Updated July 7, 2023
What is Current Account Deficit?
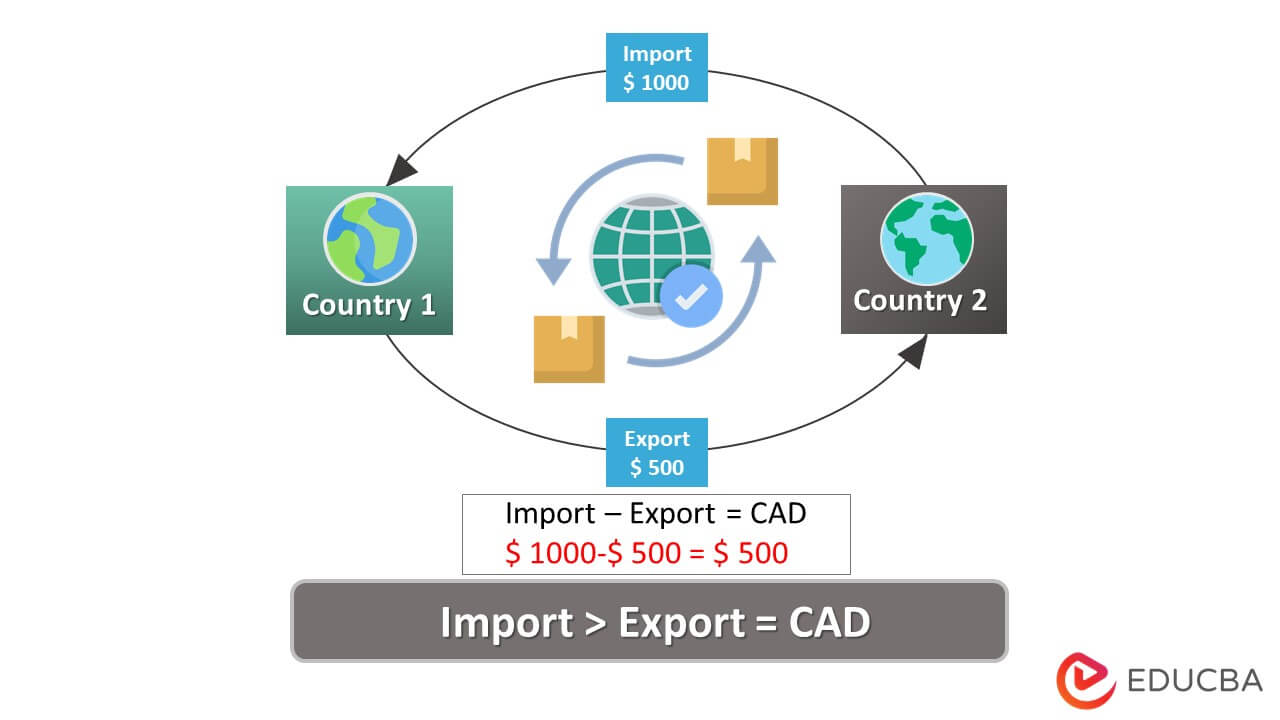
Current Account Deficit (CAD) is the difference between the money a country makes by exporting and the money it incurs to import goods/services from other economies.
For example, the deficit for the United States fell from $2.776 trillion in 2021 to $1.375 trillion in 2022. It implies that the US government reduced imports and increased exports.
In simple terms, a mismatch between the value of goods exported and imported results in a deficit in the current account. It also includes factor payments received from national citizens living outside the country. The current account computes net income, interest, dividends, and foreign aid transfers.
Key Highlights
- A current account deficit indicates a country’s substantial engagement in importing than exporting
- Significant consequences can be economic inflation, currency devaluation, increased interest rates, a fall in domestic product demand, and much more
- Some prominent causes are a higher value of money, positive income, other country’s recession, and even soaring inflation
- Even though it can lead the nation to extensive economic growth, it can also turn otherwise if it does not make wise investments.
How Does the Current Account Deficit Work?
- Nowadays, countries depend on other countries to fulfill needs like defense and development machines, medical sciences development, food, and more
- When companies seek resources from neighboring countries, it is called imports. In contrast, export is when the neighbor seeks resources in exchange
- The country that spends more money than it receives will always be in deficit. It is similar to the profit-loss situation, where spending more money than one receives leads to a financial crisis.
Consequences of Current Account Deficit
- The decreasing exports and increasing imports lead to a reduction in domestic currency value and a loss of confidence in domestic assets. As a result, the products witness a lack of demand
- If borrowed money is the base to fund imports, it can be unsustainable in the long run. Additionally, the country will also have to deal with interests
- Devaluation of the economic factors can persuade investors and creditors to retract their investments
- An enormous account deficit value can indicate an unbalanced and non-competitive economy and lead to currency depreciation.
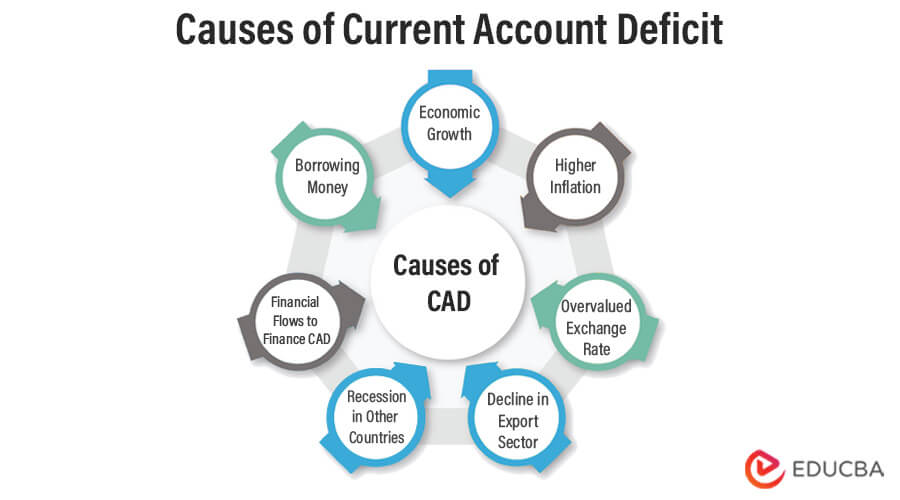
Causes of Current Account Deficit
- When the value of money in the economy is high, imports get cheaper, and exports are expensive. Hence, imports increase, and exports decrease
- When an economy grows, citizens earn more and, in turn, spend more. In case the country can’t meet the demand, they choose to import those products
- When inflation causes a rise in prices, people refrain from buying from their nations. As a result, they buy from other economies, which leads to a gap in imports and exports
- If other countries are going through a recession, they may cut down on importing products from other countries. It will cause a fall in other countries exports.
How to Calculate Current Account Deficit?
The formula to calculate it is,
- The trade gap is the difference between exports and imports
- Net current transfers are the total of all current transactions within or among nations
- Net income abroad totals a nation’s citizen’s income from outside the country.
Current Account Deficit Examples
- Europe’s deficit value rose to $570 million in a quarter. It now stands at $4.43 billion as of May 2022. The reason was the Russia-Ukraine war, due to which Europe had to import metals and natural gas raw materials
- India sees a deficit rise because of increasing commodity prices and massive capital outflows. The trade ministry reports it at $27.98 billion as of August 2022
- As recorded in June 2022, Pakistan’s current deficit saw an increase of $0.2 billion and is now at $4.2 billion.
Current Account Deficit vs. Trade Deficit vs. Fiscal Deficit
| Current Account Deficit | Trade Deficit |
Fiscal Deficit |
|
Definition |
||
| It is when there is a mismatch between a country’s exports and imports of all goods and services | It is when the imports of visible/tangible goods are more than their exports | It signifies a government’s spending and earnings for a financial year |
|
Includes |
||
| It is inclusive of a country’s income through nationals working in foreign countries, transfer of goods/services, and more | It includes all visible merchandise goods like textiles, stationery, etc | It consists of the amount that a government earns through citizen taxes and other revenues, along with the government budget |
|
Formula |
||
| It totals the trade gap, foreign income, and net current transfers. | It simply subtracts the exports from the imports. | It is total government expenditure less the total government receipts. |
Advantages of Current Account Deficit
- It can induce exponential economic growth when there are higher growth rates and productivity due to an external cash supply
- As a nation’s currency devalues, more neighboring countries will prefer to import goods. Therefore, the government might foresee higher exports
- Economies can avail products without domestic production
- With effective management, reinvesting incoming capital for long-term gains can be beneficial.
Disadvantages of Current Account Deficit
- It can reflect an unstable economy while the rate of inflation rises exponentially
- Due to inflation, a consumer’s purchasing power decreases
- A country with a widened current deficit will face currency devaluation
- To diminish inflation, governments will need to raise interest rates
- In addition, if countries take more loans to eradicate the current deficit, they should repay the amount as soon as possible. Otherwise, it can add to economic burdens.
Conclusion
The current account deficit signifies the impact of imports and exports on an economy. A high CAD predicts imbalances, which they can solve by adjusting currency valuation. On the other hand, a drop in currency valuation can cause inflation. To narrow down the deficit, central banks decrease imports.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between the current account deficit (CAD) and the balance of trade?
Answer: The primary difference is that the CAD considers income from nationals based outside the country. In contrast, the balance of trade(BoT) only accounts for cash inflow and outflow regarding the export and import of a nation.
Q2. What happens if the current account deficit increases?
Answer: An increase in CAD can go two ways. It can lead to a fall in the currency valuation, high inflation, low competitiveness, and much more. On the other hand, the country may produce more, invest in essential infrastructure, and soar in growth and productivity.
Q3. How does the current account deficit lead to inflation?
Answer: When the CAD increases, the currency devalues, growing imports and inflation rates.
Q4. What is the effect of interest rates on the current account deficit?
Answer: When increased imports lead to inflation, regulatory bodies have to raise interest rates to control inflation in the country. It then causes a decline in consumer spending, less liquid availability, and high cash burnouts for the producers. However, it may help in managing the CAD.
Q5. How to reduce the current account deficit?
Answer: Governments can implement policies to reduce the value of CAD. Lowering export rates while increasing import rates is one of the techniques. They can also apply deflationary and monetary policies by raising interest rates.
Recommended articles
This article explains the current account deficit. To learn more, visit the following articles,