Updated July 7, 2023
Circular Flow of Income Meaning
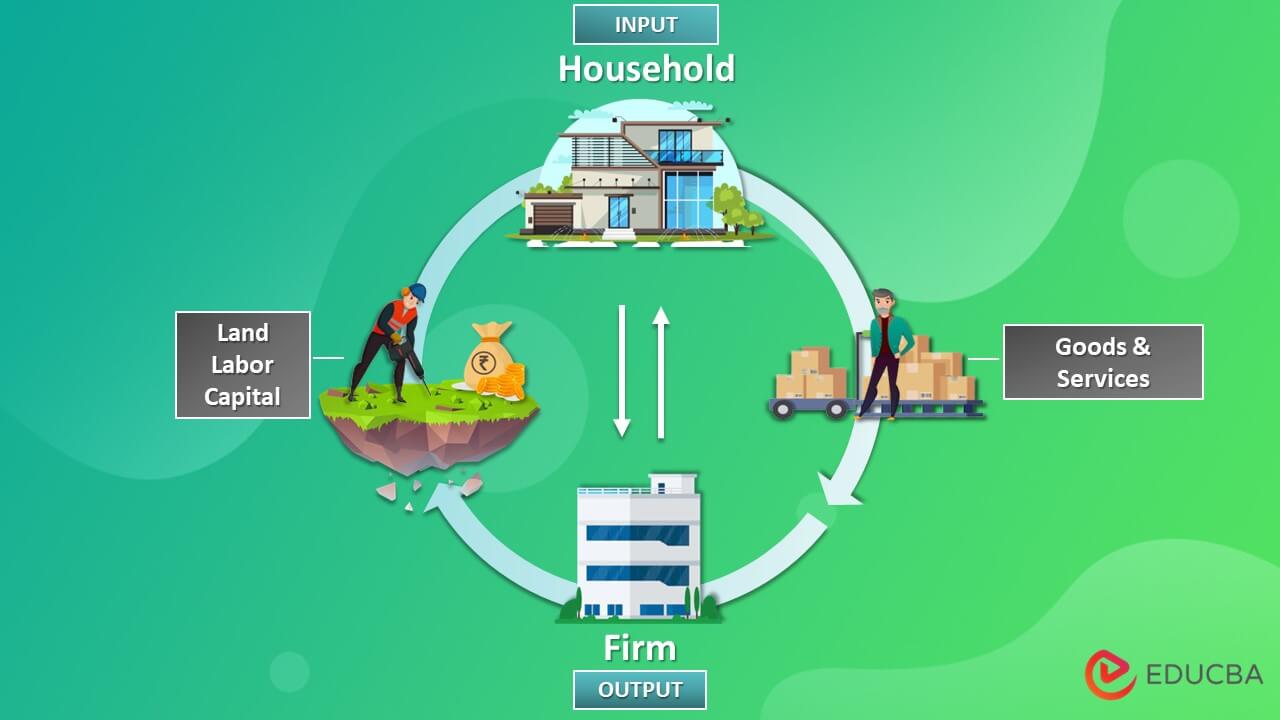
The Circular Flow of Income is a macroeconomic concept explaining how income or money flows through various sectors of an economy.
For example, McDonald’s uses dollars to pay the landlord for the space it rents or its employees’ salaries. In either scenario, the dollar returns to someone’s wallet after entering their household’s income. The family or someone from the family then uses the received payment to spend on food at McDonald’s. Thus, the money finally returns to the beginning of the flow.
It explores the phenomena of money distribution between households and production units. It generally includes the economic flow of income, expenses, and products (goods/services). These factors further classify property, funds, labor, and more. In the US, to enhance this economic style, EPA began a national recycling strategy, which helps create a sustainable environment and an excellent economy.
Key Highlights
- The circular flow of income explains the flow of money from producers to households and back to the producers.
- There are two aspects to this concept, namely, real flow and money flow
- The three primary methods involved in the process are value-added, income, and expenditure method
- Its analysis helps the government determine and adjust its monetary and fiscal policy.
Circular Flow of Income- How Does it Work?
- Usually, businesses, individuals, and the government runs an economy
- In a free market, companies produce and sell products to earn revenue. They use the income to pay wages to people who outsource their services to these firms
- The households then partially spend their income on food, clothing, entertainment, etc., and use the rest for savings and buying things outside of the economy (imports), also called leakages
- To equalize the leakages, some firms do business outside the country (exports), and some borrow money for investment. It is known as an injection, as the money eventually returns to the flow
- The money spent on necessities by the citizens returns to the firms, which explains the Circular Flow of Income.
Example of Circular Flow of Income
Example #1:
A ketchup factory’s factors of production are tomatoes, industrial land, and laborers. As a result, the households enjoy monetary compensation for the rented industrial land, farmers profit from selling tomatoes, and the laborers get wages.
Once the final ketchup bottles are in the market, the households purchase the ketchup bottles using wages, rent, or profits. The money goes to the producers, and factory owners, eventually completing the circular flow.
Example #2:
Mary is a real estate owner who has lent her land to the XYZ manufacturing industry. The XYZ company produces furniture like chairs, tables, etc. When required, Mary purchases furniture from the XYZ company.
As a result, she uses the money from the rent to buy the furniture. Therefore, the money the XYZ company paid as the rent came back to them as business profits. It explains the income circular flow.
Circular Flow of Income Types
Real Flow
- It is the flow of factor services, like land, labor, and entrepreneurship, from households to companies
- There is no involvement of money; both sides only exchange services
- It generally helps determine an economy’s growth.
Money Flow
- It explains the movement of money from the flow of factor payments, such as rent, wages, and interest from firms to households.
- Here, there is an exchange of funds between households and firms
- Nominal flow is another name for money flow.
Methods of Calculation & Formulas
Value-added Method
- This method calculates the national income as per the different production phases of goods and services
- It aims to calculate the value added to the product during the various stages of production.
Income Method
- This method totals the income individuals earn in exchange for their services. It takes into account the rent, interest payments, wages, and profits
- It is also known as NDPfc, i.e., net domestic product at factor cost.
Expenditure Method
- It calculates the expenditures of individuals, businesses, and the government
- The formula sums the consumer purchase (C), government expenditure (G), investments by business firms (I), and net exports (NX).
Final Thoughts
The Circular Flow of Income is the economic concept of the constant flow of money. It shows the interdependence of different economic sectors. In addition, it highlights the link between earning and spending in an economy. Thus, it becomes vital to understand the income flow to understand the economic wealth of a nation.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What are the four sectors in the circular flow of income?
Answer: The four sectors involved in the circular flow of income are household, government, firm, and foreign. These sectors, on the whole, account for GDP expenditures.
Q2. What are the three primary income flows of an economy?
Answer: Total production, income, and spending are the three ways income flows in an economy. Production concerns the entire demand and supply of goods and services. On the other hand, income and spending consider the cash inflow and outflow through the economy.
Q3. What are Leakages and Injections in the Circular Flow of Income?
Answer: While leakages are withdrawals of money from the circular flow, injections are the addition of money. Leakage happens when individuals save money that does not pass through the regular flow—for example, savings, imports, and taxes. Injection occurs when households/firms borrow money from institutes like banks. It helps increase the flow of income in an economy—for example, investment, exports, and government expenditure.
Q4. What are the different phases of the Circular Flow of Income?
Answer: There are three phases in the circular flow of income: Generation, distribution, and disposition. In the generation phase, the firms initiate the production of goods and services with the aid of the factor service. In the distribution phase, income factors like rent, wages, etc., move from the firms to households. The last phase, i.e., the deposition phase, the public utilizes their income on the goods and services the firms generate.
Recommended Articles
This article entails information about the circular flow of income. It explains its types, examples, and more. You can learn more about similar topics from the following articles,