What is Climate Finance?
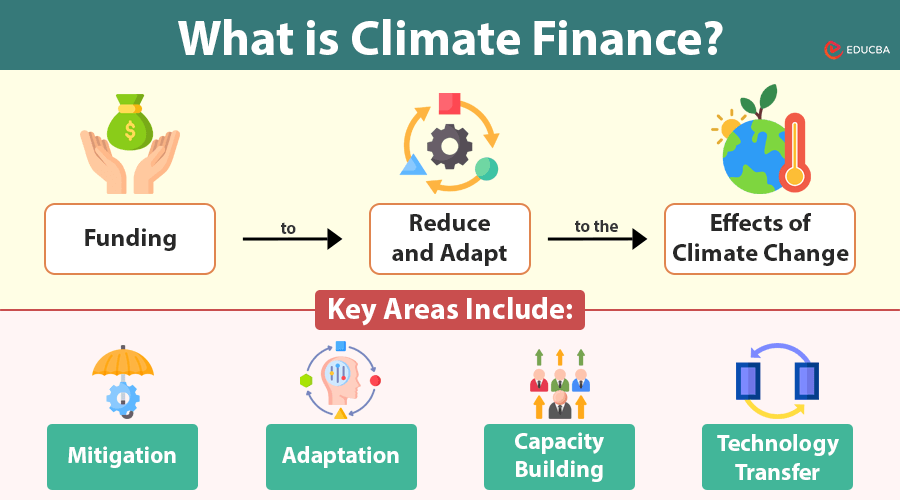
Climate finance means funding to reduce and adapt to the effects of climate change. It is important for global efforts to shift to a low-carbon, sustainable economy, and support communities affected by climate change. This article explores climate finance’s concept, significance, mechanisms, and challenges and its role in fostering international cooperation.
Understanding Climate Finance
Climate finance encompasses various funding sources, mechanisms, and investments to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and enhance resilience to climate impacts. It includes public, private, and alternative funding sources, focusing on supporting climate-related projects in developing countries.
Key areas include:
- Mitigation: Investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, reforestation, and sustainable transport to reduce GHG emissions.
- Adaptation: Providing funding for infrastructure, technology, and practices to help communities better cope with climate change impacts.
- Capacity Building: Supporting the development of technical, institutional, and human resources to implement climate actions effectively.
- Technology Transfer: Facilitating the exchange of technologies that enable low-carbon and climate-resilient development.
Importance of Climate Finance
- Meeting Global Goals: The Paris Agreement seeks to keep global warming below 2°C, preferably at 1.5°C, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring that vulnerable populations, who often contribute the least to climate change but suffer its greatest consequences, receive adequate support.
- Economic Growth: Driving innovation and creating green jobs while transitioning to a sustainable economy.
Mechanisms of Climate Finance
Various mechanisms and channels facilitate climate finance, including:
1. Multilateral Funds
- Green Climate Fund (GCF): The GCF, created by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), helps fund projects in developing countries to address climate change through mitigation and adaptation.
- Global Environment Facility (GEF): Provides grants for environmental projects, including climate change mitigation and biodiversity protection.
- Adaptation Fund: Focused on adaptation initiatives, particularly in vulnerable communities.
2. Bilateral Aid
Developed countries provide climate finance directly to developing countries through bilateral agreements.
3. Private Sector Investments
The private sector contributes greatly by investing in clean technologies, renewable energy, and sustainable infrastructure. Mechanisms like green bonds and carbon markets incentivize private sector participation.
4. Innovative Financing
- Carbon Pricing: Includes carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems to generate revenue for climate projects.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: Enable individuals and organizations to contribute to climate initiatives.
- Blended Finance: Combines public and private resources to de-risk investments and mobilize larger funding.
Challenges in Climate Finance
Despite its critical role, climate finance faces several challenges:
- Funding Gap: The current levels of climate finance are insufficient to meet the estimated trillions of dollars needed annually to achieve climate goals.
- Access and Equity: Many developing countries face barriers to climate finance due to complex procedures and a lack of institutional capacity.
- Transparency and Accountability: People still worry about using funds properly and ensuring they reach their goals.
- Political Will: The willingness of governments to commit to and sustain climate finance varies and is often influenced by domestic priorities and economic pressures.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation is crucial for scaling up climate finance and ensuring its effective deployment. The annual COP meetings under the UNFCCC offer a platform for negotiating agreements and monitoring progress. Developed countries pledged to mobilize $100 billion annually in climate finance by 2020 but have not fully met this target.
Collaboration among governments, multilateral institutions, the private sector, and civil society is essential for:
- Aligning investments with global climate goals.
- Sharing best practices and technologies.
- Strengthening accountability and transparency frameworks.
The Way Forward
The following steps are essential to make the most of climate finance:
- Enhancing Financial Commitments: Increasing contributions from developed countries and leveraging private sector investments.
- Simplifying Access: Streamlining application processes and building institutional capacities in developing countries.
- Promoting Innovative Solutions: Expanding mechanisms like blended finance, green bonds, and nature-based solutions.
- Strengthening Monitoring Systems: Implementing robust frameworks to track and evaluate the effectiveness of climate finance initiatives.
Final Thoughts
Climate finance is key to fighting climate change and promoting sustainable development worldwide. Bridging the funding gap, promoting equity, and driving innovation can transform the global response to one of humanity’s most pressing challenges. Ensuring that climate finance is adequate, accessible, and effectively utilized will be key to building a resilient and sustainable future for all.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide helped you understand the importance and mechanisms of climate finance. Check out these recommended articles for more insights on sustainable development and climate action.

