Updated August 10, 2023

Overview of CIFS Protocol
CIFS protocol stands for Common Internet File System protocol, as the name suggests, is a type of file transfer protocol that allows the user to access the files in the network. It entails three main components that are, the Client, the server and the application for placing & accessing the files. An additional in CIFS protocol, that is not observed in other type of file transfer protocol, is the file can be sent to the printing queue with the help of in-built remote procedures called ‘subprotocols’
What is CIFS?
CIFS is a file transfer/share protocol over a network to access between the same file and the printers. A user who has access to a shared folder can either read or write or edit the files on the network area. It also gives the client user access to print queues, communicate between the services and a secure file transfer for remote procedures called subprotocols.
The CIFS Protocol is well explained with its acronym below:
- Common: It is a commonly used or commonly available networking system. It is a very secure way of files to share/access over the network.
- Internet: It is the Network over which the file shares take place.
- File System: CIFS permits the share of files, directories, queues, etc, over the network.
There are three main entities to define CIFS. They are the client, the server and the application.
- Client: The client starts initiating the messages and the protocol is built.
- Server: Stores the messages in the network and most of the implementation functionality is performed in the server.
- Application: Here the client accesses the shared files over the network.
There are subsystems associated with CIFS to perform the functionality to get through to implement the CIFS Protocol over the network to transfer secured files to the other systems.
These functionalities include User secured file transfer, Distributed File System, Remote Procedural Call. These functionalities can be separated or integrated as a single functionality to implement the CIFS Protocol.
Features of CIFS Protocol
Following are the features of CIFS.
- Authenticate Transfer: A Client can create a secured file transfer within the network so that no data loss happens.
- Transport Independent: To pass the SMB messages between the client and the server, we do not require any external transport protocol.
- Resource access: A Client can access a number of shared services like editing the files, removing the files or print queues on the server concurrently.
- RPC Transport: CIFS provides authenticated file transfer for RPC protocols like RPC and RAP.
Safe Caching: CIFS supports record tracking and allows the clients to cache the data for better performance. - Extended attributes: CIFS also supports attributes like author name, content, description which comes under nonfile system.
- File Access: The client can access the files over the network. Access includes read, write, edit, etc.
- Notification: When the contents of a file are modified over the network by a user or client, the server gets notified about the change.
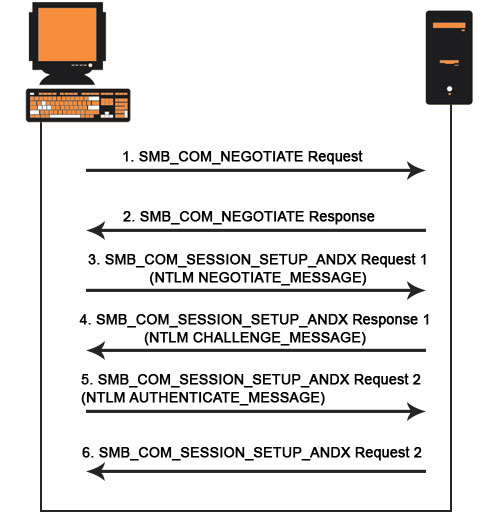
How does CIFS Protocol Work?
CIFS is a simple file share protocol over a network to access the file. The following is the process to share a file across the network:
- The client sends a request to the server to which he wants to access.
- The server accepts the request.
- The servers then send the response back to the client.
- Servers get interconnected to the other servers and share the files to the client.
CIFS Mechanism Example
File copy from a client to share server:
The file share that is used is taken from Windows NT server OS. It was directed to Y Drive on Windows 98 OS. This file transfer was taken place in MS-DOS OS.
C:\> copy file1.txt y:\file2.txt
CIFS vs Other File System
Following are the difference between CIFS and other file systems explained in detail.
CIFS vs NFS
NFS is a client-server protocol that allows transferring authenticates files between servers, laptops, desktops and other devices. Clients are given access to save, edit, view, and replace the contents in the files very efficiently. In this client requests to access the file in the server that is located on another computer. NFS was earlier used in Linux and Unix OS whereas CIFS is used by Windows OS.
CIFS vs SMB
SMB is a network layer application that was developed by IBM in the early 1980s. SMB helps the client to read and write the files over a local network. At later state, CIFS was introduced by Microsoft which was supported by Windows, Linux Operating systems. CIFS uses TCP/IP protocol that was used earlier like HTTP, FTP, etc. CIFS was difficult to manage as there were many sub functionalities, commands to process.
This complexity is been replaced by SMB which was developed by Microsoft. There were many versions of SMB then released to improve their performance year by year. Currently, SMB 3.1.1 is available for Windows 10 OS with AES 128 CCM encryption. It also has SHA-512 hash keys for the pre-authentication check to secure the data over the network.
CIFS Server Security
As per the business requirement, you can change the security settings of the CIFS server. We need to modify the Kerberos security settings, use LDAP security settings, enable ASES encryption to secure the file transfer across the network.
Conclusion
Due to its robust features which include easy access to the server, authenticated file transfer, safe file cache, CIFS is well used. There is still a gap in using CIFS Protocol in this era. Methods are taken to improve the specifications over the present CIFS.
CIFS uses the session services to send and receive the commands to implement the safe and authenticated file transfer over a shared network. We can also say that CIFS is a File transfer protocol that allows file sharing between the working network nodes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to CIFS Protocol. Here we discuss the top 7 features of CIFS protocol along with the difference between CIFS vs NFS and CIFS vs SMB file systems. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –