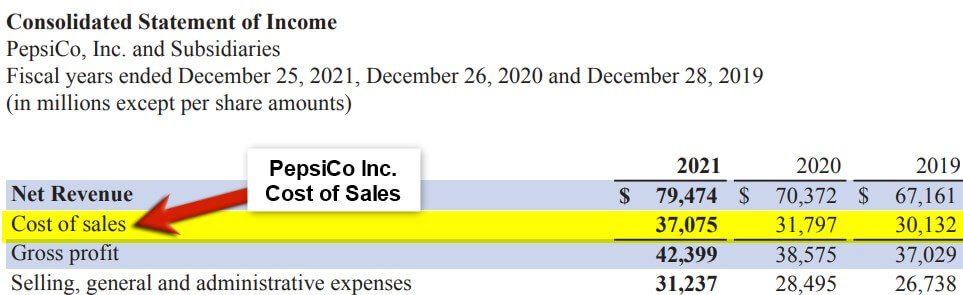Updated November 21, 2023
Days Payable Outstanding Meaning
Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) measures how quickly a company pays its bills to suppliers and vendors. It shows how many days, on average, it takes a company to pay for goods and services that were purchased on credit.
For example, a company named Beauty Junction has a DPO of 15 days. This means that Beauty Junction has a time period of 15 days to use the resources and pay back to the suppliers.
A lower DPO means that a company pays its bills faster, while a higher DPO means that it takes longer to pay its bills. This is an important financial metric because it can show whether a company is managing its cash flow well or not.
Key Highlights
- Days payable outstanding is a computation of the average days it takes a business to settle its payables.
- To calculate the DPO, multiply the specific period by accounts payables and divide the outcome by the cost of sales (COGS)
- If the value is high, it indicates the company has a good funds optimization strategy. In contrast, when the value is lower, the company is not utilizing in-hand capital efficiently.
- While DPO states the period it takes to resolve payables, DSO states the time it takes to collect all receivables.
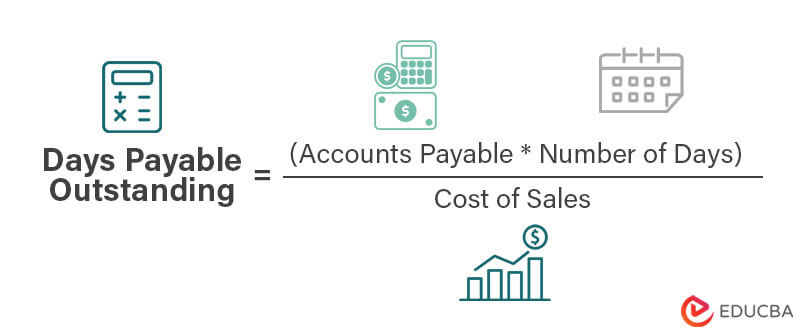
Days Payable Outstanding Formula
The days payable outstanding formula is,
Here,
- Accounts Payable: A short-term liability that is yet to be paid.
- Number of Days: The period over which the DPO is calculated. It could be either weekly, monthly, or annual.
- Cost of Sales: The sum of all expenses incurred for manufacturing a product that is worth selling. Usually, it includes raw materials, transportation, and rent costs. Also, any exceptional cost that occurs is also included in it.
Examples
Example #1
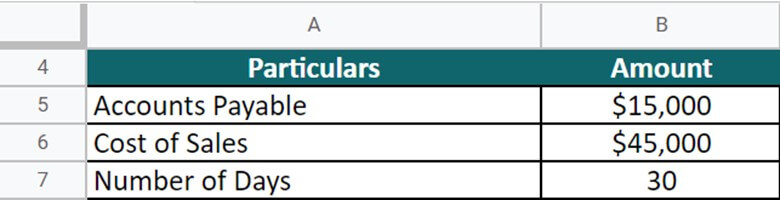
A coffee manufacturing company has an outstanding payable of $15,000, and the cost of sales in producing the coffee is $45,000. Calculate the DPO on a monthly basis (Days = 30).
Given,
Solution:
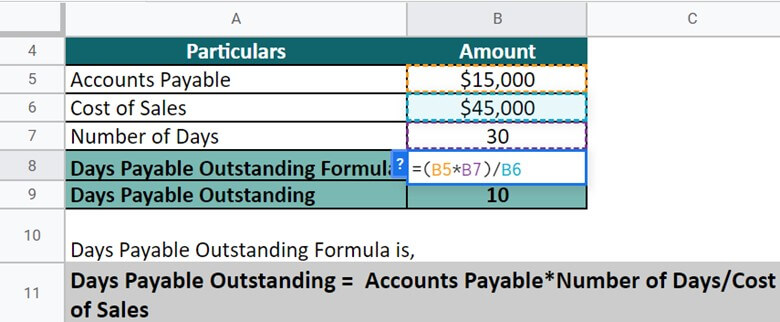
Implementing the formula, let’s calculate DPO for the coffee manufacturing company. Here, DPO = Accounts Payable*Number of Days/ Cost of Sales.
= $15,000 * 30 / $45,000 = 10
Thus, the DPO for the company is 10 which means the company takes 10 days to pay off the pending invoices.
Example #2
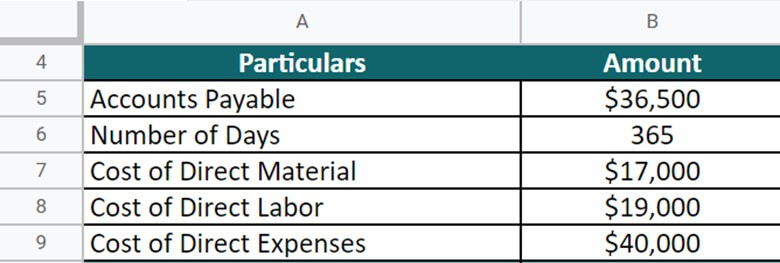
The Storylane Pvt. Ltd. company has an account payable of $36,500 at the end of FY 22.
The direct costs incurred are as follows:
- Material = $17,000
- Labor = $19,000
- Expenses = $40,000
Calculate the DPO on an annual basis (Days = 365).
Given,
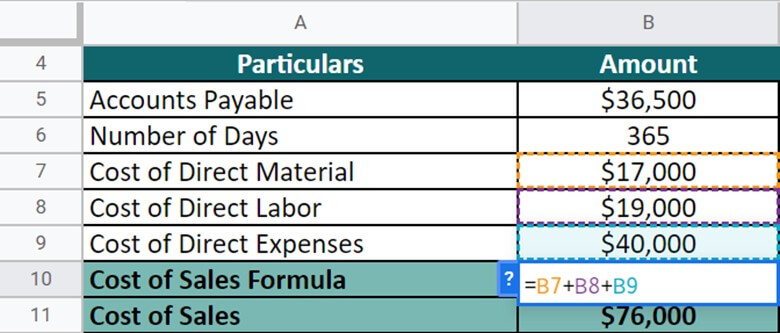
First, we will have to calculate the cost of sales by doing the sum of all the incurred costs.
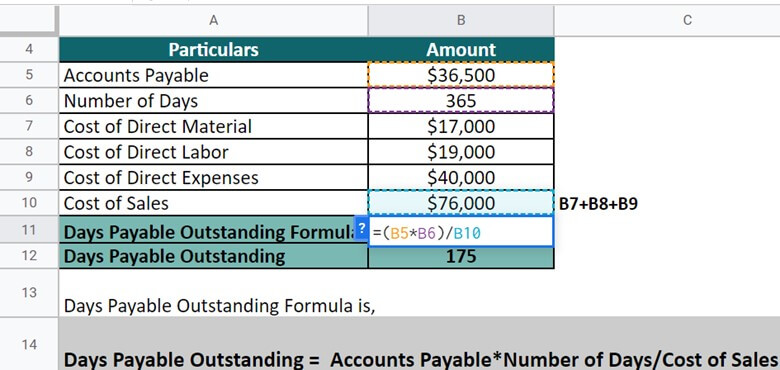
Now, by implementing the formula, let’s calculate the DOP for the company.
Here, DPO = Accounts Payable*Number of Days/ Cost of Sales.
= $36,500 * 365 / $76,000 = 175
Example #3
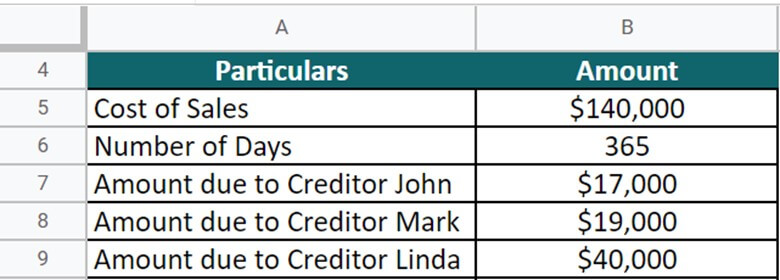
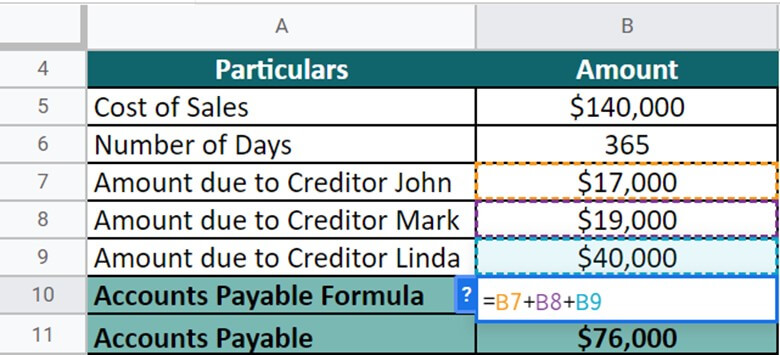
Smith Logistics is a company that is getting funded by the following creditors with the respective amount:
Amount due to Creditor
- John = $13,000
- Mark = $10,500
- Linda = $20,000
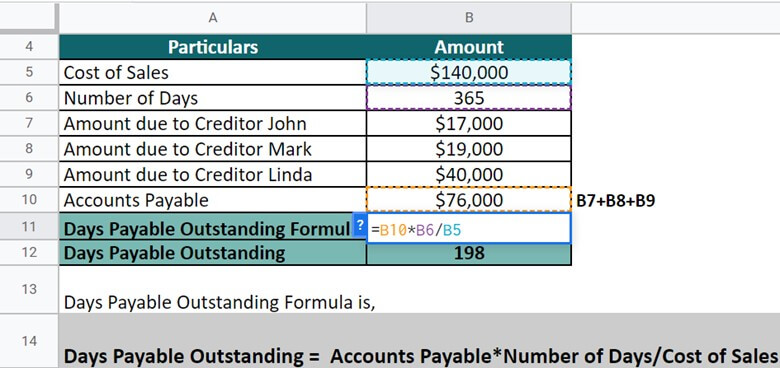
Moreover, the cost of sales during FY22 was recorded $140,000. Calculate the DPO for the upcoming year. (Days = 365).
Given,
First, we take a sum of all liable expenses to compute the accounts payable.
By putting the values, let’s calculate DPO for the company.
DPO = $76,000 * 365 / $140,000 = 198
Real-World Examples
#1 PepsiCo Inc.
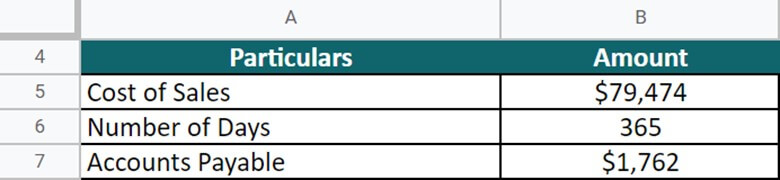
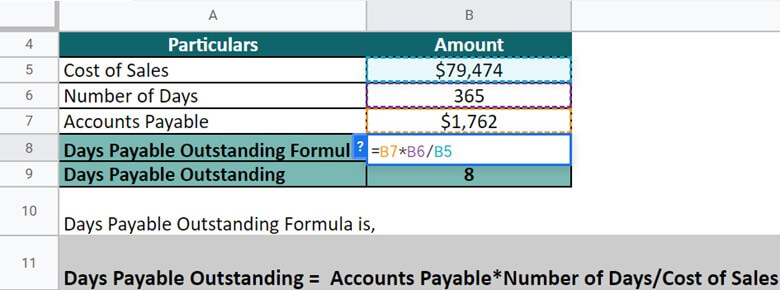
Let’s take the example of PepsiCo Inc. to understand the real-world concept of DPO. The cost of sales of the company in 2021 is $79,474, and accounts payable are $1,762. Calculate the DPO on an annual basis (Days = 365).
(Source: Annual Report of PepsiCo for FY21)
Given,
Solution:
DPO = $1,762 * 365 / $79,474 = 8
So, the DPO for PepsiCo is 8. The company is liable to pay off all its invoices after 8 days.
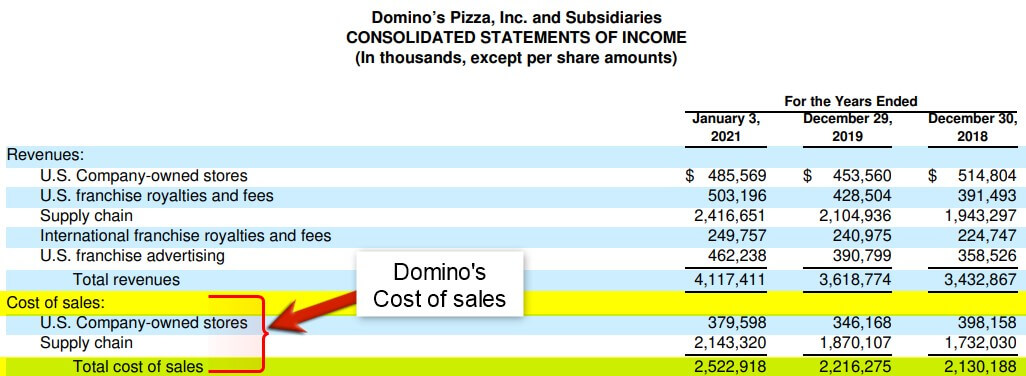
#2 Domino’s Pizza Inc.
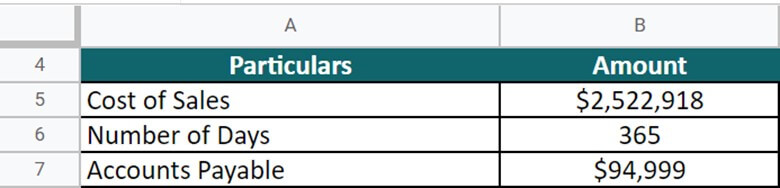
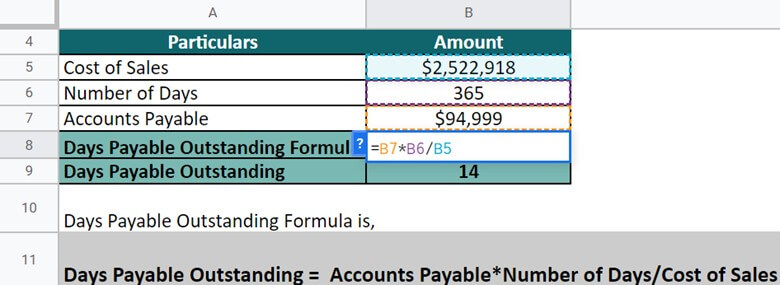
Let’s take the example of Domino’s Pizza Inc. to understand the real-world concept of DPO. The cost of sales of the company in 2021 is $2,522,918, and the accounts payable are $94,499. Calculate the DPO on an annual basis (Days = 365).
(Source: Annual Report of Domino’s for FY21)
Given,
Solution:
For calculating the DPO, we have to implement the following formula. DPO = Accounts Payable*Number of Days/ Cost of Sales. Putting the values, DPO = $94,999 * 365 / $2,522,918 = 14
Thus, the DPO of Domino’s Inc. is 14. This shows that the company is in a good state and can pay off all its invoices in 14 days.
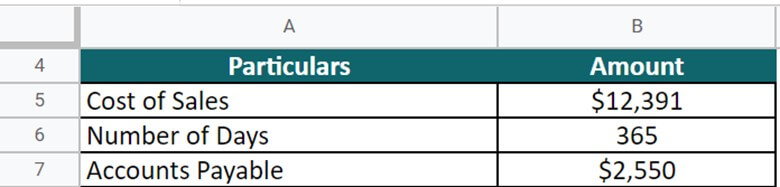
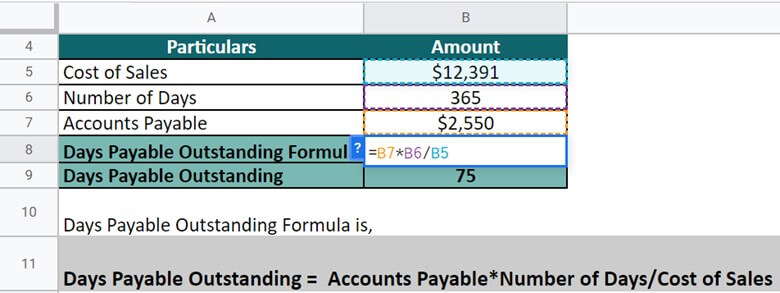
#3 AstraZeneca
Let’s take the example of AstraZeneca to understand the real-world concept of DPO. The cost of sales of the company in 2022 is $12,391, and the trade payable is $2,550 (the company has used this term interchangeably with accounts payable) Calculate the DPO on an annual basis (Days = 365).
(Source: Annual Report of AstraZeneca for FY22)
Given,
Solution:
DPO = $2,550 * 365 / $12,391 = 75
Thus, the result means that AstraZeneca has 75 days to utilize its credit in the company.
Days Payable Outstanding Calculator
Use the following calculator for Days payable outstanding calculations.
| Accounts Payable | |
| Number of Days | |
| Cost of Sales | |
| Days Payable Outstanding = | |
| Days Payable Outstanding = | (Accounts Payable x Number of Days) / Cost of Sales |
| = | 0 x 0 / 0 = 0 |
Days Payable Outstanding Interpretation
DPO is an important financial metric that companies should use to manage their cash flow effectively. Companies can compare their DPO with industry averages, the DPO of similar companies, Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), and Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) to get a better picture. This comparison can help analyze whether the company’s DPO is relatively supportive or needs improvement.
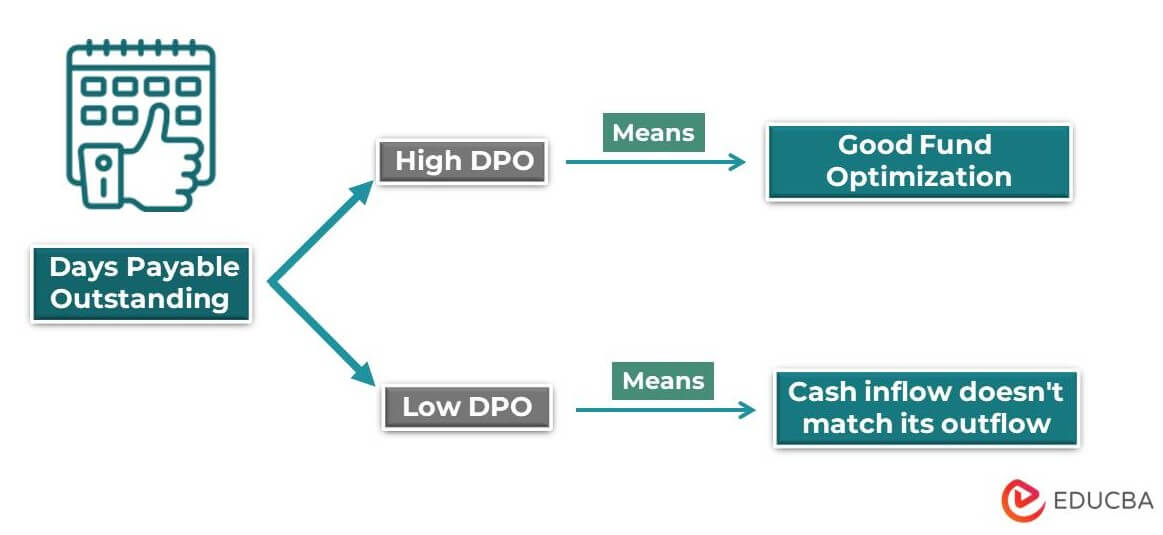
A high DPO is beneficial because it gives the company more time to use its capital. However, delayed payments can make suppliers lose trust in the company.
An extremely high DPO can mean the company doesn’t have enough funds. This can lead to strained relationships and loss of trust among these suppliers, making it difficult for the company to maintain its supply chain and operations. In the long run, this could negatively impact the company’s financial performance and overall success.
A low DPO means the company’s cash inflow (money from customers) doesn’t match its outflow (money to vendors), which can lead to poor financial management. It could also mean the company doesn’t have good relationships with its creditors, only making short-term payment deals.
Industry-wise DPO – Examples
#1 IT Industry Examples (2022-23)
| Company | Market Cap ($) | DPO |
| Apple | $2.35 T | 109 days |
| Microsoft | $1.88 T | 86 days |
| Alphabet | $1.1 T | 16 days |
| Amazon | $ 969.19 B | 63 days |
| AT&T | $136.96 B | 298 days |
#2 Automobile Industry Examples (2022-23)
| Company | Market Cap ($) | DPO |
| Volkswagen AG | $81.0 B | 47 days |
| Toyota Motor Corp. | $189.4 B | 50 days |
| Stellantis | $45.2 B | 39 days |
| Tesla | $435 B | 71 days |
| Ford Motor Co. | $46.1 B | 65 days |
#3 Airline Company Examples (2022-23)
| Company | Market Cap ($) | DPO |
| Delta Airlines | $23.78 B | 20 days |
| Air China | $22.79 B | 13 days |
| Ryanair | $20.97 B | 52 days |
| Southwest Airlines | $20.45 B | 42 days |
| United Airlines Holdings | $15.76 B | 35 days |
DPO and Cash Conversion Cycle
- Daya Payable Outstanding (DPO) and Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) are important financial metrics that relate to a company’s ability to manage its cash flow.
- The cash conversion cycle measures how long it takes to convert inventory into cash.
- The formula is, Cash Conversion Cycle = Days Inventory Outstanding + Days Sales Outstanding – Days Payable Outstanding
- A higher DPO can lead to a longer cash conversion cycle, while a lower DPO can lead to a shorter cash conversion cycle.
How to Improve Days Payable Outstanding?
Various factors affect DPO and can lead to its improvement.
- The company needs to align its short and long-term goals with the credit sale and purchasing. Once they coincide, the company can optimize and improve DPO.
- Every company can delay the payment to an extent. Paying right before the absolute payment date gives the company extra access to the capital.
- Choosing suitable suppliers is also an important aspect. The company should select vendors that provide longer durations, affordable pricing and agree on flexible terms.
- The company should always be in check with industry standards. Regularly compare the terms on an industry level and make changes if necessary.
- Having an up-to-date technology-equipped invoice processing system can be beneficial.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Days Payable Outstanding
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It helps companies manage their cash flow effectively | High DPO may lead to strained relationships with suppliers and vendors |
| Provides insight into how quickly a company pays its bills for goods and services purchased on credit | Delayed payments can damage the company’s reputation and affect business operations |
| Allows companies to compare their DPO with industry averages, and similar companies’ DPO, DSO, and DIO to identify areas of improvement | Extremely high DPO can indicate a lack of funds or poor financial management |
| High DPO can provide more time to optimize available capital | Low DPO can suggest inefficient use of available finances |
| Helps companies maintain control over their payables and ensures that they pay their bills in a timely manner | Low DPO may indicate suboptimal relationships with creditors and short-term payment arrangements |
Days Payable Outstanding vs. Day Sales Outstanding
| Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) | Day Sales Outstanding (DSO) |
| It represents the cash outflow of a company | Days sales outstanding (DSO) depicts the company’s cash inflow |
| It shows how often a business makes payments to the suppliers | It shows how many days it takes a business to receive payments from its customers |
| The high ratio value is considerably good, as the company has in-hand capital to invest in short-term | A low value is better as it signifies that the customers are fast to pay all their pending invoices |
| It uses accounts payable to calculate the ratio. | Accounts receivable is the primary metric this ratio is based on. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is days payable outstanding ratio? Is it good at high or low?
Days payable outstanding (DPO) measures the total days a company takes to clear all accounts payable payments. A higher ratio signifies a good fund strategy in place. However, DPO should not be too high as it can lead to bad supplier relationships.
What is a good payables turnover ratio?
A payables turnover ratio of 6 or higher is typically considered good, suggesting that a company pays off its accounts payable every two months or less. Anything less than six indicates that a company is extending its payment periods to finance its other activities. However, it’s important to note that this is just a general benchmark. A good payables turnover ratio can vary based on the industry, company size, and specific circumstances.
How to improve days payables outstanding?
Typically, to improve your DPO ratio, you must optimize your accounts payable first. By adopting a strategic strategy, you may simplify the processing of accounts payables, strengthen corporate cost control, and free up working capital to support and expand your business.
Can days payable outstanding be negative?
No, DPO cannot be negative. It denotes the days a business takes to fulfill supplier invoices, thus, it will always start with positive numbers.
How long can accounts payable be outstanding?
Generally, these periods differ due to businesses, vendors, and payable terms. However, the minimum period for DPO is 30 days (a month), lasting up to a maximum of 365 days (a year). Most businesses prefer not to cross this limit.
How to reduce days payable outstanding?
To reduce the DPO ratio, a company can follow these strategies:
- Negotiate longer payment terms with suppliers.
- Streamline the accounts payable process to avoid delays.
- Use electronic invoicing and payment methods to speed up transactions and reduce processing time.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Days Payable Outstanding. Here we discuss its meaning, formulas, calculations, and the difference between DSO and DPO. We give you the excel template and outline the advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through suggested articles to learn more,