Understanding Crypto Cybersecurity
Bitcoin, the revolutionary digital currency, has captured worldwide interest for its ability to disrupt traditional financial systems. The importance of crypto cybersecurity and privacy keeps growing as individuals and institutions increasingly adopt Bitcoin.
Crypto cybersecurity includes implementing security measures to protect cryptocurrencies and traders from cybersecurity threats such as hacking, unauthorized access, etc.
As Bitcoin (BTC) is currently the number one digital asset we can invest in, it is also necessary to learn how to invest in it. For this, you can learn at Immediate Frontier and make informed and wise decisions about investing on the go.
Additionally, to understand cybersecurity in the crypto world, in this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between a specific cryptocurrency – Bitcoin – and cybersecurity.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Crypto Cybersecurity
- Privacy in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
- Types of Security Threats
- How to Stay Safe Against Crypto Cybersecurity Threats?
- Crypto Cybersecurity Global Regulations
- The Future of Crypto Cybersecurity
Understanding Privacy in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
➔ Pseudonymity vs. Anonymity in Bitcoin Transactions
One of the fundamental features of Bitcoin is its pseudonymous nature. It means instead of using real names, users employ cryptic addresses to send and receive transactions.
While this provides privacy, it still does not give absolute anonymity. That is because every transaction is recorded on the public blockchain, allowing anyone to trace the flow of funds. Thus, privacy-conscious users often employ multiple addresses to complicate and cover their transaction history.
➔ Address Reuse and Its Privacy Risks
Address reuse is a common practice among Bitcoin users, but it can compromise privacy. When a user repeatedly sends and receives funds to and from the same address, it becomes easier for observers to identify the user.
Therefore, privacy advocates recommend using a new address for each transaction to enhance anonymity.
➔ Bitcoin Mixers and Privacy-Enhancing Techniques
To support privacy, Bitcoin users use techniques like CoinJoin and Bitcoin mixers. These services pool transactions from multiple users, making it challenging to trace individual payments. However, they are not without controversy, as some regulators view them as facilitating money laundering.
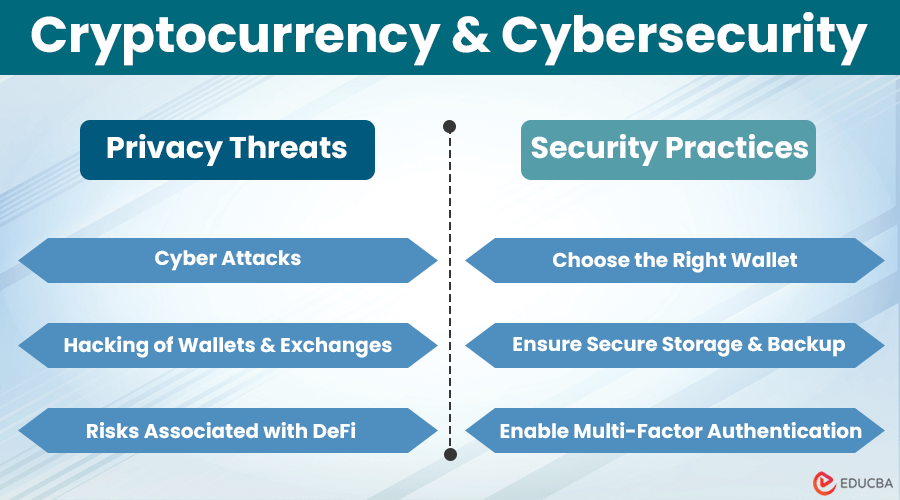
Types of Security Threats in Crypto Cybersecurity
➔ Cybersecurity Threats
The cryptocurrency ecosystem is a prime target for cybercriminals. Common threats include phishing attacks, ransomware, and malicious software. As Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, victims of theft or fraud often have no recourse.
➔ Hacking of Bitcoin Wallets and Exchanges
Bitcoin wallets and exchanges are frequent targets of cyberattacks. High-profile breaches have resulted in millions of dollars in losses. In such cases, users must exercise caution when choosing a wallet. To protect their holdings, they must also employ security measures, like using multi-factor authentication or hardware wallets.
➔ Risks Associated with Smart Contracts and DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms have gained popularity. However, they are not immune to vulnerabilities and security risks. Smart contract bugs, flash loan attacks, and rug pulls have exposed users to substantial losses. Understanding the risks and conducting due diligence is paramount when participating in the DeFi space.
How to Stay Safe Against Crypto Cybersecurity Threats?
➔ Choose the Right Wallet
Selecting a secure and reputable wallet is the first step in crypto cybersecurity. As hardware wallets operate offline, they are immune to online threats, offering the highest level of security.
➔ Ensure Secure Storage & Backup
Proper storage of private keys is crucial. Users should store backups offline in multiple secure locations, such as safety deposit boxes or hardware devices. Neglecting this step can result in irreversible losses.
➔ Enable Multi-Factor Authentication & Secure Password Management
Enabling multi-factor authentication (2FA) on accounts and using strong, unique passwords for each service are essential security practices. Furthermore, password managers can help users generate and store complex passwords securely.
Overview of Crypto Cybersecurity Global Regulations
➔ Government Efforts to Regulate Cryptocurrencies
Clear cryptocurrency regulations safeguard users’ rights and maintain financial system stability. Governments worldwide are struggling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. While some countries embrace innovation, others seek stricter controls.
➔ Balancing Privacy and Compliance – Challenges and Solutions
Balancing between user privacy and regulatory compliance can be complex. Industries are exploring privacy-enhancing technologies like zero-knowledge proofs and confidential transactions to maintain privacy while meeting regulatory requirements. However, businesses and regulators need to team up to find practical solutions.
The Future of Crypto Cybersecurity
- As Bitcoin adoption and the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, so does the sophistication of cyber threats.
- Predictions suggest that increased focus on privacy and security by both users and developers can lead to a more robust and resilient ecosystem.
- Moreover, ongoing research and development in privacy-enhancing technologies, such as confidential transactions and bulletproofs, can provide stronger privacy guarantees.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the nuanced relationship between cryptocurrency and cybersecurity is essential for users and policymakers alike. Implementing best crypto cybersecurity practices allows the Bitcoin ecosystem to evolve while safeguarding user interests. The journey towards a more secure and private Bitcoin ecosystem is ongoing, requiring vigilance, adaptation, and a commitment to the principles of decentralization.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on crypto cybersecurity helped you learn about privacy concerns and security practices in the crypto ecosystem. For similar articles, refer to the following recommendations.
