Updated December 15, 2023
Clinical Research Definition
Medical researchers use clinical research to test and investigate new medicines and drugs to see if they are safe and effective.
Clinical research is where medical scientists investigate diseases, medical equipment, etc., to understand the root causes and symptoms of these health issues and to know if the medical treatments will be safe and effective. This research is often carried out with the help of volunteers who are willing to participate in the study.
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Goals
- Phases (with Example)
- Types
- Job Positions & Salary
- Top Organizations
- How do Researchers Decide on Volunteers?
Goals
Researchers use clinical research for several purposes, such as,
- Understanding Treatment’s Long-Term Effects: It is when researchers observe how the participants’ body reacts to the medical procedure or treatment in the long term.
- Compare and Find Alternate Treatments: Researchers can compare how effective different treatments are for the same health condition and accordingly choose the most effective one.
- Study Inconsistency in Effects & Cure of Health Conditions: Medical professionals can also use clinical research to learn how some people are highly affected by a disease while others are not, as well as how some individuals have higher chances of getting a disease than others.
- Identify Biomarkers: It makes it easier to find any markers in the blood that can help detect a particular medical condition before symptoms appear.
- Investigate Immunotherapy: It also helps understand how the human immune system fights various diseases.
- Study how Genes Affect Drug Response: Researchers can study how a person’s genes can interfere with or improve their body’s response to a particular medication.
- Explore Various Mental Health Interventions: Researchers can also experiment with several medical treatments to cure mental illnesses.
- Test and Approve Health Technologies: It lets medical professionals check how effective the latest medical technologies and mobile applications are.
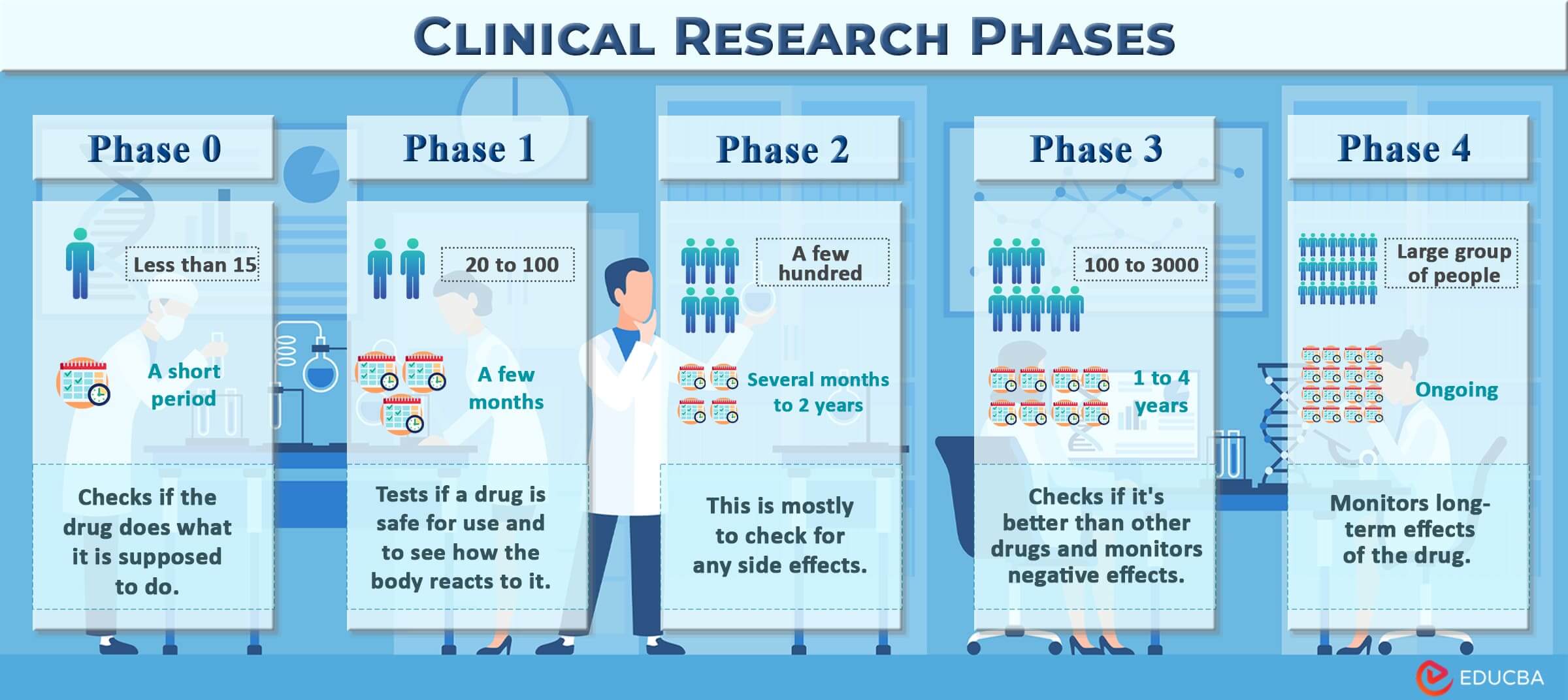
Phases of Clinical Research
These are the 5 phases (0-4) of clinical research:
Example:
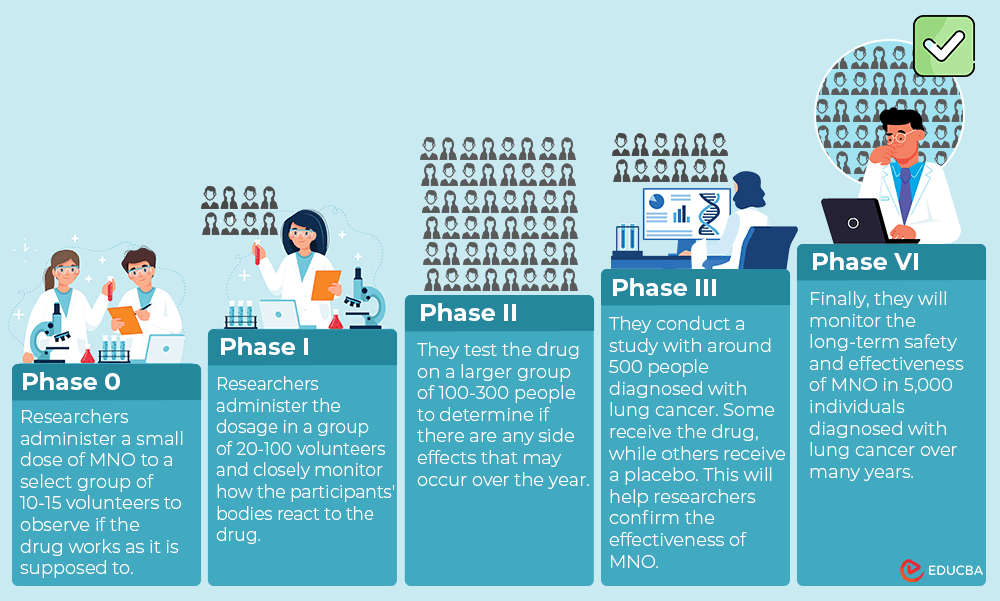
Imagine a group of medical researchers who want to see if a drug, MNO, can help treat lung cancer. They go through different stages to make sure the drug is safe and effective.
Phase 0:
First, in Phase 0, they will administer a small dose of MNO to a select group of 10-15 volunteers, both healthy and individuals diagnosed with lung cancer. Researchers will observe if the drug works as it is supposed to.
Phase I:
Next, in Phase I, they will gradually increase the dosage in 20-100 volunteers. Researchers will closely monitor how the participant’s body reacts to the drug.
Phase II:
Then, in Phase II, they will test the drug on a larger group of 100-300 people diagnosed with lung cancer to determine if any side effects may occur over the year.
Phase III:
After that, in Phase III, they will conduct a study with around 500 people diagnosed with lung cancer. Some will receive the drug, while others will receive a placebo (A drug with no therapeutic effect). It will help researchers confirm the effectiveness of MNO.
Phase IV:
Finally, in Phase IV, they will monitor MNO’s long-term safety and effectiveness in 5,000 individuals diagnosed with lung cancer over many years.
This process allows researchers to ensure the drug is safe and effective before they release it to the public.
Types of Clinical Research
In the field of medicine, different types of clinical research deal with various health challenges. Let’s see a few of them:
1. Treatment research focuses on finding new ways to treat diseases and illnesses, such as medicines, surgeries, equipment, etc.
Example: An example would be scientists working on developing a new cancer treatment.
2. Prevention research involves finding methods to prevent diseases from affecting you or reoccurring after the first treatment.
Example: An example would be researchers working on creating an effective vaccine to stop a fast-spreading virus.
3. Screening research focuses on identifying individuals at risk for specific health conditions.
Example: Researchers evaluating a blood test’s effectiveness in identifying people at risk for cardiovascular diseases is an example of screening research.
4. Diagnostic research is about improving how quickly and easily we diagnose health conditions.
Example: It may involve introducing an advanced imaging device that can quickly identify early signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
5. Quality of life research is geared towards enhancing the lives of those with long-term illnesses or disabilities. It involves developing treatments that can manage symptoms, boost mental health, etc.
Job Positions & Salary
| Job Position | Salary Range | Job Responsibilities |
| Clinical Research Coordinator | $28,000 – $60,000 per year | Selecting participants, monitoring trials, and collecting data. |
| Clinical Research Associate | $46,000 – $150,000 per year | Helps organize and monitor all clinical trial phases. |
| Clinical Data Manager | $48,000 – $159,000 per year | Creating a data management plan, designing databases, formats, queries, etc. |
| Clinical Research Nurse | $17.6 – $55.4 per hour | Collect and manage patient data and ensure that participants receive proper care. |
| Clinical Project Manager | $54,000 – $125,000 per year | Decide the necessary tests and ensure all resources, staff, and equipment are available. |
| Clinical Research Scientist | $46,000 – $141,000 per year | Perform the required clinical research as per the right protocols. |
Top Clinical Research Organizations
| Organization | Solutions Offered | Notable Achievements |
| IQVIA |
|
IQVIA and Roche have collaborated to enhance access to care for patients with rare diseases. |
| Parexel |
|
Teamed up with Partex to incorporate AI into the process of discovering and developing drugs. |
| ICON |
|
ICON is collaborating with BARDA for clinical trials on COVID-19 vaccines under “Project NextGen.” |
| PPD |
|
Received the 2023 Training magazine APEX Award for outstanding employee development programs. |
| Syneos Health
|
|
Received the 2023 ViE (Vaccine Industry Excellence) award in recognition of their achievements in the vaccine sector. |
How do Researchers Decide on Volunteers?
Researchers use a carefully planned process to determine who will participate in clinical research. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the key steps:
1. Target Population
Researchers identify the target population based on the study’s objectives. This may include individuals with a specific medical condition, age group, gender, or other relevant characteristics.
2. Specifying Criteria
Researchers define specific criteria that individuals must meet to participate (inclusion criteria) and factors that disqualify them (exclusion criteria). This helps ensure the study’s relevance to a particular population and controls for variables that could impact the results.
3. Safety Considerations
Exclude individuals who may be at higher risk for adverse effects based on their medical history. Prioritize participant safety throughout the study.
4. Feasibility
Consider logistical aspects, such as the availability of participants, resources, and facilities. Ensure that the study can be realistically conducted within the specified parameters.
5. Randomization (if applicable)
In some clinical trials, participants are randomly assigned to different groups (e.g., treatment and control). Randomization helps minimize bias and ensures that the groups are comparable.
6. Ethical Considerations & Regulatory Approval
Obtain approval from ethical review boards and regulatory authorities. Compliance with regulatory standards ensures the study meets ethical and safety standards. Researchers must also get informed consent from the participants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What qualifications do you need to be a clinical researcher?
Answer: Pursuing any related bachelor’s degree is the basic qualification you need to become a clinical researcher. Having a master’s degree and some project or work experience can also be advantageous.
Q2. What is the entrance exam for clinical research?
Answer: In the US, SOCRA conducts the CCRP exam for clinical researcher candidates, while in India, the national exam you need to take is NEET. Similarly, the exams might differ from nation to nation.
Q3. How do I join a research institute trial?
Answer: You can start by finding the various cynical trials happening in your area and contact them to learn more about the program. Once the organization sends you the trial description, you can read it thoroughly and decide if you are a great fit for it. If yes, you can sign the consent form to be a part of the clinical research trial.
Recommended Articles
We hope you found this comprehensive article on Clinical research useful. If so, please visit the following recommendations as well.