Updated June 15, 2023
Differences Between Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing
Mainly, both Cloud Computing and Grid Computing are used to process tasks. However, grid computing is used in cloud computing but not a cloud or part of it. They both involve massive computer infrastructures and managing them. Both Cloud Computing and Grid Computing concepts have been developed for distributed computing, that is, computing an element over a large area, literally on computers separated by some or the other means.
Let us look at the differences and help you understand how Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing is different.
Head to Head Comparison Between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 Comparison Between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing:
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing
Though both Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing technologies is used for processing data, they have some significant differences, which are as follows:
- Cloud computing delivers services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and the internet. Companies providing this service are cloud providers and charge you according to your usage. Grid computing, on the other hand, is distributed computing. There are different computers on the same network that share the same resources. Every resource is shared on a computer, making it a supercomputer. Authorized users need to process power, memory, and data storage; cloud computing leverages them for specific tasks.
- Cloud computing has different services like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. These are Infrastructure, Platform, and Software. Through these services, the cloud provides servers and virtual machines (VMs), on-demand environments for development, testing, delivering, and managing software applications, and providing software applications over the Internet, on-demand, and typically on a subscription basis. It also has different deployments like public, private, and hybrid. These help in deploying resources publicly, privately, or both. Grid computing, on the other hand, has distributed computing and distributed pervasive systems. A distributed computing architecture consists of several client machines with very lightweight software agents installed with one or more dedicated distributed computing management servers. Pervasive computing uses embedded microprocessors in everyday objects, allowing them to communicate information. It helps to choose any device like kitchen appliances or any chip which could be embedded.
- When cloud computing comes into the picture, only single ownership is used. Whereas a grid has many systems in a network, multiple people can have rights. Virtualization helps in providing cloud better security.
- Grid computing is more economical. It splits the work and distributes it over the network on computers, increasing efficiency. Cloud computing is costlier and requires an initial setup. But it is faster and has quicker data restoration.
Comparison Table
Following are the lists of points that show the Comparisons Between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing:
| Basis of comparison | Cloud Computing | Grid Computing |
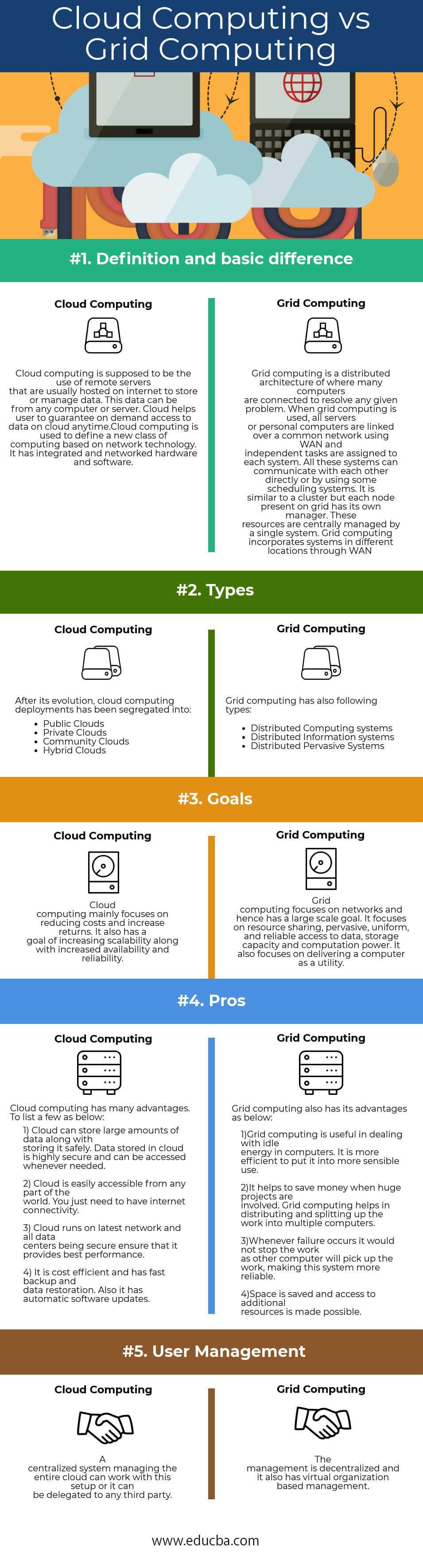
| Definition and Basic Difference |
Cloud computing uses remote servers hosted on the internet to store and manage data. This data can be from any computer or server. Cloud helps a user to guarantee on-demand access to data on the cloud at any time. Cloud computing defines a new class of computing based on network technology. It has integrated and networked hardware and software. |
In grid computing, many computers connect to solve a given problem, creating a distributed architecture. When using grid computing, all servers or personal computers link over a common network using WAN and assign independent tasks to each system. All these systems can communicate with each other directly or by using some scheduling systems. It is similar to a cluster, but each node present on the grid has its own manager. A single system centrally manages these resources.
Grid computing incorporates systems in different locations through WAN |
| Types | After its evolution, cloud computing deployments have been segregated into:
|
Grid computing also has the following types:
|
| Goals | Cloud computing mainly focuses on reducing costs and increasing returns. It also has a goal of increasing scalability along with increased availability and reliability. | Grid computing focuses on networks and hence has a large-scale goal. It focuses on resource sharing, pervasive, uniform, and reliable access to data, storage capacity, and computation power. It also focuses on delivering a computer as a utility. |
| Pros | Cloud computing has many advantages. To list a few below:
1) Cloud can store large amounts of data along with storing it safely. Data stored in the cloud is highly secure and can be accessed whenever needed. 2) Cloud is easily accessible from any part of the world. You need to have internet connectivity 3) Cloud runs on the latest network, and all data centers being secure ensures that it provides the best performance. 4) It is cost-efficient and has fast backup and data restoration. Also, it has automatic software updates. |
Grid computing also has its advantages as below:
1)Grid computing is useful in dealing with idle energy in computers. It is more efficient to put it into more sensible use. 2) It helps to save money when huge projects are involved. Grid computing helps in distributing and splitting up the work into multiple computers. 3)Whenever a failure occurs, it will not stop the work as other computers will pick up the work, making this system more reliable. 4) Space is saved, and access to additional resources is made possible. |
| User Management | A centralized system can manage the entire cloud in this setup, or the management can be delegated to a third party. | This setup decentralizes the management, incorporating virtual organization-based management. |
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.