Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction
Business Intelligence is the process of collecting and analyzing data to influence business decision-making. Data Science, on the other hand, focuses on extracting insights from large and complex datasets to inform decision-making and solve business problems. The following article is a detailed comparison between Data Science vs Business Intelligence.
Data Science vs Business Intelligence: Head-to-Head Comparison (Infographics)
Here are the top 20 comparisons between Data Science vs Business Intelligence:
Data Science vs Business Intelligence: Key Differences
From the above comparison, it can be concluded that both are analytical and information-focused, but the level of insight value differs. Data Science provides more advanced and forward-looking insights, making it an evolution from Business Intelligence.
Generic steps followed in Business Intelligence are as follows:
- Set a business outcome to improve.
- Decide which datasets are most relevant.
- Clean and prepare the data.
- Design KPIs, reports, and dashboards for better visualization.
Generic steps followed in Data Science stream are as follows:
- Set a business outcome to improve or predict.
- Gather all possible and relevant datasets.
- Choose an appropriate algorithm to prepare a model.
- Evaluate the model for accuracy.
- Operationalize the model.
Data Science vs Business Intelligence: Comparison Table
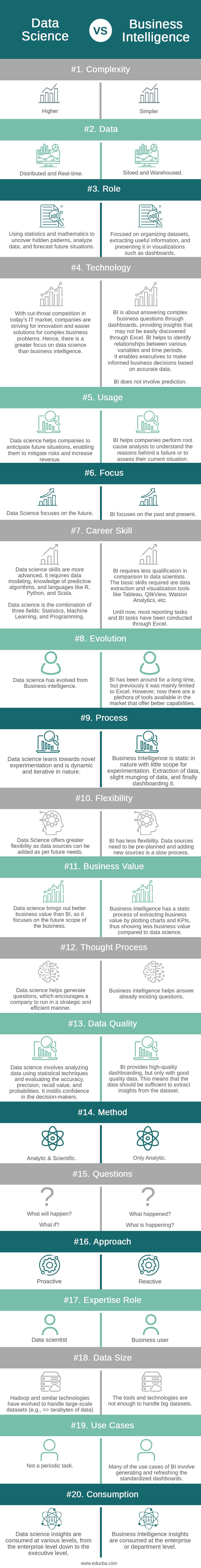
| Basis Of Comparison | Data Science | Business Intelligence |
| Complexity | Higher | Simpler |
| Data | Distributed and Real-time | Siloed and Warehoused |
| Role | Using statistics and mathematics to uncover hidden patterns, analyze data, and forecast future situations. | Focused on organizing datasets, extracting useful information, and presenting it in visualizations such as dashboards. |
| Technology | With cut-throat competition in today’s IT market, companies are striving for innovation and easier solutions for complex business problems. Hence, there is a greater focus on data science than business intelligence. | BI is about answering complex business questions through dashboards, providing insights that may not be easily discovered through Excel. BI helps to identify relationships between various variables and time periods. It enables executives to make informed business decisions based on accurate data.
BI does not involve prediction. |
| Usage | Data science helps companies to anticipate future situations, enabling them to mitigate risks and increase revenue. | BI helps companies perform root cause analysis to understand the reasons behind a failure or to assess their current situation
|
| Focus | Data Science focuses on the future. | BI focuses on the past and present. |
| Career Skill | Data science skills are more advanced. It requires data modeling, knowledge of predictive algorithms, and languages like R, Python, and Scala.
Data science is the combination of three fields: Statistics, Machine Learning, and Programming. |
BI requires less qualification in comparison to data scientists. The basic skills required are data extraction and visualization tools like Tableau, QlikView, Watson Analytics, etc.
Until now, most reporting tasks and BI tasks have been conducted through Excel. |
| Evolution | Data science has evolved from Business intelligence. | BI has been around for a long time, but previously it was mainly limited to Excel. However, now there are a plethora of tools available in the market that offer better capabilities. |
| Process | Data science leans towards novel experimentation and is dynamic and iterative in nature. | Business Intelligence is static in nature with little scope for experimentation. Extraction of data, slight munging of data, and finally dashboarding it. |
| Flexibility | Data Science offers greater flexibility as data sources can be added as per future needs. | BI has less flexibility. Data sources need to be pre-planned and adding new sources is a slow process |
| Business Value | Data science brings out better business value than BI, as it focuses on the future scope of the business. | Business intelligence has a static process of extracting business value by plotting charts and KPIs, thus showing less business value compared to data science. |
| Thought Process | Data science helps generate questions, which encourages a company to run in a strategic and efficient manner. | Business intelligence helps answer already existing questions. |
| Data Quality | Data science involves analyzing data using statistical techniques and evaluating the accuracy, precision, recall value, and probabilities. It instills confidence in the decision-makers. | BI provides high-quality dashboarding, but only with good quality data. This means that the data should be sufficient to extract insights from the dataset. |
| Method | Analytic & Scientific | Only Analytic |
| Questions | What will happen?
What if? |
What happened?
What is happening? |
| Approach | Proactive | Reactive |
| Expertise Role | Data scientist | Business user |
| Data Size | Hadoop and similar technologies have evolved to handle large-scale datasets (e.g., => terabytes of data) | The tools and technologies are not enough to handle big datasets. |
| Use cases | Not a periodic task. | Many of the use cases of BI involve generating and refreshing the standardized dashboards. |
| Consumption | Data science insights are consumed at various levels, from the enterprise level down to the executive level. | Business intelligence insights are consumed at the enterprise or department level. |
Conclusion
Business intelligence is undoubtedly a beneficial starting point for any industry. However, in the long run, adding a layer of data science will ultimately set it apart. The ability to predict the future by analyzing data is an achievement of data science. Therefore, data science plays a pivotal role and is superior to business intelligence.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles to the subject: