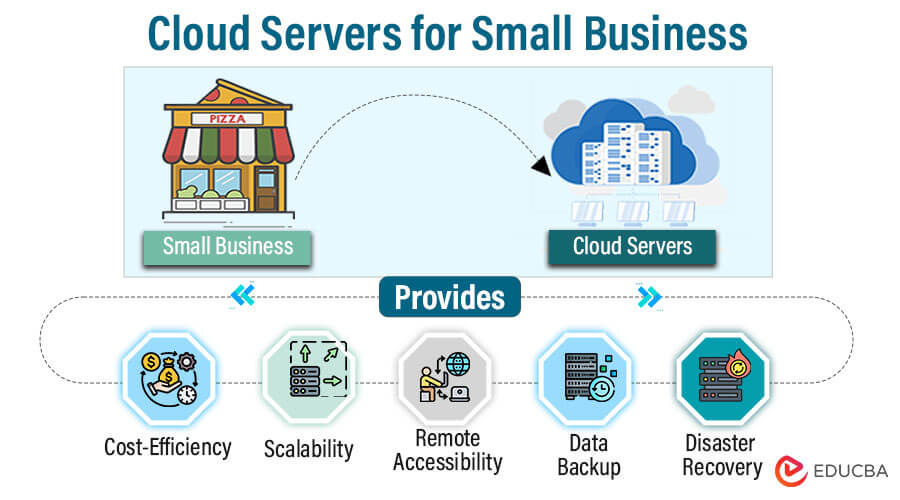
Introduction to Cloud Servers for Small Business
In the fast-paced world of modern business, small enterprises are increasingly relying on cloud servers as an essential technological backbone. Cloud servers offer unparalleled flexibility and scalability, providing robust solutions for data storage, application hosting, and security. This article serves as a comprehensive guide for small business owners, empowering them with the knowledge and insights needed to make informed decisions when choosing the right cloud server solutions. With the right choices, small businesses can ensure efficiency, reliability, and growth in the digital era.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Cloud Servers for Small Business
- What is a cloud server?
- Types of Cloud Servers
- Assessing Business Needs
- Best Cloud Server for Small Business
- How to Setup a Cloud Server for Small Business
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid
What is a Cloud Server?
A cloud server, often known as a virtual private server (VPS), is a type of computing resource hosted in a data center and accessed remotely via the internet. It operates within a virtualized environment and is made available as a service by cloud providers. Cloud servers allow users to run applications, store data, and perform various computing tasks without requiring physical hardware, which makes them a cost-effective and flexible solution for businesses and individuals. Users can also configure and manage cloud servers remotely, making them an increasingly popular choice for hosting websites, software applications, and data storage.
Types of Cloud Servers
The three primary types of Cloud Servers are:
1. Public Cloud Servers:
- These are owned and run by third-party cloud service providers (e.g., Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud).
- Customers share resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Public cloud servers are highly scalable, cost-effective, and require no on-premises hardware management.
- They are suitable for a variety of applications and workloads.
2. Private Cloud Servers:
- Private cloud servers are only available to one enterprise.
- They can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider and offer more control, security, and customization.
- Ideal for enterprises with strict security and compliance requirements or those seeking greater control over their infrastructure.
3. Hybrid Cloud Servers:
- The term “hybrid cloud” refers to infrastructure that combines elements of both public and private clouds.
- Organizations use a combination of on-premises resources, private cloud servers, and public cloud services.
- A hybrid cloud allows data and workloads to move seamlessly between environments, providing flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
- It’s suitable for businesses looking to balance control and agility while optimizing their IT infrastructure.
Assessing Business Needs
1. Identifying Data Storage Requirements:
- This involves assessing the volume of data your business generates and needs to store. Determine the data type (e.g., documents, databases, multimedia) and how frequently it’s accessed.
- Consider data retention policies, backup requirements, and data access speed. Identify any specific data security or compliance regulations that apply to your industry.
- Understanding your data storage needs is crucial to selecting the right amount of storage space and the appropriate storage solutions, whether it’s standard file storage, object storage, or database storage.
2. Evaluating Application Hosting Needs:
- Analyze the software applications your business relies on. Determine whether these applications can run in a cloud environment and assess any special requirements they have.
- Consider factors like application performance, dependencies, and compatibility with cloud platforms. Some applications may benefit from serverless computing, while others require dedicated virtual machines.
- Evaluating your application hosting needs helps ensure that your chosen cloud server environment can efficiently support your software, improving performance and user experience.
3. Considering Scalability and Future Growth:
- When selecting a cloud server, assess its ability to scale resources to meet demand for future business growth.
- Evaluate the ease with which you can add or remove virtual servers, storage, and other resources to accommodate changes in your workload.
- Scalability is essential to avoid resource limitations that can hinder business growth or lead to overprovisioning and increased costs.
4. Analyzing Security and Compliance Requirements:
- Security is a top priority for any business. Identify the security measures required to protect your data and applications, such as firewalls, encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Consider compliance regulations that pertain to your industry, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Ensure your cloud server solution complies with these regulations and offers necessary audit trails and reporting.
- Assess the cloud provider’s security certifications, practices, and data center security to ensure they align with your business’s security and compliance needs.
Best Cloud Server for Small Business
Here are a few of the most popular options:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- AWS is known for its extensive service offerings, scalability, and reliability.
- It provides various tools and services to accommodate diverse business needs.
- AWS provides a free tier for new users to begin using fundamental cloud services.
Microsoft Azure:
- Azure is Microsoft’s cloud platform, offering various services and strong integration with Microsoft products.
- It provides a user-friendly environment for businesses that rely on Windows-based applications and services.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- GCP is known for its data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- It’s a strong choice for businesses looking to leverage Google’s expertise in data and AI.
IBM Cloud:
- IBM Cloud offers a range of cloud solutions, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
- It’s a solid option for businesses that require a mix of traditional and cloud-based services.
Oracle Cloud:
- Oracle Cloud is suitable for businesses that rely on Oracle databases and enterprise applications.
- It offers robust database and application hosting capabilities.
Alibaba Cloud:
- Alibaba Cloud is a strong choice for businesses with an international presence or those looking to tap into the Asian market.
- It provides a diverse range of services at reasonable prices.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
Here’s a structured approach to help you make an informed choice:
1. Research Reputable Providers:
- Start by researching well-established cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and others.
- Explore providers that have a strong track record and a good reputation for reliability and security.
2. Compare Service Offerings and Pricing Plans:
- Examine the range of services and solutions offered by each provider. Look for services that align with your business needs.
- Compare pricing structures, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances. Ensure the pricing model fits your budget.
3. Read Customer Reviews and Testimonials:
- Search for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the experiences of businesses similar to yours.
- Pay attention to feedback regarding customer support, service uptime, and ease of use.
4. Evaluate Customer Support and SLAs:
- Assess the quality of customer support and responsiveness of each provider.
- Review Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to understand uptime guarantees, performance metrics, and compensation for service interruptions.
5. Consider Data Center Locations:
- Check the geographical locations of the provider’s data centers. Proximity can affect latency and data access speed.
- Consider if the provider has data centers in regions that align with your customer base or compliance requirements.
6. Analyze Security Measures:
- Evaluate the provider’s security features, including firewalls, encryption, access controls, and identity management.
- Consider compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, or HIPAA, if they are relevant to your industry.
7. Review Integration Capabilities:
- Determine how well the provider’s services integrate with your existing tools, applications, and workflows.
- Look for compatibility with third-party services you may need to use.
8. Start with a Trial or Proof of Concept:
- Many providers offer trial periods or free tiers for testing their services. Use these opportunities to assess the provider’s offerings.
- Run a proof of concept to see how well the cloud services work for your specific use case.
9. Consider Long-Term Scalability:
- Think about how the provider’s services can accommodate your business’s growth over the long term.
- Consider scalability options and the ability to adjust resources as needed easily.
10. Seek Recommendations and Consult Experts:
- Talk to other small business owners or industry experts for recommendations and insights.
- Consulting with cloud specialists can help you make a well-informed decision.
How to setup a Cloud Server for Small Business
Setting up a cloud server for a small business involves several steps. Below is a structured guide to help you through the process:
- Define Your Requirements:
- Identify your business needs, including data storage, application hosting, and scalability requirements.
- Determine the type of cloud server (public, private, or hybrid) that best suits your needs.
- Choose a Cloud Service Provider:
- Research and select a reputable cloud service provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Consider factors such as pricing, service offerings, and data center locations.
- Create an Account:
- Sign up for an account with your chosen cloud provider and complete the necessary registration and billing information.
- Set Up Your Cloud Server:
- Launch a virtual server instance based on your requirements. This may be called a virtual machine (VM), an instance, or a compute resource, depending on the provider.
- Configure the server’s operating system, choosing from available images (e.g., Linux or Windows).
- Configure Security:
- Implement security measures to protect your cloud server, such as:
- Configuring firewalls to control network traffic.
- Enabling encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- To restrict access, implement access controls and identity management.
- Install Necessary Software:
- Install applications and software your business requires on the cloud server.
- Set up databases, web servers, email servers, and other essential services.
- Data Migration:
- If you’re moving data from on-premises servers to the cloud, plan and execute a data migration strategy.
- Maintain data integrity while minimizing downtime throughout the migration process.
- Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Thoroughly test your cloud server and the applications running on it to ensure they function as expected.
- Conduct load testing to assess the server’s performance under various workloads.
- Employee Training:
- Train your team on how to manage and use the cloud server effectively.
- Provide guidelines for best practices and security procedures.
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Implement monitoring tools to monitor server performance, security, and resource utilization.
- Schedule regular updates, patch management, and backups.
- Scalability and Optimization:
- Periodically review your server’s resource usage and scale up or down as needed to optimize costs and performance.
- Implement cost-saving measures, such as rightsizing instances and utilizing reserved instances or spot instances.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup:
- Set up disaster recovery and backup solutions to ensure data resilience and business continuity.
- Your disaster recovery strategy should be tested and updated on a regular basis.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance:
- Stay informed about cloud provider updates, security patches, and new features.
- Keep your server and software up to date.
- Review and Adjust:
- Periodically review your cloud server setup to ensure it aligns with your business goals and technology needs.
- Make adjustments and improvements as your business evolves.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Here are some key pitfalls and tips to prevent them:
1. Overlooking Security Concerns:
- Pitfall: Neglecting to implement robust security measures can expose your data and applications to cyber threats.
- Tip: Prioritize security by implementing firewalls, encryption, access controls, and regular security updates. Keep up to date on security best practices and potential vulnerabilities.
2. Ignoring Scalability Requirements:
- Pitfall: Failing to plan for scalability can lead to performance issues during periods of high demand or business growth.
- Tip: It is important to choose a cloud provider that allows for easy scaling of resources. Regularly monitoring server resource usage and adjusting as necessary can optimize performance.
3. Not Considering Data Compliance Regulations:
- Pitfall: Ignoring industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements can result in legal and financial consequences.
- Tip: Understand the data compliance regulations relevant to your industry and choose a cloud provider that offers compliance certifications and tools to help you meet those requirements.
4. Neglecting to Plan for Downtime and Disaster Recovery:
- Pitfall: Failing to prepare for server downtime or data loss can cause disruption to business operations and lead to data loss.
- Tip: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, including regular backups, data replication, and strategies for rapid server recovery in case of failures.
5. Inadequate Monitoring and Management:
- Pitfall: Insufficient monitoring and management can lead to performance issues, security breaches, and unexpected costs.
- Tip: Implement monitoring tools to track server performance and security. Regularly review logs and data to proactively identify and resolve issues.
6. Not Optimizing Costs:
- Pitfall: Overlooking cost-saving opportunities can result in unnecessary expenses.
- Tip: Implement cost optimization strategies, such as rightsizing instances, using reserved instances, and taking advantage of spot instances or discount programs when applicable.
7. Failing to Keep Software Up to Date:
- Pitfall: Neglecting software updates and patches can create vulnerabilities and compatibility issues.
- Tip: Regularly apply updates and security patches to the server’s operating system and software. Automate this process when possible.
8. Lack of Employee Training:
- Pitfall: Inadequate training for your team can lead to mismanagement of cloud resources and security risks.
- Tip: Provide training for your employees to ensure they are familiar with cloud server management best practices and security procedures.
9. Poor Documentation:
- Pitfall: Inadequate documentation can lead to confusion, inefficiency, and difficulties in troubleshooting.
- Tip: Maintain comprehensive documentation for your cloud server setup, including configurations, procedures, and disaster recovery plans.
10. Not Staying Informed:
- Pitfall: Failing to stay updated about the latest cloud technologies, security threats, and best practices can hinder your ability to adapt and make informed decisions.
- Tip: Continuously educate yourself and your team about cloud advancements, security trends, and industry best practices.
Conclusion
In this digital age, small businesses can thrive by using cloud servers. To improve their efficiency, security, and scalability, they must carefully examine their particular demands, select the proper cloud service provider, and avoid typical errors. As technology advances, small business owners should remain adaptable, keep themselves informed, and continuously optimize their cloud server setup to ensure long-term success. The cloud is a dynamic and invaluable resource that enables small businesses to compete, innovate, and flourish in a constantly evolving business landscape.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cloud servers for small business” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.