What is Data Loss Prevention?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a strategy and tool to protect sensitive information against unauthorized access, sharing, or loss. It involves identifying, monitoring, and protecting critical data through various measures like encryption, access controls, and user training. DLP aims to mitigate risks associated with accidental or intentional data breaches, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and safeguarding an organization’s financial health and reputation. By proactively managing data throughout its lifecycle, DLP empowers businesses to prevent, detect, and respond to potential threats, creating a robust defense against the ever-evolving landscape of data security challenges.
Table of Contents
- What is Data Loss Prevention?
- Importance of Data Loss Prevention
- Types of Data Loss
- How does DLP work?
- Technologies and Tools in Data Loss Prevention
- Consequences of Data Loss
- Key Components of Data Loss Prevention
- Challenges in Data Loss Prevention
- Future Trends in Data Loss Prevention
Importance of Data Loss Prevention
For several reasons, data loss prevention, or DLP, is crucial for individuals and organizations.
- Protection of Sensitive Information: DLP protects sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property, to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse.
- Maintaining Trust and Reputation: DLP measures contribute to building and maintaining trust among customers, clients, and stakeholders. Protecting sensitive information instills confidence in an organization’s commitment to data security.
- Compliance with Regulations: DLP helps organizations comply with data protection regulations and industry standards, avoiding legal consequences, fines, and reputational damage associated with non-compliance.
- Prevention of Financial Loss: By minimizing the risk of data breaches and leaks, DLP helps organizations avoid financial losses associated with remediation efforts, legal proceedings, and potential business disruptions.
- Mitigation of Insider Threats: DLP strategies address insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, by monitoring and controlling user activities to prevent unauthorized data access or sharing.
- Preservation of Intellectual Property: For businesses, DLP is crucial in preserving intellectual property and trade secrets, protecting the competitive advantage and innovation that these assets represent.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture: DLP is integral to a comprehensive cybersecurity framework, adding layers of defense against external cyber threats and internal vulnerabilities.
- Prevention of Identity Theft: By protecting personal information from unauthorized access and exploitation, DLP lowers the risk of identity theft and financial crime, which benefits individuals.
- Operational Continuity: DLP measures contribute to maintaining operational continuity by preventing data breaches that could disrupt business processes and compromise critical systems.
- Proactive Risk Management: DLP enables proactive identification and management of data loss risks, staying ahead of threats, and adapting security measures.
Types of Data Loss
Data loss can occur through various avenues, each presenting challenges to information security. The primary types of data loss include:
- Accidental Deletion: Unintentional removal of critical files or information, often due to human error or system glitches.
- Malicious Attacks: Deliberate actions by cybercriminals, such as hacking, malware, or ransomware, aimed at stealing, corrupting, or rendering data inaccessible.
- Hardware Failures: Damage or malfunction of storage devices, servers, or other hardware components, leading to the loss of stored data.
- Data Corruption: Unintended alterations to data, rendering it unreadable or unusable, often caused by software bugs, power outages, or system crashes.
- Insider Threats: Malicious actions or negligence by employees, contractors, or other internal entities, intentionally or unintentionally compromising sensitive information.
- Data Theft: Unauthorized access and extraction of confidential data for illicit purposes, including identity theft, financial fraud, or industrial espionage.
- Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes, floods, fires, or other disasters can physically damage infrastructure and result in data loss if proper backup and recovery measures are not in place.
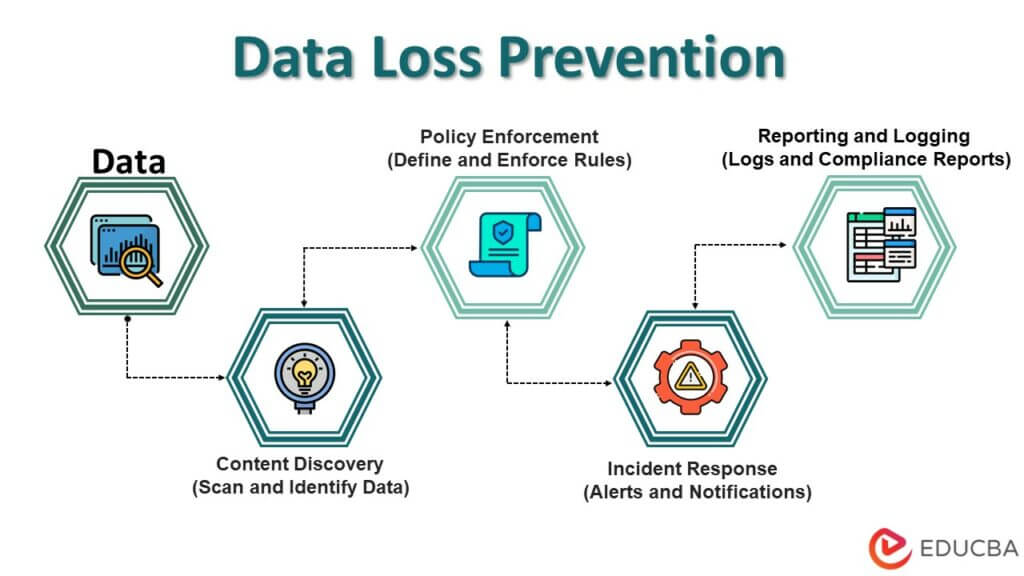
How does DLP work?
DLP, or Data Loss Prevention, is a set of practices and technologies to prevent unauthorized access, use, or transmission of sensitive data or information. The goal of DLP is to ensure that sensitive data is not leaked, intentionally or unintentionally, both within an organization and outside of it. Here’s a general overview of how DLP works:
- Identification of Sensitive Data: DLP solutions start by identifying and classifying sensitive data within an organization. This can include sensitive information such as personally identifiable data (PII), financial records, intellectual property, and health data.
- Policy Creation: Policies explain how sensitive data should be handled in organizations. Policies can include rules about who can access certain types of data, where it can be stored, how it can be transmitted, and what actions are allowed or prohibited.
- Content Discovery: DLP solutions use various methods to discover sensitive data within the organization. This may involve scanning databases, file servers, email systems, and other repositories for patterns or keywords that match the criteria defined in the policies.
- Endpoint Protection: DLP software is often installed on endpoints such as computers, smartphones, or servers to monitor and control the flow of sensitive data. This can involve monitoring file transfers, clipboard actions, printing activities, and more.
- Network Monitoring: DLP solutions can also monitor network traffic for the transfer of sensitive data. This includes web traffic, email communication, and other network activities. Network-based DLP tools can inspect data packets and apply policies to prevent unauthorized data transfers.
- Encryption and Masking: DLP may involve using encryption and data masking techniques to protect sensitive information. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be easily understood without the proper decryption key. Data masking involves replacing sensitive information with fictional or pseudonymous data.
- Incident Response and Reporting: DLP solutions provide tools for incident response, notifying administrators when a potential data breach is detected. They may also generate reports for compliance purposes and help organizations understand data usage patterns and potential vulnerabilities.
- User Education: DLP is not solely a technological solution. Employee education and awareness are crucial components. Training programs can help individuals understand their responsibility in preventing data loss and enhancing data security.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: DLP solutions often integrate with other security tools, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and identity management systems, to provide a comprehensive security posture.
Technologies and Tools in Data Loss Prevention
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) employs diverse technologies and tools to safeguard sensitive information, mitigating the risks linked to data breaches. Here are key components and solutions commonly used in DLP strategies:
1. Endpoint DLP Solutions: Endpoint DLP solutions focus on protecting data at individual devices or endpoints, such as computers, laptops, and mobile devices.
Functionality:
- Monitoring and Control: These solutions monitor and control data transfer and storage on individual devices.
- Encryption: Endpoint DLP may include encryption features to safeguard data stored on endpoints.
- Device Control: Restricts or allows specific devices (USB drives, external hard drives) based on DLP policies.
Benefits:
- Granular Control: Offers precise control over data on each device.
- User Awareness: Helps in educating users about responsible data handling.
2. Network DLP Solutions: Network DLP solutions focus on monitoring and controlling data in transit over a network.
Functionality:
- Packet Inspection: Analyzes data packets flowing through the network for sensitive information.
- Policy Enforcement: Implements policies to prevent unauthorized data transfer.
- Real-time Monitoring: Constantly monitors network traffic for potential data breaches.
Benefits:
- Centralized Control: Provides a centralized point for managing and enforcing DLP policies across the network.
- Prevention of Data Exfiltration: Helps prevent the unauthorized transfer of sensitive data outside the network.
3. Cloud DLP Solutions: Cloud DLP solutions are designed to protect data stored in cloud environments, including public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Functionality:
- Cloud Application Monitoring: Monitors data usage within cloud applications.
- Encryption in the Cloud: Provides encryption for data stored in cloud services.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensures adherence to data protection regulations in the cloud.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Adapts to the dynamic nature of cloud environments.
- Collaboration Support: Facilitates secure collaboration and sharing of sensitive data in the cloud.
4. Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Integration with SIEM enhances the overall security posture by combining DLP insights with broader security event management.
Functionality:
- Correlation of Events: Connects DLP incidents with other security events for a comprehensive view.
- Incident Response: Integrating DLP and broader security alerts enhances incident response capabilities.
- Centralized Reporting: Provides a centralized reporting and analysis platform for security incidents.
Benefits:
- Holistic Security: Offers a unified approach to security management.
- Faster Incident Response: Enables quicker response to potential threats by leveraging a broader security data set.
Consequences of Data Loss
Data loss can severely affect individuals and organizations, impacting operations and reputation. The consequences include:
- Financial Impact: Data loss often leads to financial losses, including the costs of data recovery, potential legal fees, and the impact on productivity and revenue generation.
- Reputational Damage: Losing sensitive or confidential data erodes customer, client, and stakeholder trust. A damaged reputation can take a long time to rebuild and may result in losing business opportunities.
- Legal Ramifications: Organizations may face legal consequences for failing to protect sensitive information, especially in industries with strict data protection regulations.
- Operational Disruption: Data loss can disrupt daily operations, leading to downtime, decreased productivity, and increased stress on employees as they work to recover or recreate lost information.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: For businesses, the loss of proprietary information or intellectual property can have long-term consequences, impacting competitiveness and market position.
- Customer Trust Erosion: Customers may lose confidence in an organization’s ability to protect their data, leading to customer churn and difficulty acquiring new clients.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: Individuals face severe consequences from data loss, including identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized access to personal accounts.
- Non-Compliance Penalties: Failure to protect sensitive data in accordance with data protection regulations can result in regulatory penalties and fines, further adding to the financial impact.
Key Components of Data Loss Prevention
Effective data loss prevention (DLP) entails a number of essential components that work together to identify, monitor, and preserve sensitive data. The main components include:
1. Data Discovery and Classification:
- Identification: Leverage business activity monitoring tools to automatically identify and track sensitive data across your organization.
- Classification: Categorize data based on sensitivity, ensuring a clear understanding of what needs protection.
2. Access Controls and Permissions:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement access controls that restrict users’ permissions based on their organizational roles.
- Least Privilege Principle: Grant users minimal access to perform job functions, reducing unauthorized data access risk.
3. Encryption:
- Data Encryption Methods: It is important to use encryption algorithms to protect data while it is being processed, in transit, and at rest.
- Key Management: Establish secure key management practices to control and monitor access to encryption keys.
4. Endpoint Security:
- Endpoint DLP Solutions: Deploy tools that monitor and control data transfer on end-user devices (laptops, smartphones) to prevent data leakage.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Monitor endpoints for policy violations and enforce DLP policies to prevent unauthorized data activities.
5. Employee Training and Awareness:
- Education Programs: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about the importance of data security and their role in preventing data loss.
- Phishing Awareness: Train employees to recognize and avoid phishing attacks, a common entry point for data breaches.
6. Network Security:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Implement network security measures to monitor and control data traffic, identifying and blocking potential threats.
- Network DLP Solutions: Deploy solutions that monitor data movement within the network and enforce policies to prevent unauthorized transfers.
7. Incident Response Plan:
- Detection and Analysis: Establish processes for detecting and analyzing potential data breaches promptly.
- Response and Mitigation: Develop a well-defined incident response plan to address and mitigate the impact of data loss incidents.
8. Comprehensive Policies:
- Data Usage Policies: Define clear policies governing how sensitive data should be handled, shared, and stored.
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Use UBA tools to examine user behavior and find irregularities that may indicate a potential data breach.
Challenges in Data Loss Prevention
Organizations face several challenges when implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies to protect sensitive information. These challenges include:
- Balancing Security and Productivity: Striking a balance between strong security measures and smooth, efficient corporate operations may take time and effort.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Adapting DLP strategies to keep pace with cyber threats’ constantly evolving tactics and stay ahead of emerging risks.
- Ensuring Compliance: Maintaining operational efficiency while meeting the needs of numerous data protection rules and industry standards.
- Employee Awareness and Cooperation: Overcoming the challenge of ensuring that employees are fully aware of DLP policies and actively cooperate in safeguarding sensitive data.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamlessly integrating DLP solutions with existing IT infrastructure and applications without causing disruptions or compatibility issues.
- Data Visibility Across Cloud Environments: Extending DLP coverage to effectively monitor and protect data in cloud environments, considering the increasing adoption of cloud-based services.
- Insider Threats: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, remains a complex challenge.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establishing and maintaining continuous monitoring of data activities to promptly detect and respond to potential breaches.
- Encryption Key Management: Effectively managing encryption keys to ensure the security of encrypted data without compromising accessibility for authorized users.
- Cost Considerations: Managing the costs associated with implementing and maintaining DLP solutions, which can vary based on the scale and complexity of the organization.
Future Trends in Data Loss Prevention
It is essential to anticipate future trends in Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to stay ahead of emerging threats and technologies. Here are a few potential trends:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: To enhance DLP capabilities, AI and ML are utilized for advanced threat detection, behavior analysis, and pattern recognition.
- Cloud-Based DLP Solutions: Increasing adoption of cloud-based DLP solutions to secure data in dynamic and decentralized environments, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Implementing a Zero Trust approach, where trust is never assumed, and continuous verification is required for users and devices accessing sensitive data.
- Data-Centric Security: Shifting towards a more data-centric security model, focusing on protecting the data rather than just the perimeter or endpoints.
- Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Privacy-preserving technologies like homomorphic encryption safeguard sensitive data, enabling analysis without revealing raw information.
- Automated Incident Response: Implementing automated incident response systems to detect and address data breaches in real-time, minimizing potential damage.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Expanding the use of UEBA to analyze and detect abnormal user behavior, helping identify potential insider threats.
- Regulatory Evolution: Adapting DLP strategies to comply with evolving data protection regulations, with an increased focus on consumer privacy.
- Integration with Collaboration Tools: Enhancing DLP solutions for seamless integration with collaborative platforms, ensuring secure data sharing and communication.
- Human-Centric Security Training: Prioritizing human-centric security training empowers employees to recognize and prevent potential data breaches.
Conclusion
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is an indispensable guardian of sensitive information, offering a multifaceted defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. Its significance extends beyond regulatory compliance, encompassing trust, financial stability, and intellectual property preservation. DLP mitigates risks and bolsters operational resilience by fostering a proactive cybersecurity posture. As data continues to be a cornerstone of modern business, investing in robust DLP measures remains paramount for individuals and organizations, ensuring valuable information’s security, integrity, and reputation.
FAQ
Q1. How do Cloud DLP Solutions protect data in cloud environments?
Answer: Cloud DLP Solutions monitor data within cloud applications, provide encryption for cloud-stored data, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations in the cloud.
Q2. Why is integration with SIEM systems important for DLP?
Answer: Integration with SIEM systems allows for a holistic approach to security, correlating DLP events with broader security events and enhancing incident response capabilities.
Q3. Are there industry-specific DLP considerations?
Answer: Yes, industries may have specific regulations and compliance requirements. DLP strategies should align with these industry standards for effective data protection.
Q4. How does DLP contribute to regulatory compliance?
Answer: DLP assists in maintaining regulatory compliance by enforcing data protection policies, ensuring the secure handling of sensitive information, and providing audit trails to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Loss Prevention” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,