Updated June 22, 2023
Introduction to Cloud Computing Tools
With the advent and popularity of cloud computing and the ease of accessibility, the risks of cloud computing are sometimes overlooked. The growing trend of cloud computing in different genres presents a group of risks exclusive of each other, and it is hard to group them under a single umbrella in common. But in the story below, in the next few parts of explaining the risks of cloud computing, we will consider the story of “How Gotham is Built (Batman Comic series).” In case the movie is unknown, Gotham is analogous to cloud computing, and How? is the way Gotham City is built brings a more intuitive flavor to this topic.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing prevailed since 1971 but gained popularity only after Amazon released Elastic Compute Cloud in 2006 and updated the version of AWS in 2018. Now to understand more about the types of tools, let us know more about the city of Gotham. The city is an environment where people share services. These services can be infrastructure, platforms, software, data, APIs, and anything one can think of sharing in public/private. This concept of cloud computing makes it easy for people planning to build their infrastructure in the city. With this idea, the cost-benefit, first-time investment, maintenance, computation, and storage capability (hardware) are tangible. Forrester, the research company, quotes cloud computing as:
“A standardized IT capability (services, software, or infrastructure) delivered in a pay-per-use, self-service way. Research coverage includes cloud security.”
Need for Cloud Computing Tools
A different cloud service provider provides different sets of services and tools for the operation and control of the cloud. These tools can be related to helping enterprises integrate, buy, manage, monitor, tweak, and track cloud services in private/public/hybrid cloud space. The complexity of each tool depends on which layer of service model architecture tools fall into (IaaS/PaaS/SaaS). For example, IaaS tools might be easier to use than PaaS because, in PaaS, the user might have to know about specific interfaces to run. The tools segregate into open-source and proprietary. In addition, to provide full transparent visibility into cloud operations, these tools must be provided by cloud service providers. In analogy, to build and manage Gotham City, we would require various tools to ensure the comfort of the people in the city and ensure no threats.
Uses of Cloud Computing Tools
The essential uses of cloud computing tools benefit enterprises in various ways leading to quantifiable improvements in their business.
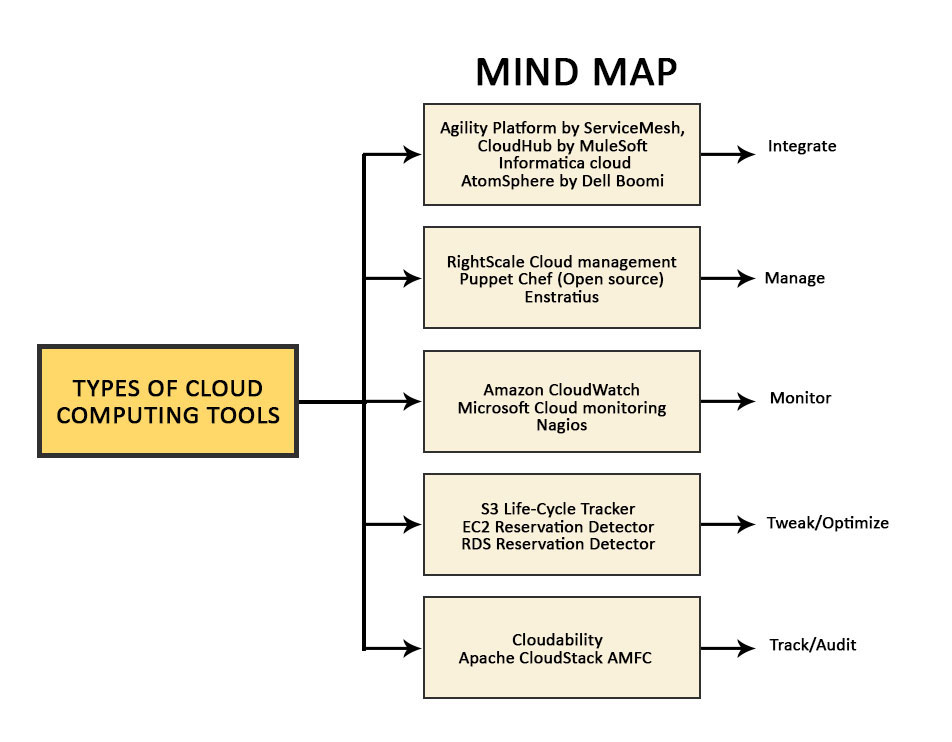
1. Help Enterprise Integrates
These tools support enterprises in any data integration-related issues and support integration deployment. These tools also pave the way for adherence to IT governance and control.
- Analogous Situation: Having a governing body to help integrate different parts of city Gotham to ensure the smooth functioning of the city.
- Examples: Agility Platform by ServiceMesh, CloudHub by MuleSoft (Open Source), Informatica cloud, AtomSphere by Dell Boomi.
2. Help Enterprise Manage
These tools help in wide genres of cloud services management, for example, infrastructure management, configuration management, automation of management services, and help follow governing rules of infrastructure and cloud computing applications. Through a single integrated control point for governance, the tools ensure adherence to compliance and security of cloud services.
- Analogous Situation: The managing of Gotham City to ensure the rules are followed and manage different areas in the city like city planning, employment planning, etc.
- Examples: RightScale Cloud management, Puppet (Open source), Chef (Open source), and Enstratius (acquired by Dell and is currently support-only).
3. Help Enterprise Monitor
These tools help in monitoring cloud computing architecture, infrastructure, and services. The tools in this category will help administrators identify possible system defects in a reactive or proactive mode to prevent minor glitches from turning into major problems.
- Analogous Situation: Monitoring Gotham City will prevent any issues in the city from turning into chaos.
- Examples: Amazon CloudWatch (Proprietary), Microsoft Cloud monitoring (Proprietary), and Nagios (Open source).
4. Help Enterprise Tweak/Optimize
These tools help the organization to overbuy resources. These help them tweak by giving insights into inefficiencies in the service and suggesting a methodology to eliminate the inefficiencies. These tools use Reservations, Rightsizing, automation, and other techniques to optimize/tweak.
- Analogous Situation: Gotham City needs an organization so that all resources can perform optimally.
- Examples: S3 Life-Cycle Tracker (Proprietary), EC2 Reservation Detector (Proprietary), and RDS Reservation Detector (Proprietary).
5. Help Enterprise Track/Audit
These tools help the enterprise track and analyze cloud computing services’ usage. For example, some tools help analyze the expense of the services being used and help identify opportunities to reduce cost/alerts/recommendations.
- Analogous Situation: Having a regulatory body in Gotham to understand and track the economy/activities will enable the city to prosper better.
- Examples: Cloudability (Proprietary), Apache CloudStack AMFC (Open source).
Conclusion
In the world of cloud computing, it is inevitable to miss the monitoring of assets and performance of the application in addition to the physical servers. The perfect fit for the services an enterprise requires depends on factors like needs, budget, and type of requirement. Some of these tools come with a tagline of “do-it-all,” and few come with specific specialized features; again, depending on the factors mentioned above, the enterprise can choose from various choices.
Mind Map
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cloud Computing Tools” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.