Introduction to Cybersecurity Best Practices for Small Businesses
In today’s digital environment, small businesses are growing increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. This guide will provide essential cybersecurity best practices to protect valuable data, thwart cyberattacks, and ensure uninterrupted operations for small businesses.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
You should be informed and proactive to protect your small business from cybersecurity attacks. You can protect your valuable data, maintain the continuity of your operations, and reduce the risk of falling victim to cyber threats in the ever-changing digital landscape.
Following security considerations, you can consider:
Why Cyberhackers Target Small Businesses?
Cyberhackers target small businesses due to limited resources, valuable data, supply chain vulnerabilities, a lack of cybersecurity awareness, ransomware opportunities, unprotected IoT devices, economic espionage, opportunistic attacks, personal vendettas, and minimal legal scrutiny.
Nowadays, many small businesses are now going online to expand their businesses. A couple of options are available, like a Facebook marketplace, Instagram, YouTube, and e-commerce websites. The hackers are targeting those businesses for the sake of money.
Cyberattacks are motivated by financial gain through data theft or ransom demands, espionage for stealing sensitive information or gaining a competitive edge, disruptive actions for revenge or sabotage, building botnets for large-scale attacks or resale, data breaches for black market sale, and opportunistic exploitation of vulnerable systems. Recognizing these motives empowers organizations to bolster their cybersecurity measures and effectively protect against diverse cyber threats.
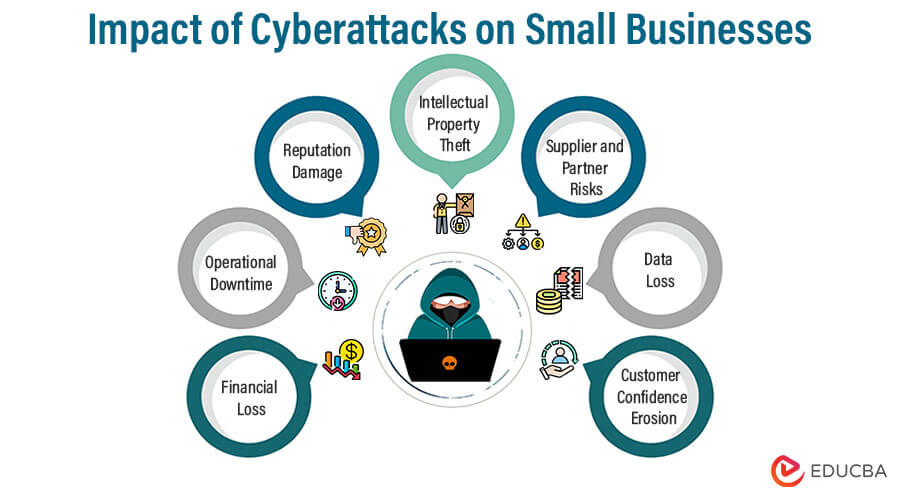
Impact of Cyberattacks on Small Businesses
Cyberattacks on small businesses can result in financial losses, reputational damage, operational disruptions, high remediation costs, intellectual property theft, supplier risks, data loss, customer confidence loss, increased insurance expenses, and prolonged recovery periods. Prioritizing cybersecurity is crucial for small businesses to mitigate these impacts and safeguard their operations and reputation.
Some of the Disruptive Consequences are as follows:
- Financial Loss: Attacks can lead to significant financial setbacks, affecting profitability and growth.
- Operational Downtime: Business operations can be paralyzed during recovery, causing delays and lost productivity.
- Reputation Damage: Customer trust may diminish, leading to customer churn and difficulty attracting new clients.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Cybercriminals may steal valuable intellectual property, affecting competitiveness.
- Supplier and Partner Risks: Attacks can impact partners and suppliers, disrupting the supply chain.
- Data Loss: Irreplaceable data may be permanently lost, hindering business continuity.
- Customer Confidence Erosion: Customers may lose confidence in data protection practices.
Recognizing these consequences underscores the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures for small businesses.
Common Cyberattack Methods
Here are some common cyberattack methods:
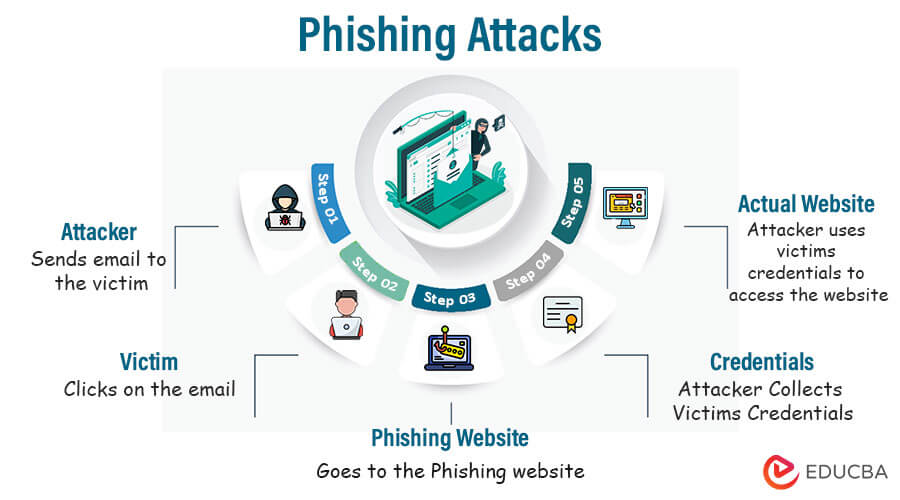
1. Phishing Attacks
Identifying Deceptive Messages and Websites
Phishing attacks are deceptive cyber threats in which attackers pose as legitimate entities to fool people into providing sensitive information such as login passwords or bank information.
These attacks often come via email, text messages, or social media, urging recipients to click malicious links or download infected attachments. Identifying such deceptive messages and websites is crucial to preventing phishing scams.
Look for suspicious email addresses, grammatical errors, urgent requests for personal data, and unexpected attachments or links. Hover over links to see where they take you before clicking. Legitimate organizations will never request critical information by email. Always verify requests through official channels to effectively thwart phishing attempts.
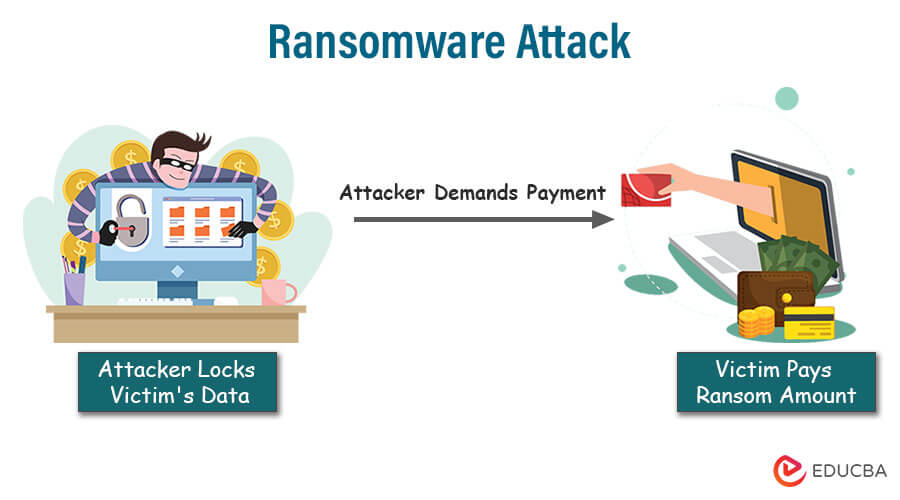
2. Ransomware
Understanding the Menace of Data Hostage Situations
Ransomware is one of the most dangerous types of cyberattacks. It occurs when an attacker locks a victim’s data using encryption and then demands a ransom payment to release it.
Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in systems or use social engineering to deliver malware. After the data is secured, hackers demand payment for the decryption key, often in the form of cryptocurrency.
Ransomware attacks can cripple businesses, lead to data loss, and cause significant financial and reputational damage. Understanding this menace is vital for businesses to implement robust cybersecurity measures, conduct regular backups, and stay vigilant to protect against and respond effectively to ransomware threats.
3. Malware Infections
Recognizing the Signs of Intrusive Software
Malware infections pose significant threats to computer systems. Identifying signs of intrusive software is crucial for early detection and mitigation.
Watch for slow performance, unusual pop-ups and ads, unexpected network activity, disabled security software, altered browser settings, and unauthorized system changes.
Locked files and ransom demands indicate ransomware attacks. Be cautious of phishing emails and social engineering attempts. Unusual login attempts may point to brute-force attacks.
Stay vigilant against unexpected requests for personal information. Recognizing these signs empowers users and businesses to take immediate action, such as running antivirus scans, disconnecting from the network, and seeking professional assistance to remove malware and safeguard their systems from further harm.
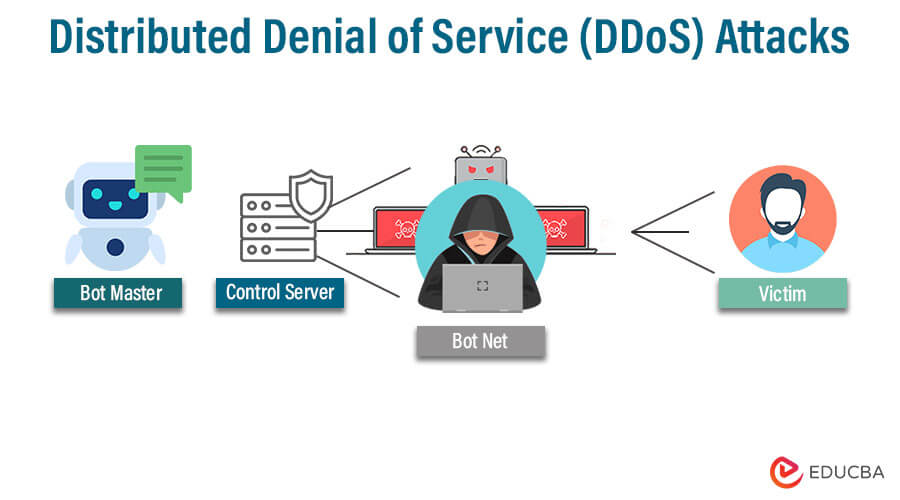
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Overwhelming Your Online Presence
DDoS attacks are hostile attempts to overwhelm a target’s online presence by flooding it with massive amounts of traffic from various sources.
The massive influx of data exhausts the target’s resources, causing service disruptions or complete outages. Cybercriminals use botnets or hijacked devices to execute DDoS attacks, making them challenging to trace and mitigate.
DDoS attacks can cripple websites, online services, and networks, leading to financial losses, tarnished reputation, and customer dissatisfaction.
Defending against DDoS attacks requires robust network infrastructure, traffic filtering, and real-time monitoring to identify and thwart malicious traffic effectively.
5. Insider Threats
Navigating Risks Posed by Employees and Insiders
Insider threats are risks posed by employees and trusted insiders who exploit their access to an organization’s systems, data, or facilities for malicious purposes. These threats can be intentional, such as data theft and sabotage, or unintentional, like accidental data breaches.
Insider threats are challenging to detect as perpetrators have legitimate access. To navigate these risks, businesses must implement strict access controls, monitor employee activities, and conduct regular security awareness training.
Encouraging a culture of trust while emphasizing the importance of reporting suspicious behavior can help mitigate insider threats and safeguard sensitive information and assets from internal vulnerabilities.
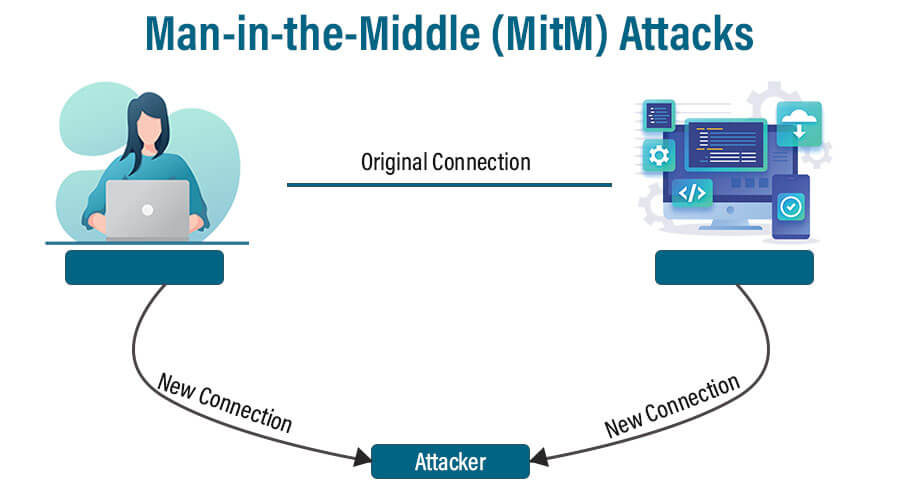
6. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Intercepting and Manipulating Communication
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks involve cybercriminals intercepting and manipulating communication between two parties.
The attacker surreptitiously relays and possibly modifies the communications, giving the victims the impression that they speak directly with each other.
This allows the attacker to listen in on sensitive information such as login passwords, financial information, or personal information.
MitM attacks are especially dangerous in unsecured public Wi-Fi networks. To prevent MitM attacks, users should avoid public Wi-Fi when handling sensitive data, use encrypted communication channels like VPNs, and regularly update their devices and software to patch vulnerabilities.
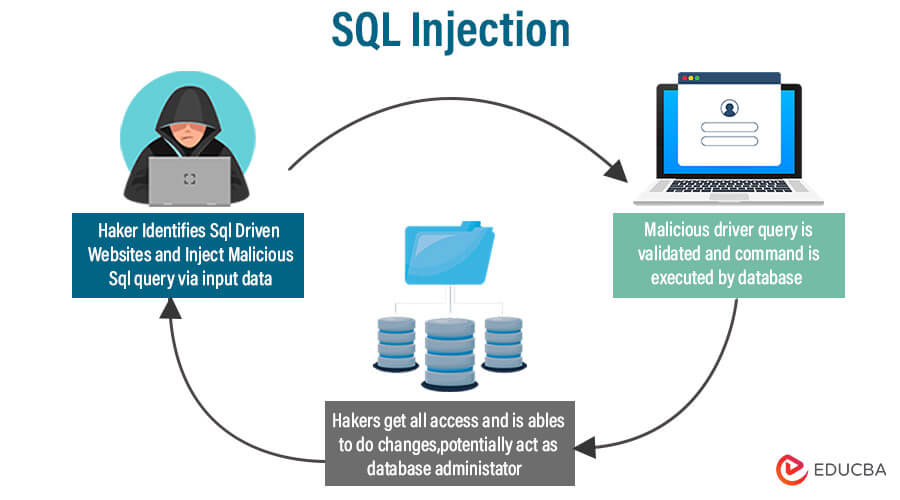
7. SQL Injection
Exploiting Vulnerabilities in Web Applications
SQL injection is a cyberattack in which hackers exploit flaws in web applications that do not check user inputs adequately.
Attackers can gain unauthorized access to databases, extract sensitive information, edit or destroy data, and even take control of the entire system by introducing malicious SQL code into input fields.
To prevent SQL injection attacks, developers must use parameterized queries and input validation to ensure user inputs are treated as data, not executable code. Regular security audits and upgrades are critical for identifying and correcting any vulnerabilities and protecting online applications from exploitation.
8. Zero-Day Exploits
Dealing with Unpatched Software Vulnerabilities
Zero-day exploits target software vulnerabilities unknown to the vendor and for which no fix is available.
Cybercriminals take advantage of these vulnerabilities to launch attacks before developers can fix them, giving users zero days to defend themselves.
Organizations should adopt proactive cybersecurity measures, such as network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and behavior-based anomaly detection, to deal with zero-day exploits. Employing strong access controls, using virtual patching, and staying informed about emerging threats can help mitigate the risks.
Additionally, responsible disclosure of zero-day vulnerabilities to vendors can facilitate timely patch development, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
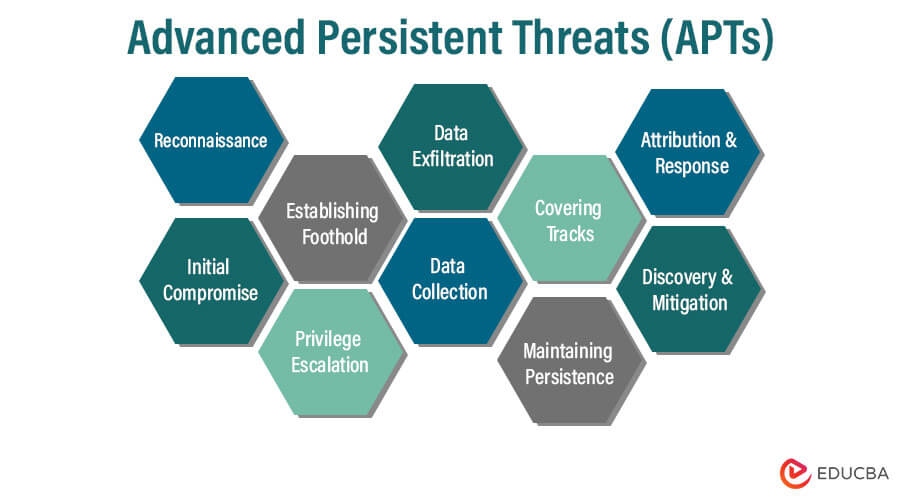
9. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Facing Long-Term Covert Attacks
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated and stealthy cyberattacks conducted by skilled adversaries. APTs seek illegal access to a target network and remain undetected for extended periods, frequently for espionage or data theft.
These attacks involve multiple stages, including reconnaissance, infiltration, lateral movement, and data exfiltration. APT actors use advanced techniques, such as zero-day exploits and social engineering, to bypass traditional security measures. Defending against APTs requires continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, network segmentation, and strong access controls.
Timely incident response and regular security audits are vital to detect and mitigate APTs effectively.
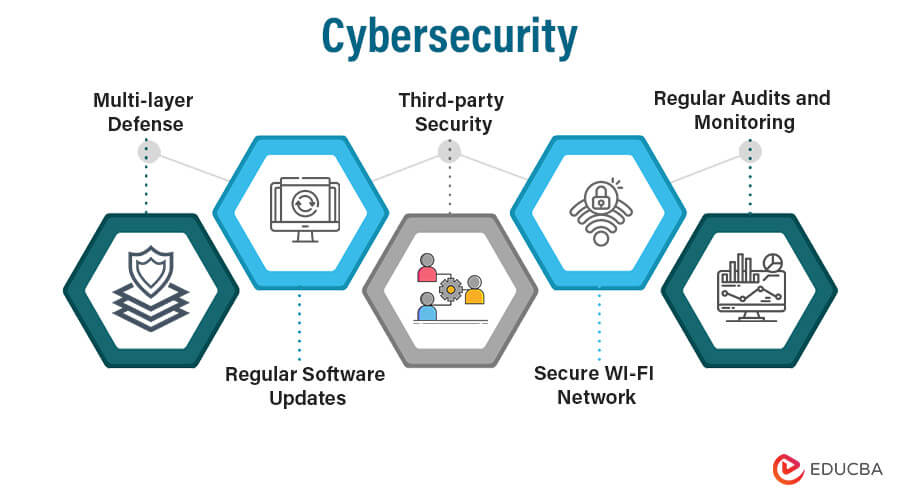
Securing Networks and Systems
Let’s discuss some effective strategies and best practices to secure networks and systems, safeguarding against cyber risks and safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access or hostile assaults.
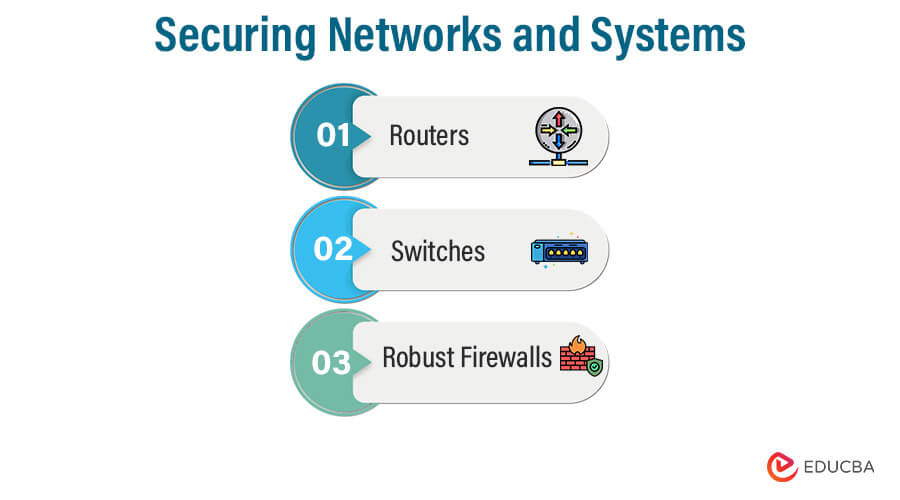
1. Use Strong Network Equipment and Firewalls
Strong network equipment, such as routers and switches, and robust firewalls are vital for enhancing network security.
These components act as the first line of defense against cyber threats, filtering and monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to the network.
2. Regularly Update Network Devices and Software
Regularly updating network devices and software is crucial for maintaining network security. Software updates often comprise patches for known vulnerabilities, which can prevent cyber attackers from exploiting them. Keeping network devices up-to-date ensures they have the latest security features and bug fixes, reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring a resilient network infrastructure.
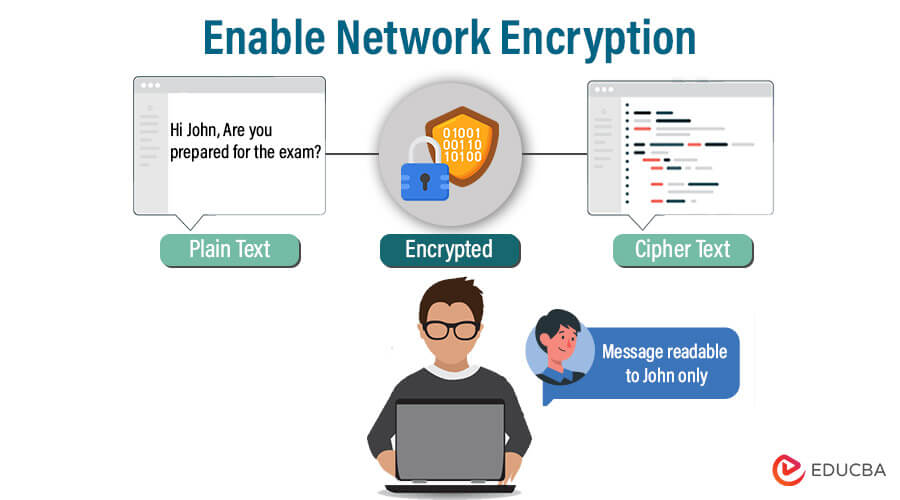
3. Enable Network Encryption
Enabling network encryption is essential for enhancing data security. Encrypting data as it travels through the network makes sensitive information unreadable to unauthorized users.
This prevents eavesdropping and data interception, protecting against potential cyberattacks. Utilizing protocols like SSL/TLS for web traffic and VPNs for remote access ensures that data remains confidential and secure, safeguarding your network and sensitive data from threats.
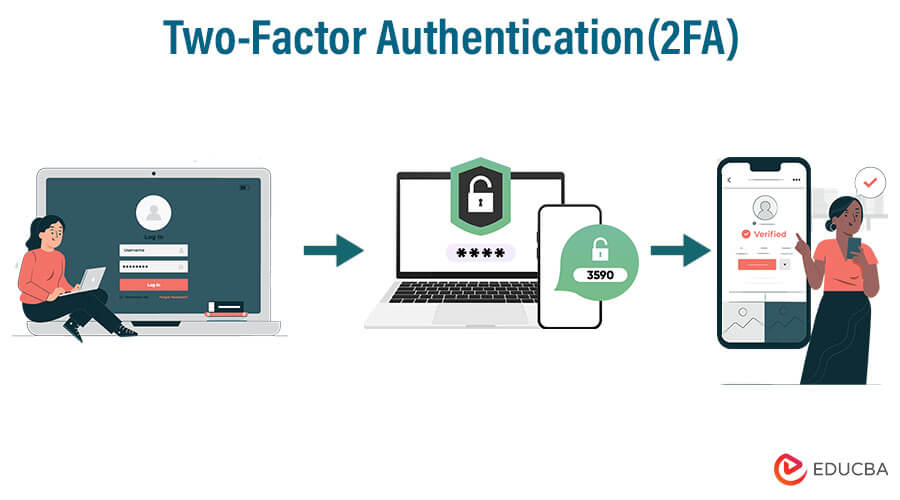
4. Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security characteristic that provides enhanced protection to user accounts. Before gaining access, users must present two pieces of identity —typically something they know (like a password) and have (like a one-time code sent to their phone).
2FA minimizes the danger of unwanted access while also improving account security and defending against password-related assaults.
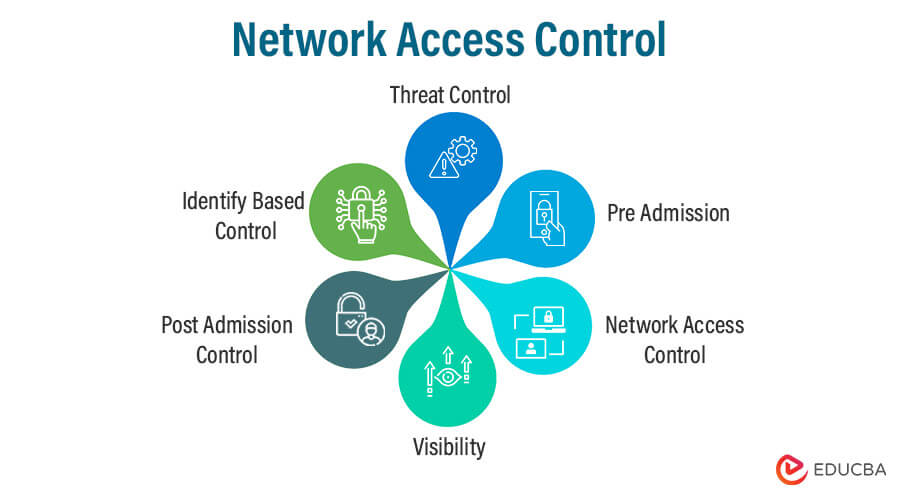
5. Network Access Control (NAC)
Network Access Control (NAC) is a security system that governs and limits network access based on established criteria.
Only authorized and conforming devices can connect to the network while banning or quarantining illegitimate or non-compliant devices.
NAC helps prevent unauthorized access, enforce security policies, and enhance network visibility and control, contributing to a more secure and efficiently managed network environment.
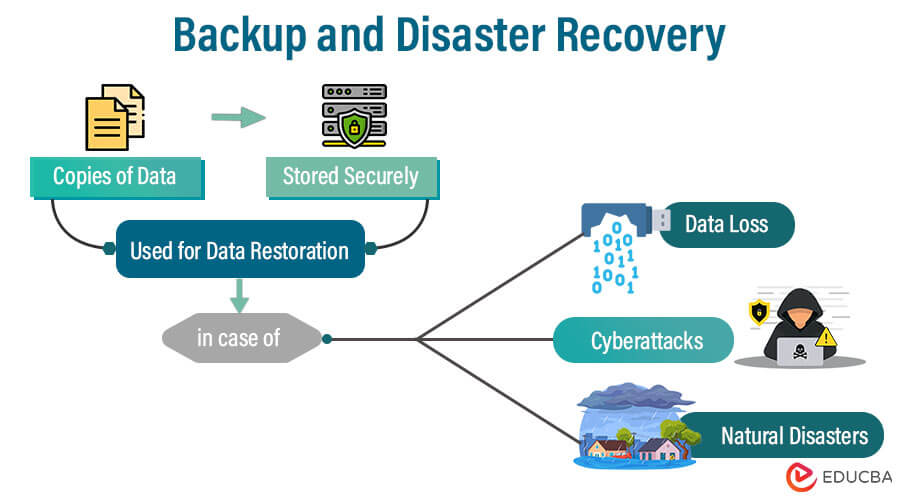
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) is a critical component of cybersecurity strategy. It involves regularly creating copies of important data and storing them securely, allowing for data restoration in case of data loss, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
BDR ensures business continuity, minimizes downtime, and protects against data loss, providing a safety net to recover and resume operations efficiently after adverse events.
It is an essential practice for safeguarding valuable data and maintaining the resilience of businesses in the face of various threats.
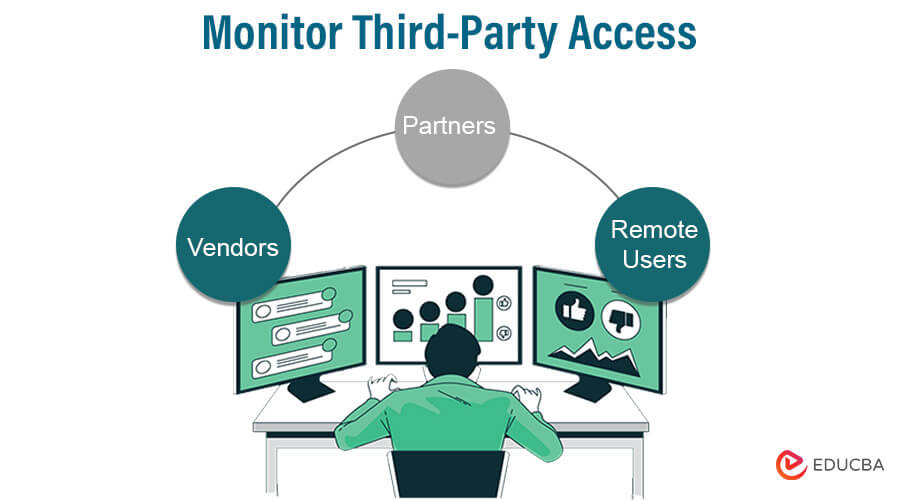
7. Monitor Third-Party Access
Monitoring third-party access is crucial to ensure your network’s and data’s security. Regularly review and audit the access permissions granted to external vendors and partners.
By monitoring their activities and ensuring compliance with security policies, you can mitigate potential risks and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
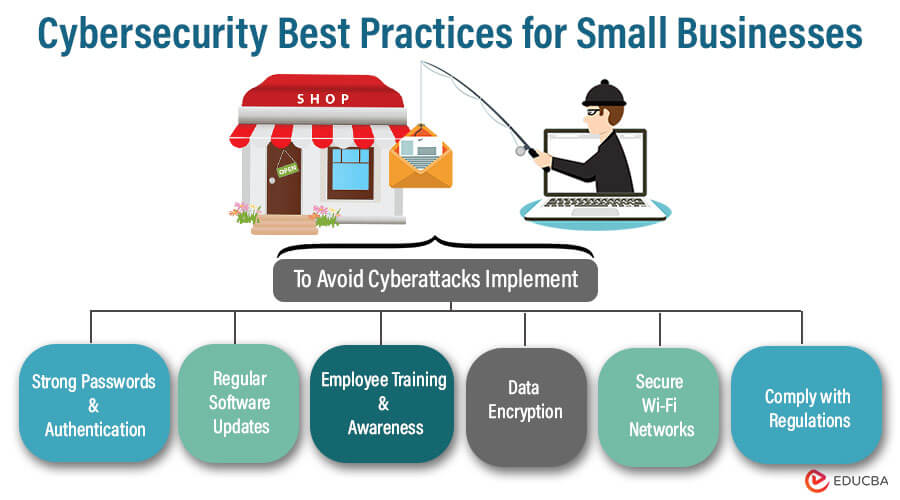
Key Cybersecurity Best Practices
Here are some key cybersecurity best practices for a secure digital environment in small businesses:
- Strong Passwords and Authentication: Strong passwords and authentication are vital for cybersecurity. Enforce complex password policies with a mix of characters, numbers, and symbols. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add a layer of protection by forcing users to provide additional verification, minimizing the danger of unlawful access and data breaches.
- Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: Patch management and regular software updates must be performed in cybersecurity practices. Keep operating systems, applications, and software up-to-date with the latest patches and security updates. Patch management reduces the risk of data breaches, malware infections, and other cyber threats, maintaining a secure digital environment for your organization.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Employee training and awareness are critical for a strong cybersecurity posture. Educate employees about cybersecurity risks, best practices, and how to recognize and respond to threats like phishing and social engineering.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption is a fundamental cybersecurity measure that ensures sensitive information remains confidential and secure. Access to the data is limited to authorized users who possess the decryption key. This requires converting the data into an unreadable format using encryption algorithms.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Secure Wi-Fi networks are vital to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Use strong encryption protocols like WPA2 or WPA3 and unique, strong passwords for Wi-Fi access. Regularly update Wi-Fi router firmware and employ additional security measures like MAC filtering and disabling SSID broadcasting for enhanced network security.
- Comply with Regulations: Compliance with cybersecurity regulations is crucial to maintaining a secure digital environment. Stay informed about relevant laws and industry standards, and ensure your organization adheres to them.
Staying Informed: Resources and Practices for Ongoing Cybersecurity Education
Staying informed about cybersecurity is essential to keep up with the evolving threat landscape. Let us discuss some valuable resources and best practices for ongoing cybersecurity education for Small Businesses:
- Cybersecurity Websites: Follow reputable websites, blogs, and news outlets that cover cybersecurity topics, providing the latest trends, threats, and best practices.
- Training Courses and Certifications: Enroll in cybersecurity training Courses and certificates to help you advance your knowledge and competence in the subject.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds that provide real-time updates on emerging threats.
- Internal Training Programs: Organizations can conduct internal training sessions to educate employees about cybersecurity risks and preventive measures.
- Security Awareness Programs: Regularly conduct security awareness programs to educate employees and users about safe online practices.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage in cybersecurity-related online forums and communities to discuss issues, ask questions, and learn from peers.
- Exercises and Simulations: Conduct cybersecurity exercises and simulations to practice incident response and hone defensive skills.
By continuously educating ourselves and leveraging available resources, we can better understand the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape and strengthen our ability to protect against cyber threats.
Conclusion – Cybersecurity Best Practices for Small Businesses
In conclusion, maintaining a secure digital environment requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. By implementing essential best practices like strong passwords, regular updates, employee training, data encryption, secure Wi-Fi, compliance, and continuous learning, organizations can safeguard against cyber threats, protect valuable data, and foster a resilient cybersecurity posture in small businesses.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cybersecurity Best Practices for Small Businesses” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.