Updated June 22, 2023
Introduction to CSS z-index
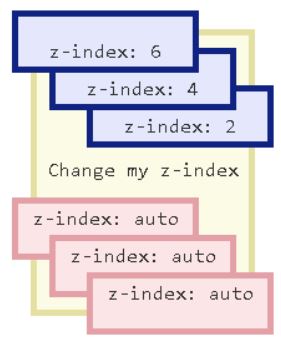
The z-index property in CSS decides the stack order of the element like an image or box or any character content or button etc. An element with the highest or greater stack order value will always be in front of the element with the lower stack order value. Remember that the z-index only worked with position elements like absolute, position: relative, and position: sticky. This clears a point that the z- index property can be applied with positioned elements in the z-order. Element with a higher z index value always overlapped by the z index with a smaller value.
Real-Time Example: We have a requirement to overlap images with content. In general, CSS properties can’t provide this feature, which will give the image on top of the text, but we don’t want this. So by using the z-index property, we can make content on top of the image.
Why do we use CSS in HTML?
- Provide common Logic between all the pages. Instead of writing the same style logic in each HTML page, we use CSS files for writing common logic.
- And it includes a CSS page in each HTML page with a <link> tag.
How does the Z-index property work in CSS?
Z- index property only works with position elements like:
- position: absolute
- position: relative
- position: sticky
Syntax:
positioned element{
position: absolute or relative or sticky;
left: value;
top: value;
z-index: value;
}Z-index image with values:
Examples of CSS z-index
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
Z index with an Image.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Z index</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="ZIndexFile.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Z Index with Image</h1>
<div class="content">
<img alt="" src="bs2.jpg">
<p>The z-index property in CSS decides the stack order of the
element like image or box or any character content or button etc. An
element with highest or greater stack order value will be always in
front of the element with lower stack order value. Keep in mind that
z-index only worked with position elements like position: absolute,
position: relative, position: sticky. This clear a point that z-
index property can be applied with positioned elements in z order.
Element with a higher z index value always overlapped by the z index
with smaller value.</p>
<p>Real Time Example: We have requirement that we want overlap
image with a content. In general CSS properties can't provide this
feature, this all will give the image on top of the text but we don't
want this. So by using z-index property we can make content on top of
the image.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>CSS Code: ZIndexFile.css
img {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
z-index: -10;
}
h1
{
color:red;
text-align: center;
}
p
{
color:brown;
border: solid 2px yellow;
font-size: 28px;
}Output:
Explanation:
As we see above, we got a text on top of the image, but the text overlaps if we remove the z index property.
Example #2
Z index with an Image.
HTML Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Z index</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="ZIndexFile.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Z Index with Content</h1>
<div class="topDiv">
The z-index property in CSS decides the stack order of the element
like image or box or any character content or button etc. An element
with highest or greater stack order value will be always in front of
the element with lower stack order value. Keep in mind that z-index
only worked with position elements like position: absolute, position:
relative, position: sticky. This clear a point that z- index property
can be applied with positioned elements in z order. Element with a
higher z index value always overlapped by the z index with smaller
value. <span class="spanContent">Real Time Example: We have
requirement that we want overlap image with a content. In general CSS
properties can't provide this feature, this all will give the image
on top of the text but we don't want this. So by using z-index
property we can make content on top of the image.</span> <span
class="boxSpan">Paramesh Box</span>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>CSS Code: ZIndexFile.css
h1 {
color: blue;
text-align: center;
}
.topDiv {
position: relative;
height: 8em;
color: navy;
margin-bottom : 1em;
margin-top : 2em;
z-index: 1;
border: solid;
margin-bottom: 1em;
margin-top: 2em;
font-size: 28px;
}
.spanContent {
position: absolute;
width: 80%;
background : fuchsia;
left: 60px;
top: 3em;
z-index: 3; <!-- z index value is greater so it always on top of all the elements -->
font-size: 28px;
}
.boxSpan {
position: absolute;
z-index: 2; <!-- z index value is greater than topDiv content so it overlaps it -->
width: 20%;
top: -25px;
height: 7em;
opacity: 0.9;
left: 65%;
background : lightgreen;
font-size: 28px;
}Output:
Explanation:
As you can see above, whichever z index value is more significant always overlaps the lower index value content.
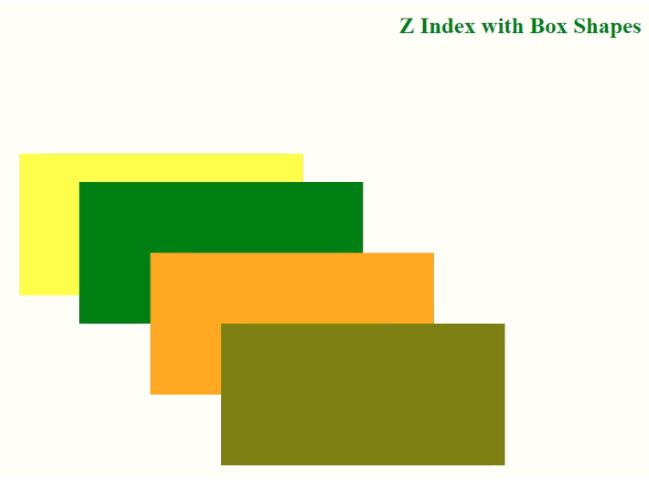
Example #3
Z index with an Image.
HTML Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Z index</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="ZIndexFile.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Z Index with Box Shapes</h1>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="box4"></div>
<div class="box5"></div>
</body>
</html>CSS Code: ZIndexFile.css
h1 {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
.box1 {
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 80px;
z-index: 2 background-color: red;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
}
.box2 {
position: relative;
top: -60px;
left: 35px;
z-index: 1;
background-color: yellow;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
}
.box3 {
position: relative;
top: -220px;
left: 120px;
z-index: 3;
background-color: green;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
}
.box4 {
position: relative;
top: -320px;
left: 220px;
z-index: 4;
background-color: orange;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
}
.box5 {
position: relative;
top: -420px;
left: 320px;
z-index: 5;
background-color: olive;
width : 400px;
height: 200px;
width: 400px;
}Output:
Explanation:
As you can see above, whichever z index value is greater always overlaps the lower index value box.
Conclusion
Z index in CSS property is used to put any element on top of the other element. But the Z index can be applied with only positioned elements like absolute, relative, sticky, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CSS z-index” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.