Updated July 25, 2023
Difference Between Contango vs Backwardation
Contango and Backwardation are the terms used to define the price of the futures curve for a commodity. The forward curve is just a prediction of the future delivery of commodities. Contango and Backwardation give us the relationship between the forward proof (price in the future market) and spot price (current price).
Contango is a situation in the future market when the future price is higher than the spot. Conversely, backwardation is when the future delivery price is lower than the spot. These terms are of great importance for speculators and hedgers e.g., In 1993; German company Metallgssellschaft lost $1bn because management could not anticipate the contango effect.
What is Contango?
Contango is said to take place where the future is above the expected future spot price, but the future price has to be the same as the spot on the expiry date.
There are two types of contango –
- Contango: A situation with a higher future price than the current spot.
- Normal Contango: A situation where the future price is higher than the expected spot price. The term positive carry and normal market are the same as contango.
What is Backwardation?
Backwardation occurs when the future is below the expected spot price, but the future price has to be the same as the spot on the expiry date.
There are two types of Backwardation –
- Backwardation: A situation where the future price is lower than the current.
- Normal Backwardation: A situation where the future price is lower than the expected spot price. The term negative carry means backwardation.
Head To Head Comparison Between Contango vs Backwardation (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between Contango vs Backwardation:
Key Differences Between Contango vs Backwardation
Let us discuss some of the major Difference Between Contango vs Backwardation:
- The future price is expected to be higher than the spot price in Contango, as the cost of carrying keeps on increasing ( cost of storage and interest cost ) because the producer assumes that in the future, the price would be higher and hence would give a greater output as a return to the investment. The future price is expected to be lower than the spot price in Backwardation. The cost of carrying is negative because the producer doesn’t store the good and wants to get the returns as soon as possible because he expects future returns to be lower than the current state.
- For Contango, the basis is negative, i.e., The difference between the spot and futures prices is the basis. The basis is negative because the future price is greater than the spot price in Contango. As the future price is lessee than the spot price in Backwardation, the basis is positive in the case of Backwardation.
- During Contango, as the future price is higher, the profit is maximum when you sell it. During Backwardation, as the future price will decrease further, purchasing it later for an investor would be a greater profit.
- Contango is a generic case where the future price is higher than the spot price. This case happens almost all the time. It is also called the market curve. However, Backwardation doesn’t usually happen. It occurs in the case of oil and other industry.
- The slope of the Contango curve is an upward-sloping futures curve. The slope is upward as the future price keeps growing compared to the current spot. The slope of the Backwardation cover is a downward-sloping futures curve. The slope is downward as the future price decreases further than the current spot.
- Contango has a current supply surplus scenario due to the premium and future price being higher than the spot. In contrast, backwardation has a current demand surplus scenario due to the discount and future price being lower than the spot.
- Contango is a general behavior that mainly occurs in the commodity markets. Backwardation is a rare case.
- Let us understand the working of the curve by an example:
Suppose you want to know the forward price of food. Assume the graph’s origin is today (time t=0), and you want to extrapolate for future price. What would be the cost of food in the future? Consider there are two cases:
Case 1: One producer stores food instead of selling it immediately. For that, he needs storage cost, which is added to the cost price and passed on to the buyer. The producer could have also earned by interest if he had sold, but the producer forgoes it. So both this cost is added to the buyer and the cost of carrying.
Cost of carrying = Storage cost + Interest cost+Other miscellaneous cost
Cost of carry + Spot price = Future price
When the cost of carrying is positive, a commodity’s future prices are higher than the spot I.e. Contango.
Case 2: Suppose the producer anticipates war in the future. There will be a future shortage. Therefore Buyers will store them and purchase all food items.
Therefore Future price = Spot+ cost of carrying.
When the cost of carrying is negative, the future price of a commodity is lower than the spot i.e. Backwardation.
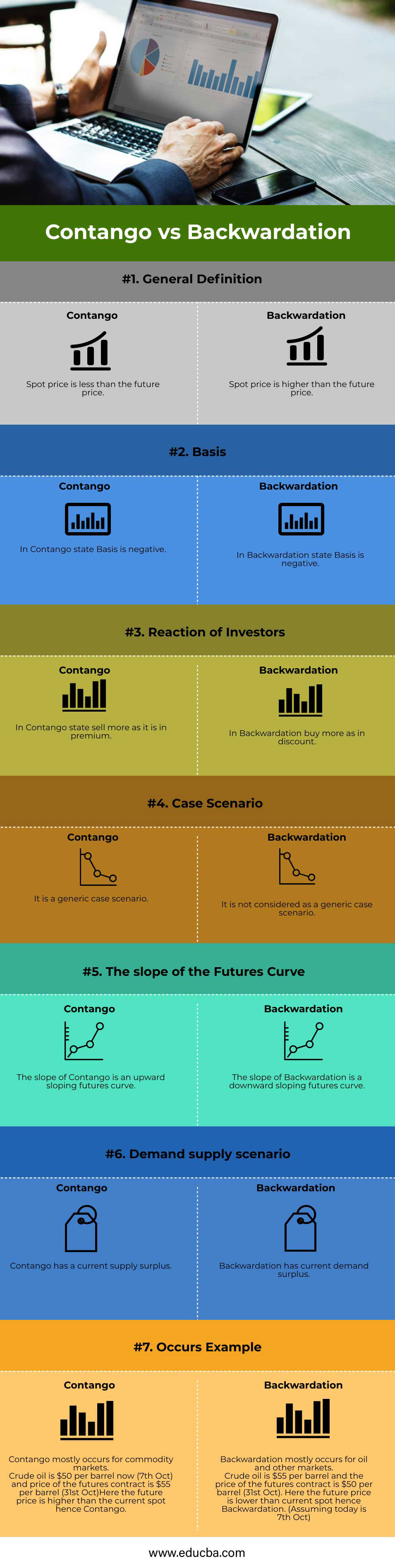
Contango vs Backwardation Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Contango vs Backwardation:
| Basics of Comparision |
Contango |
Backwardation |
| General Definition | A spot price is less than the future price. | A spot price is higher than the future price |
| Basis | In the Contango state Basis is negative. | In the Backwardation state, the basis is negative. |
| Reaction of Investors | In the Contango state, it sells more as it is in premium. | In Backwardation, buy more at in discount. |
| Case Scenario | It is a generic case scenario. | It is not considered as a generic case scenario. |
| The Slope of The Futures Curve | The slope of the Contango is an upward-sloping futures curve. | The slope of Backwardation is a downward-sloping futures curve. |
| Demand-Supply Scenario | Contango has a current supply surplus. | Backwardation has a current demand surplus. |
| Occurs Example | Contango mainly occurs in commodity markets.
Crude oil is $50 per barrel now (7th Oct), and the futures contract price is $55 per barrel (31st Oct). Here the future price is higher than the current spot hence Contango. |
Backwardation mainly occurs for oil and other markets.
Crude oil is $55 per barrel, and the futures contract price is $50 per barrel (31st Oct). Here the future price is lower than the current spot hence Backwardation. (Assuming today is 7th Oct) |
Conclusion
Contango and Backwardation are terms needed for future commodity markets. It shows the basic relationship between demand and supply. These curves are also used for financial modeling. In future contract approaches, the future price should be equal to the spot price, or arbitrage would be possible.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Contango vs Backwardation. Here we have discussed the Contango vs Backwardation key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –