Updated June 14, 2023
Difference Between Cloud Computing and Data Analytics
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of IT as a service from data centers. The word cloud is used as a metaphor to represent the internet due to its vast resource repository and information to suit different user needs. Resources in the cloud include servers, bandwidth, network, storage, etc., along with software and OS platforms. Cloud makes IT resources available as a utility, which is similar to the power utility we have in our homes.
Cloud involves the centralizing of resources (hardware and software) made available as a service. Cloud services are provided by a cloud service provider (CSP). Some examples of CSPs are Amazon Web services, Microsoft Azure, Google, IBM, etc. Consumers/Users are billed based on each resource consumed and for the resource availed over time. Clouds have many advantages, which make them the ideal option for organizations, big or small. Some of the characteristics of clouds include,
- Scalability, availability, reliability, and robustness
- Cost-effective and flexible
- Enhanced business value and agility
- Improved operational efficiency
Cloud services are classified as service models and deployment models. The service models are:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Cloud deployment models are:
- Private clouds: This model is an in-house or an outsourced privately-owned data center infrastructure with good levels of security and is expensive.
- Public clouds: This is a cost-effective model and is mostly available for free on the internet. Examples include Google Gmail, Google Drive, etc. Here the data is not fully secure.
- Hybrid Clouds: This model combines private and public cloud models. Security is an issue here.
All cloud resources and models are made available through the internet. Access to the resource is possible with any standard browser software or with any device that connects to the internet.
Due to the emergence of new technologies, we are witnessing a big data deluge due to substantial changes made in the interactions in business to consumer or business to business and between organizations. New data is generated continuously, especially in customer-oriented organizations and at every stage of all transactions. All this data, when modeled correctly, can be analyzed to support effective decision-making in organizations. Hence, the data growth fueled by various devices and the internet has the potential for unprecedented opportunities.
Data analytics can be understood as analytical modeling or preparing data for accurate quantitative analysis. Data analytics is required for extracting insightful information to drive continuous improvements and to understand trends and business performance. Thus analytics is understood as measuring and estimating data from big data sources. New analytics trends in real-time streaming data can quickly respond to volatile demands and better quality and value, which pave the way for a digitally-driven organization.
Processing big data from multiple sources needs high-end computing systems and networks that are easily available from cloud service providers. Hence data analytics has become a necessity for organizations to gain valuable insights related to their products or services from different sources of data.
Data analytics is important for organizations because it helps to,
- Reduce costs by identifying redundant processes or operations
- Understanding customer preferences to provide customized products or services leads to better competitiveness
- Make faster and more effective decisions based on current information
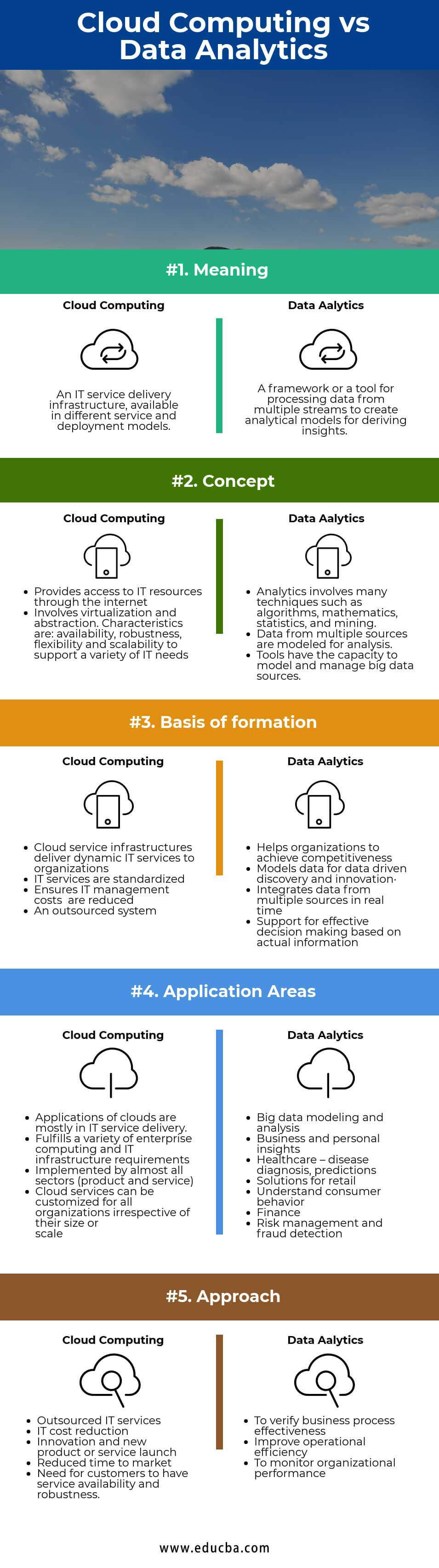
Head-to-Head Comparison Cloud Computing and Data Analytics (Infographics)
Below is the Top 5 Comparison Between Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics
 Key Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics
- Both cloud computing and data analytics platforms offer cost reduction and efficiency for organizations towards achieving business agility. However, cloud computing is a technology or infrastructure to provide continuous and dynamic IT services. In contrast, data analytics is a technique aggregating data from multiple sources for data modeling and data preparation for deeper analysis.
- Clouds provide scalable compute, storage, and network bandwidth capacities for big data applications. On the other hand, data analytics need IT infrastructures to process and model incoming data streams at high speed. Thus clouds and data analytics can go together.
- Clouds services provide solutions for all types of data-intensive processes.
- Cloud infrastructures can integrate well with existing systems, and hence they can link different departments and data across the organization to build a centralized data model. Thus the organization can use developed analytical models to collaborate with other organizations, monitor markets and gain competitiveness.
Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics Comparision Table
The differences between cloud computing vs data analytics are explained in the points presented below:
| Basis for Comparison | Cloud Computing | Data Analytics |
| Meaning |
|
|
| Concept |
|
|
| Basis of formation |
|
|
| Application areas |
|
|
| Approach |
|
|
Conclusion
In organizations, both Cloud Computing and Data Analytics technology implementations will complement each other towards better performance and value. This is because, with rapid growth in big data, organizations need an appropriate and adequate environment for managing big data processes which are enabled by cloud services.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics, their Meaning, Head to Head Comparison, Key Differences, Comparision Table, and Conclusion. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
 Key Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Data Analytics