Introduction to Comparison Operators in Java
Operators are considered special characters or symbols used to perform certain operations on variables or values (operands). In Java, there are several operators that are used to manipulate variables. It includes Arithmetic operators, Bitwise operators, Comparison operators, Logical operators, Misc. operators, Assignment operators, etc. In this article, we will discuss more details on comparison operators in java.
Comparison Operators in Java
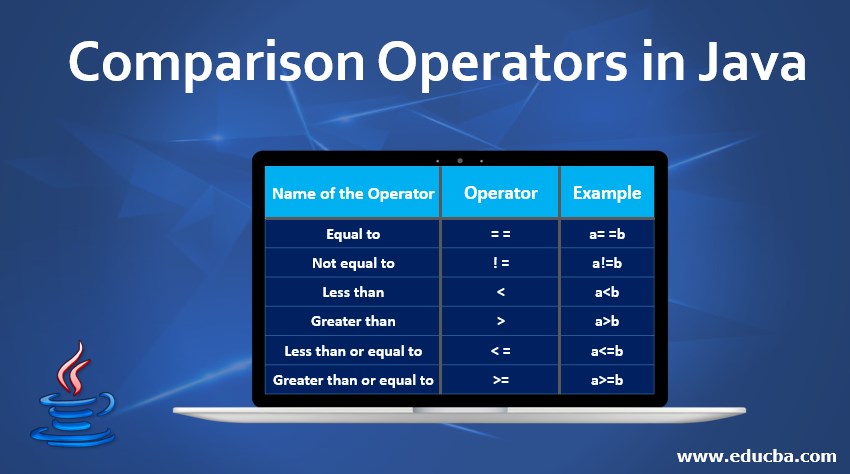
Following are the various comparison operators in Java.
| Name of the Operator | Operator | Example |
| Equal to | = = | a= =b |
| Not equal to | != | a!=b |
| Less than | < | a<b |
| Greater than | > | a>b |
| Less than or equal to | <= | a<=b |
| Greater than or equal to | >= | a>=b |
1. Equal to
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is equal to the value in the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are equal; Return true if it is same, else returns false
System.out.println(x == y);
}
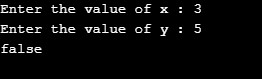
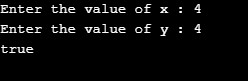
}Output:
Case 1: x = 3; y =5; Returns false as they are not equal
Case 2: x = 4; y =4; Returns true as they are equal
2. Not equal to
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is not equal to the value on the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are not equal; Return true if it is not equal, else returns false
System.out.println(x != y);
}
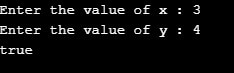
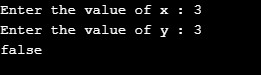
}Output:
Case 1: x = 3; y =4; Returns true as they are not equal
Case 2: x = 3; y =3; Returns false as they are equal
3. Less than
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is less than the value on the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is less than y, else false
System.out.println(x < y);
}
}Output:
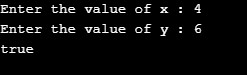
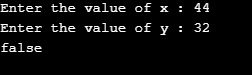
Case 1: x = 4; y =6; Returns true as x is less than y
Case 2: x = 44; y =32; Returns false as x is not less than y
4. Greater than
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is greater than the value on the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is greater than y, else false
System.out.println(x > y);
}
}Output:
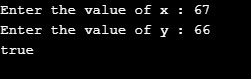
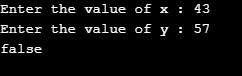
Case 1: x = 67; y =66; Returns true as x is greater than y
Case 2: x = 43; y =57; Returns false as x is less than y
5. Less than or equal to
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is less than or equal to the value on the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user and store it in variable y
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is less than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x <= y);
}
}Output:
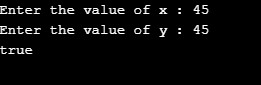
Case 1: x = 45; y =45; Returns true as x is equal to y
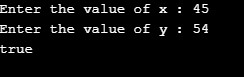
Case 2: x = 45; y =54; Returns true as x is less than y
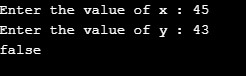
Case 3: x = 45; y =43; Returns false as x is greater than y
6. Greater than or equal to
This operator checks whether the value on the operator’s left side is greater than or equal to the value on the right side.
Example:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is greater than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x >= y);
}
}Output:
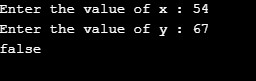
Case 1: x = 54; y =67; Returns false as x is less than y
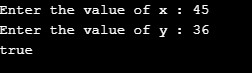
Case 2: x = 45; y =36; Returns true as x is greater than y
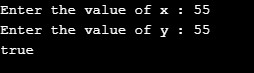
Case 3: x = 55; y =55; Returns true as x is equal to y
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Comparison Operators in Java. Here we discuss the introduction and top 6 comparison operators in java with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-