capability to list all the available timezones.
Command:
timedatectl list-timezonesExplanation:
As per the above command, we are able to list out the available timezone. As per the requirement, we can choose anyone of the timezone and use it.
Output:
3. CentOS set timezone : How to set the timezone
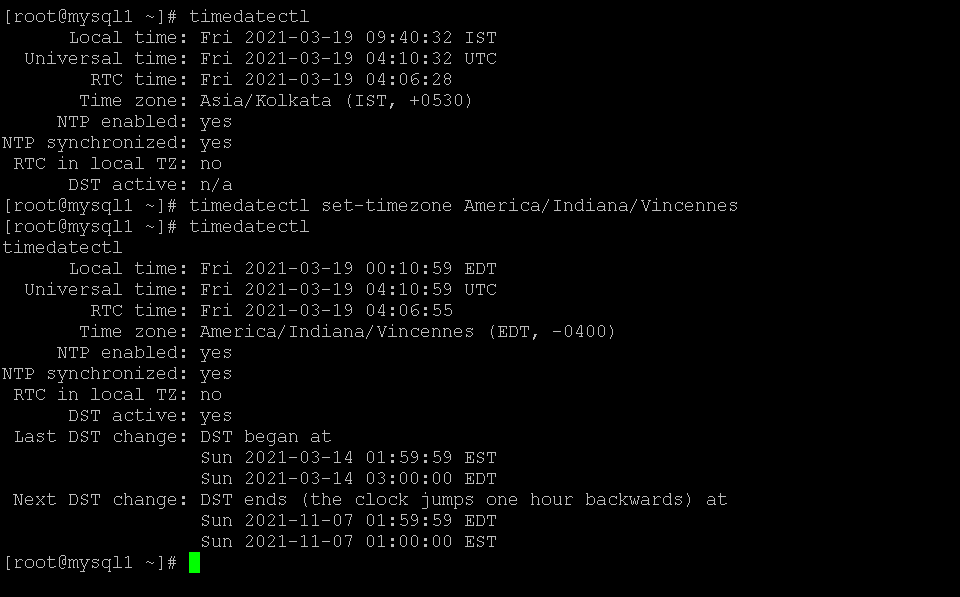
In the CentOS environment, we are able to set different timezone also.
Command:
timedatectl list-timezones | grep -i America/Indiana/Vincennes
timedatectl set-timezone America/Indiana/VincennesExplanation:
As per the above command, we are using two commands. First, it is for getting the timezone. Because we are having a number of timezone in the environment. Hence we are directly griping it. Then we are passing the same timezone as an input to the timedatectl command. As per the below screenshot, previously, we are getting the time in IST hrs. But after changing it to the “America/Indiana/Vincennes” timezone, we can get the time in EDT hrs.
Output:
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of the “CentOS set timezone” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. By default, the timezone was set at the time of installation only. But if we need to change it further, we can also change it with the timedatectl utility’s help. The timezone setup is very important in terms of the cronjob, sync process, application jobs, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CentOS Set Timezone” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.