What is Accounting
Accounting plays an important role in assisting all forms of economic activity in the various sectors. Accounting is nothing but the language of business which is helpful in business decisions. Without accounting, Business owners or managers would not know which products were successful and which decisions were the right ones. With the help of an accountant, they would get an idea of how much to pay in taxes, capital required for further projects, whether to lease or buy an asset and so on. Accounting also helps investors to understand how efficiently their capital or economic resources are being used.
What is meant by Accounting?
Accountancy is the flow or process of communicating financial transactions about a business entity. Generally, it is a communication in the form of financial statements like Balance sheets, income statements, cash flow, etc. also, we can say that it is an information system that identifies, measures, and communicates the economic/business information of an entity to its users who need the information for decision making. Accounting identifies financial transactions and business events of a specific entity.
Definition of Accounting
“Accounting is the process of systematically recording, measuring, analyzing and communicating information about business/financial transactions of an entity.”
According to the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) –
“The art of recording, classifying, and summarizing, in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least, of financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.”
Objective of Accounting
Following are the main objectives of Accounting.
- To keeping a systematic record of financial transactions.
- To determine the results of the operation/Production.
- To interpret the liquidity position.
- To facilitate business decision-making.
- To comply with requirements of law.
Learn the skills of an account and finance manager. Master financial statement analysis. Practice tools of impressive finance and accounting.
Users of Accounting Information
Following are the users of accounting information:
- Business Owners
- Management
- Employees
- Creditors
- Government
- Investors
- Clients
Methods of accounting transaction
Business transactions are recorded in two different methods:
- Single Entry Method
- Double Entry
1. Single Entry Method:
It is an incomplete system of recording business transactions. In this entry method, the business organization maintains only cash books and personal accounts of debtors and creditors.
2. Double Entry Method:
It this method, every business transaction is having two effects with equal debits and credits.
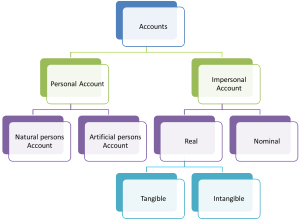
Types of Accounts
There are mainly two types of accounts
- Personal Account
- Impersonal Account
1-Personal Accounts:
Accounts recording transactions with a person or group of persons are known as personal accounts. Personal accounts are of the following types.
a) Natural person Account- An account recording transactions with an individual human being is called as a natural person’s account. E.g. John account.
b) Artificial or legal persons Account- An account recording financial transactions with an artificial person created by law or otherwise is called as an artificial person Account.
E.g. Cooperative society account.
2- Impersonal Account:
Accounts which are not personal are impersonal accounts. It can be divided into two parts.
1-Real Accounts-
Accounts relating to properties or assets are known as ‘Real Accounts’, a separate account is maintained for each asset.
Real accounts can be further classified into
- Tangible- These accounts represent assets and properties which can be seen, touched, measured, purchased, and sold. E.g. Machinery account, Furniture account.
- Intangible- These accounts represent assets and properties which cannot be seen, touched, or felt, but they can be measured in terms of money. e.g., Goodwill accounts, patents accounts.
2- Nominal Accounts
Accounts relating to income, revenue, gain expenses and losses are termed as nominal accounts.
E.g. salary account.
Golden Rules of Accounting
1.Personal accounts
First Golden Rule for Personal Account
Dr- The Receiver
Cr-The Giver
2. Real Accounts
Second Golden Rule for Real Account-
Dr- What Comes in
Cr- What Goes out
3. Nominal Accounts
Third Golden Rule for Real Account-
Dr- All expenses and losses
Cr- all incomes and gains
Branches of Accounting
Following are the branches of accounting:
i) Financial accounting;
ii) Cost accounting; and
iii) Management accounting
i) Financial accounting:
Financial Accounting is mainly concerned with the preparation of financial statements for the use of Investors or others like creditors, investors, and financial institutions. The financial statements i.e., balance sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow statement.
ii) Cost Accounting:
Cost accounting seeks to determine the cost of units produced and sold or the services rendered by the business unit with a view to control cost and increasing the profitability and efficiency of an entity. It generally relates estimation of future costs to be incurred.
iii) Management Accounting:
Management accounting is the presentation of accounting information is such a way as to assist management for decisions making.
Methods of Accounting
There are two types of accounting methods-
- Cash basis accounting
- Accrual basis accounting
This accounting method states how the company’s transactions are recorded in the company’s financial books
1. Cash basis accounting-
When cash is received for the sale of goods or services, a deposit is made, no matter when the sale was made. In this method, Revenues or sales are recorded when they are actually received and vice versa.in this method, entry of receivables are not made. Also, entry accounts payable are not made.
2. Accrual basis accounting-
This accounting method matches sales to the time frame in which they are earned and matches expenses to the time period in which they are incurred. This accounting method allows you to track Account receivables and Account payables.
Skill Required for Accountant
The field of accounting has many opportunities available however requires specific skills and attributes in order to succeed. Generally, an Accountant needs to provide financial information to management in order to decisions making by analyzing financial data and preparing reports, and financial statements. Generally following common skills are required to become an Accountant
- Education (At Least Graduation)
- Practical Experience (internship)
- Techno-Savvy (hands-on Excel)
- Excellent verbal and written communication skills