Updated April 28, 2023
Difference Between Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics
Since the New York Times published an article on how Walmart utilizes big data analytics to maximize its sales, people have been in a frenzy about Big Data. The retailer figured out that sales of Pop-Tarts, a famous brand of Sweets surges during Hurricanes and used this knowledge to increase their profits. Be it individuals who save their data for on-the-go access or businesses who cut upfront costs while maintaining disaster-proof IT operations, everyone is looking towards the sky these days. Enter cloud computing, a modern computing approach, because everyone is on cloud nine.
Post the dot-com bubble burst, information technology is gaining incredible momentum. Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics are emerging from this momentum, the two hottest trends that have an unprecedented impact on all levels of human life. In this write-up, we will look at these trends in today’s technological ecosystem and attempt to compare Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics
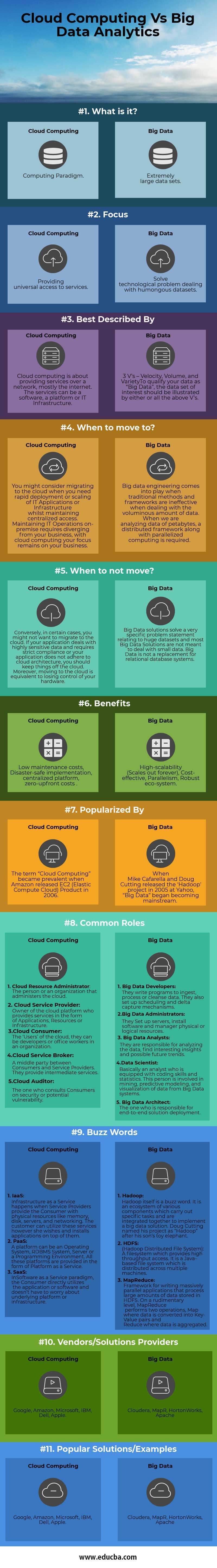
Below are the Top 11 Comparison between Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics:
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics
- Cloud computing is about providing computer resources and services over the network. Big Data is tackling problems faced when a huge amount of data is involved, and traditional methods become infeasible.
- Big Data works by breaking huge data sets into manageable ‘chunks’ and distributing these chunks across different computer systems. In Cloud computing, information is stored on physical servers maintained and controlled by Service Providers. The user can access these resources through the internet.
- It is possible to deploy Big Data Solutions on the cloud through the PaaS or SaaS service. In PaaS, the Hadoop platform is provided to the consumer, while in SaaS, various components or applications running on Hadoop are accessible. The marriage of Big Data and Cloud Computing is becoming so popular that we have a new buzzword in IT: BDaaS (Big Data as a Service).
- Big Data taps the previously ignored data of an organization and provides valuable insights which can drive its business. In contrast, Cloud Computing provides flexibility and speed concerning IT deployments which can streamline an organization’s operations.
Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics Comparison Table
The differences between cloud computing vs Big data analytics:
| Basis for Comparison | Cloud Computing | Big Data |
| What is it? | Computing Paradigm. | Huge data sets. |
| Focus | Providing universal access to services. | Solve technological problems dealing with humongous data sets. |
| Best described by | Cloud computing is about providing services over a network, primarily the Internet. The services can be software, a platform, or IT Infrastructure. | 3 V’s – Velocity, Volume, and Variety. To qualify your data as “Big Data,” the data set of interest should be illustrated by either or all of the above V’s. |
| When to move to? | You might consider migrating to the cloud when you need rapid deployment or scaling of IT Applications or Infrastructure while maintaining centralized access. Maintaining IT Operations on-premise requires diverging from your business; with cloud computing, your focus remains on your business. | Big data engineering comes into play when traditional methods and frameworks are ineffective when dealing with voluminous data. A distributed framework and parallelized computing are required to analyze petabytes of data. |
| When to not move? | Conversely, you might not want to migrate to the cloud sometimes. If your application deals with highly sensitive data and requires strict compliance or does not adhere to cloud architecture, you should keep things off the cloud. Moreover, moving to the cloud is equivalent to losing control of your hardware. | Big Data solutions solve a particular problem relating to massive datasets, and most Big Data Solutions are not meant to deal with small data. Big Data is not a replacement for relational database systems. |
| Benefits | Low maintenance costs, Disaster-safe implementation, centralized platform, zero-upfront costs | High-scalability (Scales out forever), Cost-effective, Parallelism, Robust ecosystem |
| Popularized by | “Cloud Computing” became prevalent when Amazon released EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) Product in 2006. | When Mike Cafarella and Doug Cutting released the ‘Hadoop’ project in 2005 at Yahoo, “Big Data” became mainstream. |
| Common Roles |
|
|
| Buzz Words |
|
|
| Vendors/Solutions Providers | Google, Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, Dell, Apple. | Cloudera, MapR, HortonWorks, Apache. |
| Popular Solutions/Examples |
|
Hadoop is the most popular Big Data Solution inspired by Google File System (GFS) and MapReduce papers. A Hadoop ecosystem typically has many components, such as Ambari for cluster management, Sqoop for data extraction, Hive for data warehousing, and Oozie for scheduling. |
Conclusion
Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics have truly impacted how organizations function, and humans operate. Cloud Computing provides benefits that apply to all sizes of businesses and individuals. Data is perceived as a resource, and organizations are scrambling to implement Hadoop to exploit this resource. It is interesting to know that although these technologies have become mainstream, companies are still investing huge amounts in R&D. We can expect more growth in Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics in coming years.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Cloud Computing vs Big Data Analytics. Here we discuss head-to-head comparison, key differences, comparison table, and infographics. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –