Updated May 5, 2023
Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Fog Computing
Cloud computing uses remote servers or computers across the internet to perform data operations, store, and manage data instead of using a local computer or server. Cloud computing offers delivery services directly over the internet. The services provided by Cloud computing can be of any type, such as storage, databases, software, applications, network, servers, etc. Fog computing is the term Cisco coined, which means extending services beyond cloud computing to the enterprise’s requirements. It consists of a decentralized environment for computing in which the infrastructure provides storage, applications, data, and computations. Fog Computing is also called Fog Networking or Fogging.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing
Below are the top 7 comparisons between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing:
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing
Below are the most important Differences Between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing:
1. Cloud computing architecture has different components such as storage, databases, servers, networks, etc. In contrast, Fog computing has all the features similar to that cloud computing, including some additional features of efficient and powerful storage and performance between systems and cloud networks.
2. Cloud computing architecture systems can be divided into two sections, a front end, and a back end, in which both will be connected as a network. In contrast, Fog computing extends cloud computing by providing features at the network’s edge.
3. The front-end section of cloud computing is called the User interface, where the end-users or customers use the cloud computing services, whereas the back end is the cloud computing network’s cloud section. In contrast, Fog computing aims to improve efficiency and reduce the transformation of data or data operations from and to remote networks distributed across different locations.
4. The client can access the different types of services through the front-end section of cloud computing. The user can usually access services like a local computer but will be accessed by connecting to a network. In contrast, Fog computing is being supported by a large open group consortium called Open Fog Consortium, which was formed in November 2015 by a group of companies such as Cisco, Dell, Microsoft, Intel, ARM, and Princeton University.
5. In cloud computing, the back end section includes the servers, different computers, storage, and database systems interconnected with each other to form a cloud network distributed across different locations. In contrast, Fog computing processes the data in Central Server by collecting the data from various devices deployed at long distances or locations far from the central server.
6. In cloud computing, the storage space requirement is more for the clients to access the data stored by them; almost the storage space will be made available twice the data that has been held to provide high-speed access, whereas, in Fog computing, the data operations and calculations take place in the central hub of the device to reduce the data transformations from and to the main server.
7. A central server exists in cloud computing to administer or manage the different computers or servers connected; their interactions and mechanisms will be controlled and managed, whereas Fog computing supports most of the devices in IoT – Internet of Things compared to cloud computing by providing more compliance and ease of migration.
8. A middleware exists along with the central server to establish a communication protocol among multiple servers and to communicate with each other safely and securely. In contrast, Fog Computing supports many IoT applications and big data services by handling large amounts of data and various devices.
9. We make all the data stored in the central database server storage available as a backup to ensure high availability in case of server failures, which is called redundancy. In contrast, Fog Computing has more extensive distribution across geographical areas by efficiently supporting many users across the network.
10. The main core component of cloud computing is the Internet / Network, without which the entire network collapses, and there is no way of connecting to the cloud servers. Fog Computing has different applications ranging from the Internet of Things to Human-Machine Interactions ranging wide applications.
11. Many end-users can connect to the cloud servers from the remote machines using Virtual Device Interfaces called Virtual Machines, called Virtualization. We can consider Fog computing whenever extreme edges such as railways, ships, vehicles, and roadways collect a large amount of data.
12. Cloud computing utilizes different services such as storage, software development applications, servers, and databases. Cloud computing provides more accessibility to operating servers or applications quickly without any limitations.
13. Fog computing mainly utilizes local computer resources rather than accessing remote computer resources, causing a decrease in latency issues and performance, further making it more powerful and efficient.
14. Providers offer cloud computing services based on server applications, enabling users from any location to access services from different devices such as computers, mobiles, tablets, etc.
15. Fog computing has many benefits, such as it provides greater business agility, deeper insights into security control, better privacy, and less operation. It has an extra layer of an edge that supports and is similar to that of cloud computing and Internet of Things applications. Fog computing mainly provides low latency in the network by providing instant response while working with interconnected devices.
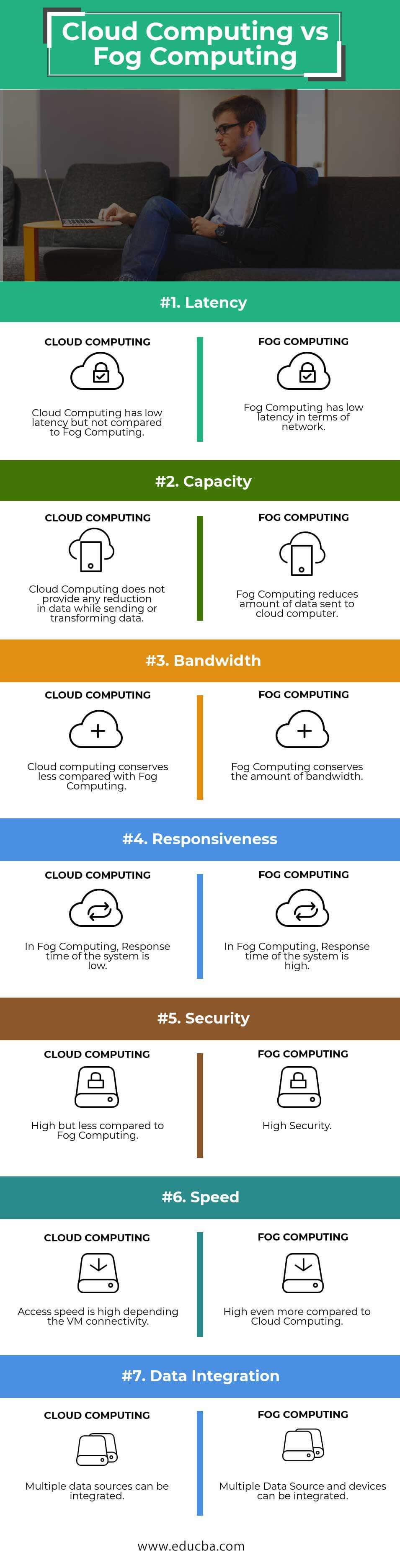
Cloud Computing and Fog Computing Comparison Table
Below are the points that describe the comparisons Between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing.
| Basis For Comparison | Cloud Computing | Fog Computing |
| Latency | Cloud Computing has low latency but not compared to Fog Computing. | Fog Computing has low latency in terms of a network. |
| Capacity | Cloud Computing does not provide any reduction in data while sending or transforming data. | Fog Computing reduces the amount of data sent to cloud computing. |
| Bandwidth | Cloud computing conserves less compared with Fog Computing. | Fog Computing conserves the amount of bandwidth. |
| Responsiveness | In Fog Computing, the response time of the system is low. | In Fog Computing, the response time of the system is high. |
| Security | High but less compared to Fog Computing. | High Security. |
| Speed | Depending on the VM connectivity, the access speed increases. | High even more compared to Cloud Computing. |
| Data Integration | Someone can integrate multiple data sources. | Someone can integrate multiple data sources and devices. |
Conclusion
Someone can obtain the main benefits from Fog computing compared to cloud computing. Fog computing has low latency and a high response rate, which has become the most recommended compared to cloud computing. It supports the Internet of Things as well as compared to Cloud Computing. People prefer and recommend Fog computing for more efficiency and high productivity regarding large users and widely distributed networks.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Cloud Computing vs Fog Computing. Here we have discussed Cloud Computing vs Fog Computing head-to-head comparisons, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –