What is a File System?
A file system is a method of storing files such as a hard disc, pen drive, DVD, etc. in the media. It lets you organize the data and enables the files to be readily available as needed. It typically consists of various types of files, such as mp3, txt, mp4, doc, etc. You can read and write data in the storage medium via a file system. It is installed directly on the computer with Windows and Linux operating systems. In this article, we will discuss the difference between DBMS vs File System.
What is DBMS?
The DBMS is a user data storage and recovery software that considers appropriate security measures. The database is manipulated through a group of programs. The DBMS acknowledges an application request for data and instructs the DBMS to provide the relevant data. A DBMS is used to store and retrieve data in major systems for users and other third-party software.
Head to Head Comparison between DBMS vs File System (Infographics)
Below the difference between DBMS vs File System:
Key Difference of File System and DBMS
Following are key differences between DBMS vs File System:
- True world knowledge does not file, it is objects. Apps map and handle the objects via the program into folders. A DBMS is designed for handling objects on the other side, which allows the program to directly control them without needing to add the object management code.
- DBMS secures the data from the system failures by providing a crash recovery mechanism whereas File system does not provide a crash mechanism.
- Most applications involve relationships between various object types. There’s no entity definition in file systems, so no relationship management capability. The DBMS is intended to create and maintain relationships between objects.
- Only the file system lock arbiter is used by different programs with the same file connection. When another lock unlocks, file systems don’t register waiting applications. The program eventually pools or handles data sharing through its code. A DBMS effectively handles simultaneous data entry, thereby allowing the application easier to access the data and better overall performance.
- Not index objects, file systems index files. The program needs to handle index information easily by accessing the objects via a file system. A DBMS handles indexing smoothly through database schemes for the program.
- In-house memory management and file-based data management is a difficult combination of real-time applications that involve complex memory and data management. RAM-based management of real-time data can be the only way to meet output needs.
- The file system does not allow complicated transactions, although complicated transactions using SQL can be conveniently enforced with the DBMS system.
Comparison Table of DBMS vs File System
Below is the topmost Comparison between DBMS and RDBMS.
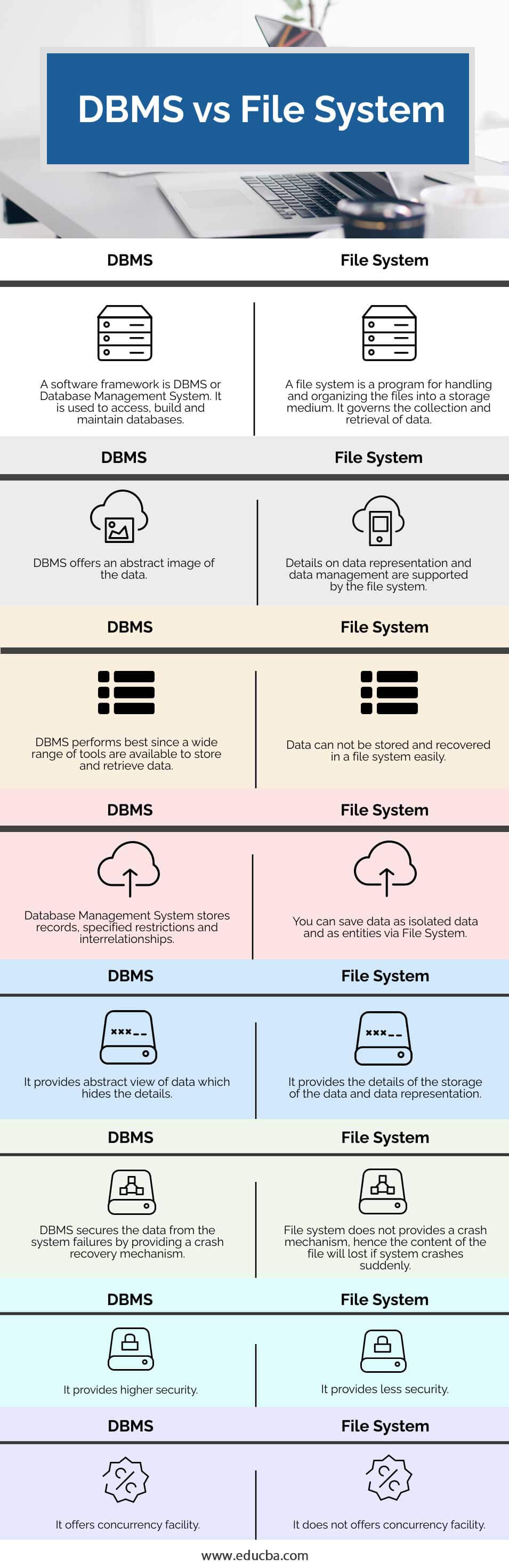
| Sr. No | DBMS | FILE SYSTEM |
| 1 | A software framework is DBMS or Database Management System. It is used to access, build and maintain databases. | A file system is a program for handling and organizing the files into a storage medium. It governs the collection and retrieval of data. |
| 2 | DBMS offers an abstract image of the data | Details on data representation and data management are supported by the file system. |
| 3 | DBMS performs best since a wide range of tools is available to store and retrieve data. | Data can not be stored and recovered in a file system easily. |
| 4 | Database Management System stores records, specified restrictions, and interrelationships. | You can save data as isolated data and as entities via File System. |
| 5 | It provides an abstract view of data which hides the details | It provides the details of the storage of the data and data representation |
| 6 | DBMS secures the data from the system failures by providing a crash recovery mechanism | The file system does not provide a crash mechanism, hence the content of the file will be lost if the system crashes suddenly. |
| 7 | It provides higher security | It provides less security |
| 8 | It offers a concurrency facility. | It does not offer a concurrency facility. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of File System vs DBMS
- The DBMS means limits on integrity that have a high degree of protection against prohibited data access. In some instances, it is more effective and less expensive than a DBMS.
- Data dependency in the file system depends on the data but the issue is not file format compliant. Many database management systems are also dynamic systems, which makes it important to teach people to use DBMS.
- Therefore, the same data may have to be processed and registered many times for each application. The hardware and development expenses of a DBMS are very high, which raises your company’s budget.
- DBMS provides different techniques to store & retrieve data and it follows Uniform administration procedures to manage data.
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen what is DBMS and File System along with key differences between them.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between DBMS vs File System. Here we also discuss the DBMS vs File System head to head comparison, key differences along with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-