Updated July 7, 2023
What is Cost-Push Inflation?
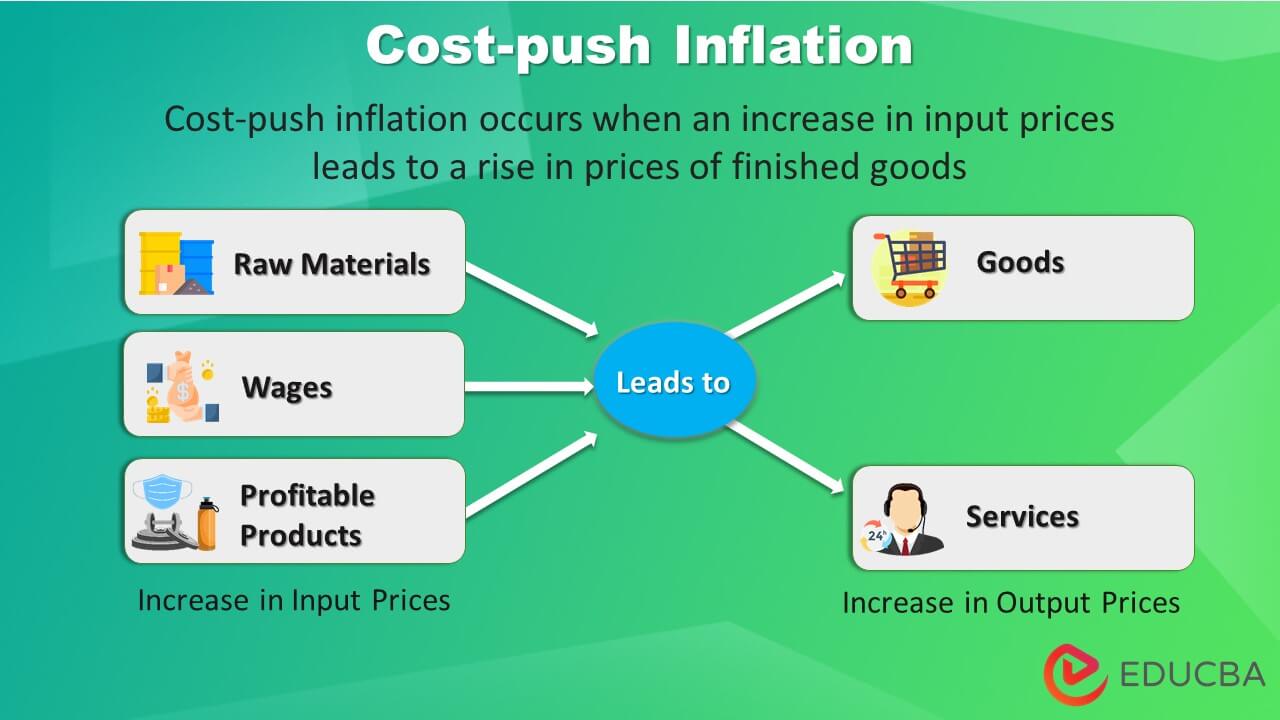
Cost-push inflation occurs when prices of inputs, such as raw materials, labor, and overheads, increase, leading to a rise in finished goods prices.
For example, in the 1970s, OPEC, an Arab petroleum organization, banned petroleum trade with countries supporting Israel. Due to this oil embargo (ban on petroleum export), oil prices spiked. As a result, the cost of production and consumer goods increased.
It harms economies and businesses, as the higher product costs decrease demand for goods. It happens due to aggregate supply shocks, such as an oil embargo. Cost-push inflation can also occur because of an increase in wages.
Key Highlights
- Cost-Push Inflation is the concept of how an increase in input prices affects the prices of finished goods and services
- We can classify it into three primary types: wage-push, profit-push, and material cost-push
- The significant causes are an increase in raw materials, wages, or energy prices
- As an economic effect, there is a decrease in the aggregate supply of products and services in the nation
- It is a crucial measure, as it helps the government control the demand and supply of essential commodities.
How Does Cost-Push Inflation Work?
- When there is a sudden increase in raw material prices, it costs firms extra to produce a product
- Thus, businesses raise the prices of their final product/service to make a profit
- As a result, the cost of living increases, and employees demand higher compensation which leads to a rise in wages
- As it becomes a continuous cycle, government institutions should try to control it in earlier stages
- They can employ measures to reduce its effects, such as improving competition and efficiency.
Real-World Examples
Example #1
In 2011, there was an earthquake and tsunami in Japan. It led to a shortage of certain raw materials. This event resulted in a contraction in Japan’s economy by 2.6%.
Example #2
Due to the current Russian-Ukraine war, costs and inflation have risen significantly worldwide. As Russia accounts for a significant proportion of oil and gas exports, it led to a considerable increase in oil prices.
Types of Cost-Push Inflation
#1 Wage-Push Inflation
- It happens due to an increase in wages. When wages go up, businesses raise prices to cover high costs
- It can lead to a cycle of wage and price increases until the economy reaches a point where it can no longer support the high prices
- The primary contributing factor is that workers demand higher wages to keep up with the rising cost of living
- Another important factor is productivity. Another vital factor is productivity. When there is slow growth, businesses raise wages to attract and retain workers.
#2 Profit-Push Inflation
- It happens when firms raise prices to maintain their profit margins. They do so in response to rising production costs
- However, some firms perform such malpractices solely for personal gains
- Government intervention through price controls, or subsidies is one of the ways to combat it
- Another impactful solution is to increase competition in the industry. When competition increases, companies reduce their prices to stay in business.
#3 Material Cost-Push Inflation
- When prices of production materials increase, companies raise product prices to cover the making costs
- If several manufacturers use a particular material, the price of that material will go up. It can also happen if there’s a decrease in the aggregate supply of crucial materials
- Another factor is if the value of a country’s currency decreases, then imported materials become expensive
- Sometimes, government policies, such as increasing tax on the import or GST of certain materials, also affect prices.
Causes of Cost-Push Inflation
- A decrease in the supply of a good/service due to disrupted production, i.e., when a manufacturer cannot produce goods due to any disaster
- Workers demanding higher wages to keep up with rising living costs
- Increase in cost of raw materials, such as oil or steel
- Businesses that face higher rent, electricity, or transportation costs, increase their final product rates.
Effects of Cost-Push Inflation
- It can decrease demand for goods and services, as consumers rarely purchase items when prices are high
- As businesses cut back on production, they lay off workers. Thus, it can lead to higher unemployment rates
- Living standards may decline as inflation reduces the purchasing power of consumers.
Benefits of Cost-Push Inflation
Stabilize Prices
- Prices are constantly rising worldwide, but they do not grow at the same rate everywhere
- Therefore, inflation can help stabilize prices overall and prevent drastic changes in the cost of living.
Encourage Savings
- When prices are constantly rising, people are more likely to save their money instead of spending it
- It helps create a buffer against the effects of inflation.
Improve Investment
- Businesses invest more to keep up with the competition. Even individuals start investing to tackle inflation
- It leads to an overall increase in productivity and economic growth.
Final Thoughts
While this inflation type can be difficult to control, governments and central banks can use fiscal and monetary policies to manage inflation. They may also increase interest rates or decrease the money supply. While it can lead to problems, like reduced demand and unemployment, it can also have some benefits, such as stable prices. Ultimately, the effects depend on the economic circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What are some benefits of cost-push inflation?
Answer: Some benefits include that it encourages people to become more efficient, look for cheaper substitutes, save money, and make wise financial decisions. Additionally, it motivates businesses to invest more to keep up with the competition.
Q2. How does cost-push inflation affect businesses?
Answer: Inflationary pressures can harm businesses, as consumers avoid purchasing expensive goods/services. In addition, companies may find it difficult to borrow money and invest in new projects during high inflation.
Q3. What happens after cost-push inflation?
Answer: After this type of inflation, the prices of goods and services continue to rise, but the inflation rate begins to slow. That is, when prices rise, people cut back on spending, which reduces demand. Hence, the prices stabilize over time, and the inflation rate returns to its original level.
Q4. What is the impact of cost-push inflation on the people?
Answer: Workers may see their purchasing power decline if wages fail to keep up with inflation. It can make it difficult to afford necessities or save for future goals. Similarly, retirees on a fixed income may need more to cover their living costs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to cost-push inflation. It explains its definition, types, causes, effects, etc. Read the following articles to learn more,