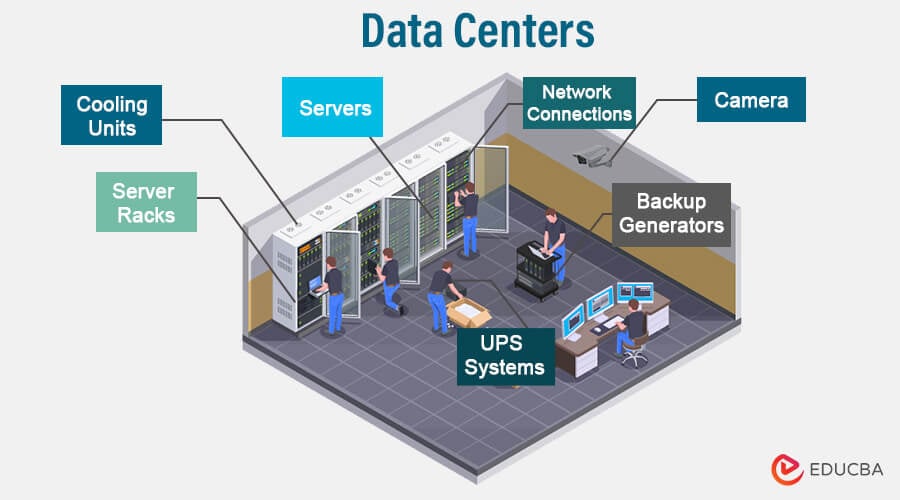
What are Data Center?
Data centers are highly specialized facilities specifically designed to house and manage a vast array of computer systems, servers, networking equipment, and storage infrastructure. The primary purpose of data centers is to process, store, and distribute data for various applications and services, such as websites, cloud computing, and enterprise operations. These facilities come in different sizes, ranging from small server rooms to massive, purpose-built complexes. They play a crucial role in the digital age, underpinning the functionality of the internet, data-driven businesses, and critical infrastructure.
Table of Contents
- What are data center?
- Significance of Data Center
- Functions
- Core components
- Types
- Security
- Modern Data Center
- Data center’s importance to Business
Significance of Data Center
The significance of data centers in the modern world is multifaceted and crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Digital Transformation: Data centers are crucial for digital transformation, enabling organizations to collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, resulting in increased efficiency, innovation, and new digital services and products.
- Cloud Computing: It plays a crucial role in providing cloud computing services. Leading providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud rely on extensive data center networks to deliver a wide range of cloud-based solutions to customers worldwide.
- Internet Services: Play a role in processing and delivering data whenever you access online services, be it social media, e-commerce, or streaming content. They ensure that the digital services we rely on are readily available and responsive.
- Business Continuity: Provides redundancy and high availability to ensure business continuity. Redundant systems and backup data help prevent data loss and minimize service downtime.
- Data Storage: Offer secure, scalable, and reliable storage solutions for an ever-growing volume of data, ranging from personal files and databases to critical government records.
- Scientific and Research Applications: Supports scientific research, simulations, and data analysis in fields such as genomics, climate modeling, and particle physics.
- Government and Public Services: It is essential for various government functions, including maintaining public records, securing sensitive data, and ensuring the smooth operation of critical public services.
Functions of Data Center
Some of their key functions include:
- Data Storage: It provides secure and scalable storage solutions for vast amounts of data, from personal files and databases to multimedia content and business records. They use sophisticated storage systems to organize and manage this data efficiently.
- Data Processing: It houses powerful servers equipped with high-performance processors. These servers handle complex calculations, run applications, and support tasks such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. Processing data at scale is essential for real-time data analysis and scientific simulations.
- Network Connectivity: Data centers host networking equipment that ensures high-speed and reliable connectivity. They manage the data flow between servers, the data center, and external networks, allowing seamless communication and data transfer.
- Virtualization and Cloud Computing: It allows virtualization, enabling multiple virtual machines to run on one physical server. This is essential for cloud computing, which optimizes resource use and enables on-demand service deployment.
- Redundancy and Reliability: To ensure continuous operation, data centers incorporate redundancy measures. This includes backup power supplies, cooling systems, and duplicate hardware configurations. Redundancy minimizes the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or power outages.
- Functions of Data Center: However, businesses in specific locations might benefit more when considering redundancy and real-time processing. For example, placing a strategic edge data center can greatly improve continuity and efficiency for companies that rely heavily on managed IT services for Orlando, Florida. By optimizing resources such as high-speed connections and scalable server capabilities, these centers cater specifically to unique regional requirements.
- Security: Data centers implement stringent security measures to protect sensitive data. Access controls, encryption, firewalls, and physical security protocols are employed to safeguard against unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches.
- Load Balancing: Data centers use load-balancing techniques to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers. Balancing the workload optimizes resource utilization, enhances performance, and prevents individual servers from becoming overwhelmed with traffic.
- Disaster Recovery: It often has disaster recovery plans in place. They create regular data backups and deploy failover systems to ensure critical services can quickly resume during a hardware failure, natural disaster, or other disruptive events.
- Energy Efficiency: Many data centers prioritize energy efficiency through renewable energy, advanced cooling, and server virtualization, reducing consumption and environmental impact.
Core Components
The key components of a data center include:
- Servers: Servers are powerful computers that process and store data. They run applications, manage network traffic, and respond to user or system requests. Servers in data centers are optimized for performance, reliability, and scalability.
- Storage Systems: Data centers utilize different types of storage systems, including hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), to store and access data. These systems provide the capacity and speed required for storing and retrieving vast amounts of information, ranging from simple text files to complex multimedia content.
- Networking Equipment: Networking equipment, including routers, switches, and firewalls, facilitates communication between servers within the data center and with external networks. They manage data traffic, ensure connectivity, and enhance security.
- Cooling Systems: Data centers produce a considerable amount of heat due to the operation of servers and other hardware components. Cooling systems like air conditioning and precision cooling units are used to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels. Proper cooling is crucial to prevent overheating and ensure the reliability of the equipment.
- Power Infrastructure: Operating servers and other critical equipment require a stable and reliable power supply supported by industrial-grade power strips. Users employ Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems and backup generators to supply power during outages and ensure continuous operation.
- Backup Power Systems: Backup power systems like generators & batteries provide uninterrupted electricity during power outages, ensuring continuous data center operations.
- Security Systems: It implements various security measures, including access control systems, surveillance cameras, and biometric authentication, to safeguard against unauthorized access, theft, and physical threats.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Includes sprinklers and specialized extinguishing agents installed to reduce fire risk and protect equipment and data.
- Environmental Monitoring: It employs sensors and monitoring systems to track environmental factors, including temperature, humidity, and airflow. Monitoring ensures conditions remain within acceptable ranges to preserve equipment functionality and longevity.
- Redundancy Systems: Redundancy systems, including duplicate servers, storage devices, and networking components, are set up to provide backup in case of hardware failures. Redundancy improves reliability and reduces the likelihood of service outages.
- Management Software: It utilizes management software to monitor and manage various components, automate tasks, optimize resource utilization, and ensure the overall efficiency of operations.
Types of Data Centers
Here are the main types of data centers:
- Enterprise Data Centers: Individual businesses or organizations own and operate these data centers to support internal IT needs. Large corporations and government agencies typically use enterprise data centers to store and manage their data, applications, and services.
- Internet Data Centers (IDCs): The Internet is a commercial facility that provides businesses and individuals hosting, storage, and Internet connectivity services. IDCs house servers and networking equipment for multiple clients and offer web hosting, email hosting, and cloud computing services.
- Colocation Data Centers: Colocation rents out space, power, and cooling infrastructure to businesses and organizations that prefer to avoid building their facilities. In a colocation center, multiple tenants share the same physical space while maintaining control over their servers and equipment. Colocation services provide security, redundancy, and professional infrastructure management benefits.
- Cloud Data Centers: Clouds are massive facilities owned and managed by cloud service providers like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Amazon Web Services (AWS). These data centers host many virtual computers and storage resources that enable cloud-based services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
- Managed Services Data Centers: Managed services are run by third-party providers that offer managed IT services to businesses. These providers handle different IT functions, such as data storage, security, and network management. By outsourcing their IT needs to these service providers, businesses can concentrate on their primary functions without worrying about managing IT-related tasks.
- Regional Data Centers: Regional data centers serve specific geographic areas or communities, providing essential IT services to local businesses and residents. These centers support localized applications, internet services, and community-oriented initiatives.
- Hyperscale Data Centers: Hyperscale data centers are massive facilities built by technology giants like Google, Facebook, and Microsoft. These centers handle the high demands of cloud computing and online services, processing enormous volumes of data and supporting services used by millions of people worldwide.
- Edge Data Centers: Edge closer to end-users brings computing resources closer to the data source and reduces latency. These designs support real-time processing applications like IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) applications.
Data Center Security
Here are key aspects of data center security:
Physical Security
- Access Control: Implement strict access control mechanisms, including biometric authentication, key card systems, and multi-factor authentication, to restrict entry to authorized personnel.
- Surveillance: Employ surveillance cameras and security personnel to monitor the facility 24/7, deterring unauthorized access and providing a record of activities.
- Perimeter Security: Secure the facility’s perimeter with fencing, gates, and barriers to prevent unauthorized individuals from approaching the building.
- Mantraps: Use mantraps and enclosed security vestibules with two sets of interlocking doors to ensure that only one person can enter or exit at a time after proper verification.
Network Security
- Firewalls: Deploy firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, protecting against unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): One effective security technique is to use IDPS to detect and respond to potential security issues in real-time. This reduces the detrimental impact of malicious activity.
- Virtual LANs (VLANs): Implement VLANs to segment the network, restricting communication between different segments and enhancing overall network security.
- Encryption: Ensure data encryption in transit and at rest to maintain its unintelligibility in case of interception without the appropriate decryption keys.
Data Security
- Regular Backups: Maintain daily backups of critical data and secure backup mechanisms. It is important to regularly test the restoration procedure to ensure that the data integrity is maintained.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to monitor and control data transfer, preventing sensitive information from leaving the data center without authorization.
- Data Masking/Anonymization: Mask or anonymize sensitive data when not in use, minimizing the risk of exposure in case of unauthorized access.
Environmental Controls
- Temperature and Humidity Monitoring: Employ sensors to monitor temperature and humidity levels, ensuring that the data center environment remains within acceptable ranges to prevent equipment damage.
- Fire Suppression: Implement fire suppression systems, such as clean agents or inert gas systems, to extinguish fires quickly without damaging the equipment.
- Water Leak Detection: Install water leak detection systems to promptly identify and address potential water leaks, protecting servers and other hardware from water damage.
Personnel Security
- Background Checks: It is important to conduct thorough background checks of employees and third-party contractors with access to the data center to minimize the risk of insider threats.
- Security Training: Provide regular security training to personnel, raising awareness about security best practices, social engineering attacks, and potential risks.
Compliance and Regulations
- Compliance: Ensure the data center complies with industry regulations and standards, like HIPAA (for healthcare) or PCI DSS (for payment card industry), to maintain data security and privacy.
- Regular Audits: Conduct security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security weaknesses proactively.
Modern Data Center
A modern is a highly advanced and technologically sophisticated facility designed to meet the ever-increasing digital age demands. It represents the pinnacle of data processing, storage, and management infrastructure.
Here are some key features and characteristics that define a modern data center:
- High-Performance Computing: Modern data centers equip state-of-the-art servers with powerful processors, ample memory, and high-speed interconnects. These servers handle intensive computing workloads, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics.
- Scalability: Companies build modern data centers to be scalable, allowing them to expand computing and storage resources as needed rapidly. This scalability is essential for accommodating the growth of digital services and data volumes.
- Virtualization and Cloud Integration: They incorporate virtualization technologies to optimize resource utilization and facilitate the deployment of cloud services. Virtual machines and containers enable efficient management of workloads.
- Efficient Cooling and Power Management: Energy efficiency is a core focus. Modern data centers use advanced cooling systems, hot/cold aisle containment, and efficient power distribution to minimize energy consumption and reduce environmental impact.
- Redundancy and High Availability: These data centers have redundant components, including power supplies, network connections, and backup systems, to ensure high availability. Failover mechanisms and disaster recovery solutions are in place to minimize service downtime.
- Security: The facility prioritizes security using access control, biometric authentication, surveillance, and intrusion detection systems for physical protection. Network security measures like firewalls and encryption safeguard data in transit and at rest.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automation tools and orchestration platform integration streamline data center operations. These technologies can provision resources, monitor performance, and respond to issues automatically.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Capabilities: Modern data centers support hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, enabling organizations to integrate on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud services seamlessly.
- Green Initiatives: To decrease their carbon footprint and promote sustainability, data centers embrace green practices, including using renewable energy and advanced cooling methods.
- Software-Defined Infrastructure: Modern data centers often utilize software-defined infrastructure (SDI) that abstracts and virtualizes computing, storage, and networking resources. This approach enhances flexibility, agility, and resource management.
- Remote Management and Monitoring: Advanced remote management and monitoring tools enable administrators to oversee data center operations, troubleshoot issues, and perform maintenance tasks from anywhere.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Designers of modern data centers prioritize compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, ensuring the security and privacy of data with a keen focus.
- Edge Computing Integration: Modern data centers are increasingly deploying resources at the edge to reduce latency and improve processing for IoT and content delivery applications.
Data Centers’ Importance to Business
Data centers play a crucial and often indispensable role in the operations of businesses across various industries. Their importance to companies can be summarized as follows:
- Data Storage and Management: It provides secure and scalable storage solutions for businesses, ensuring the safekeeping of critical data, documents, and records. This data is essential for day-to-day operations, decision-making, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: It implements redundancy and backup systems that allow businesses to maintain continuity in the face of hardware failures, power outages, or unforeseen disasters. This ensures operations can continue even in adverse conditions, reducing downtime and minimizing potential revenue loss.
- Scalability: Businesses can quickly scale their IT infrastructure by utilizing data centers. Whether a business is expanding or downsizing, data centers can adjust resources like storage and computing capacity as needed without significant capital investment.
- High Availability: It aims to offer high availability and reliability. They achieve this through redundant systems, failover mechanisms, and 24/7 monitoring to ensure that services and applications remain accessible to customers and employees, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
- Security and Compliance: It incorporates stringent security measures to protect sensitive business data. This is crucial to ensure data integrity, protect customer information, and comply with GDPR and HIPAA regulations.
- Remote Accessibility: Employees can work from different locations by remotely accessing applications and services hosted in data centers. This flexibility supports remote work arrangements, enhances productivity, and ensures business continuity in pandemics or natural disasters.
- Cost Efficiency: By outsourcing IT infrastructure to data centers, businesses can save on capital expenses for building and maintaining on-site data centers. This cost-efficient approach allows companies to focus on their core competencies and allocate resources strategically.
- Resource Consolidation: It enables resource consolidation through virtualization and cloud services. This minimizes the number of physical servers required, reducing power consumption and operational costs.
- Support for Digital Transformation: It serves as the foundation for digital transformation initiatives, allowing businesses to harness the power of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. These technologies can drive innovation, improve customer experiences, and create new revenue streams.
- Environmental Responsibility: Certain data centers prioritize green initiatives, emphasizing energy efficiency and sustainability. Partnering with such data centers can help businesses reduce their carbon footprint and meet corporate social responsibility goals.
Conclusion
Data centers play a crucial role in today’s business operations by providing the necessary data storage, processing, and security infrastructure. Their importance in ensuring business continuity, scalability, and the adoption of new technologies cannot be overstated. As companies rely on digital solutions, data centers will continue to be at the heart of their success, enabling efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in an increasingly connected world.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Center” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.