Updated April 28, 2023
Difference Between Data Science vs Statistics
Data science is one of the rapidly emerging trends in computing and is a vast multi-disciplinary area. Data science combines the application of computer science, software engineering, mathematics and statistics, programming, economics, and business management. Data science is based on collecting, preparing, analyzing, managing, visualizing, and storing large volumes of information. Data science, in simple terms, can be understood as having strong connections with databases, including big data and computer science. A data scientist has adequate domain knowledge relevant to the question addressed.
Big data is closely integrated with data science and has evolved with big data in different applications and use cases. Big data is available primarily in unstructured formats and contains non-numeric data. Useful information quickly gets buried in big data comprising blogs, audio/video files, images, text messages, social networks, etc. All this data is just noise unless it is analyzed and valuable information is extracted. In addition, nowadays, businesses consider the Internet their primary information channel due to the growing role of the social web and its business potential. All this data is of much interest to a data scientist because by using these data, many problems can be solved for organizations and also societies.
Data science is a specialized skill and can be understood as:
- Design and implementation in 4A’s – Data Architecture, Acquisition, Analysis, and Archival.
- Applying advanced techniques in mathematics and statistics to model data for deep analysis.
- Adequate programming and development skills and algorithm development skills.
- Analytical and ethical reasoning skills.
- Communication and business skills.
Therefore, it is apparent that data science is an interdisciplinary area and needs varied skill sets to gain mastery in this domain. Use cases in data science are similar to data analytics – they begin with a clear problem statement and the decision to end with well-defined metrics finally. Therefore, data scientists are familiar with business models and paradigms and ask good business questions to obtain meaningful insights from given data sets.
Statistics is another broad subject that deals with the study of data and is widely applied in numerous fields. Statistics provides the methodology for making conclusions from data. It gives different methods to gather data, analyze them and interpret results and is widely used by scientists, researchers, and mathematicians in solving problems. Statistics is synonymous with data-intensive activities – collecting, processing, and interpreting processed data.
Though statistics provide data collection and analysis methods, it helps obtain information from numerical and categorical data. Categorical data refers to unique data; examples are the person’s blood group, marital status, etc. Statistics is highly significant in data-related studies because it helps in,
- Deciding the type of data required to address a given problem.
- Organizing and summarizing data.
- Analysis to be done to conclude data.
- Assessing the effectiveness of results and evaluating uncertainties.
The methods provided by statistics include:
- Design for planning and conducting research.
- Descriptions which implies exploring and summarizing data.
- Making predictions and inferences using the phenomena represented by data.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Data Science vs Statistics (Infographics)
Below are the Top 5 comparisons between Data Science vs Statistics:
Key Differences Between Data Science vs Statistics
Given below are the key differences between Data Science and Statistics:
- Data science combines multi-disciplinary fields and computing to interpret data for decision-making. In contrast, statistics refer to mathematical analysis using quantified models to represent a given data set.
- Data science is more oriented to big data, which seeks to provide insight from huge volumes of complex data. On the other hand, statistics provides the methodology to collect, analyze and make conclusions from data.
- Data science uses tools, techniques, and principles to classify large data volumes into proper data sets or models. This is contrary to statistics which confines itself to tools such as frequency analysis, mean, median, variance analysis, correlation, regression, and so on, to name a few.
- Data science will investigate and inspect data to deduce factual, quantitative, and statistical inferences. This is opposed to statistics which focuses on analysis using standard techniques involving mathematical formulas and methods.
- A data scientist must have skill sets to analyze and simplify problems using complex data sets to figure out information. In contrast, a statistician will use the techniques of numeric and quantitative analysis.
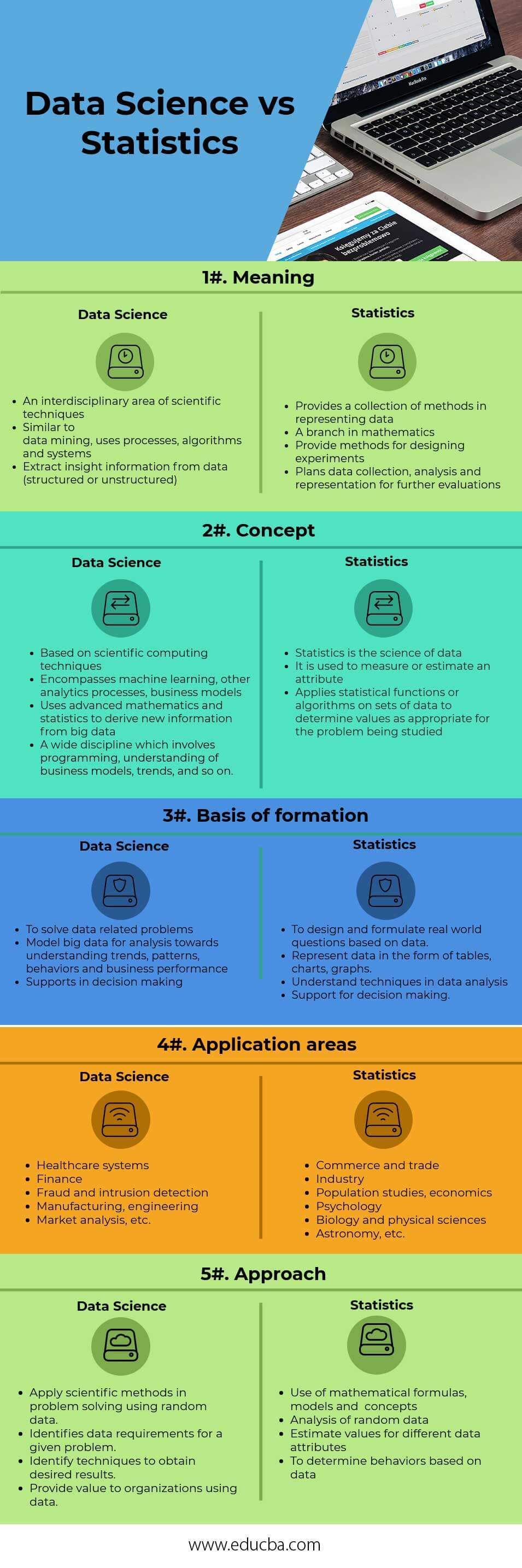
Data Science vs Statistics Comparison Table
The differences between data science vs statistics are explained in the points presented below:
| Basis for Comparison | Data Science | Statistics |
| Meaning |
|
|
| Concept |
|
|
| Basis of Formation |
|
|
| Application Areas |
|
|
| Approach |
|
|
Conclusion
In summary, it may be noted that Data science and statistics are indistinguishable and are closely linked. Statistics is a tool or method for data science, while data science is a vast domain where a statistical approach is an essential component. Data science and statistics will continue to exist, and there is a significant overlap between these two disciplines. Also to note, all statisticians cannot become data scientists and vice-versa. Data science has developed recently with big data and will continue to grow in the coming years as data growth seems to be never-ending.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Data Science vs Statistics. Here we have discussed Data Science vs Statistics head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –