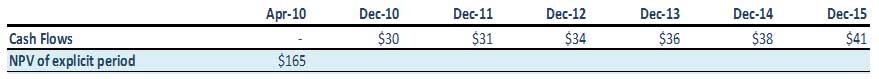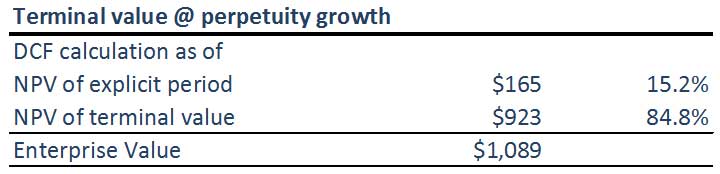Updated April 13, 2023
Part – 17
In our last tutorial, we understood equity value and sensitivity analysis. Now we will proceed to understand DCF Excel summary.
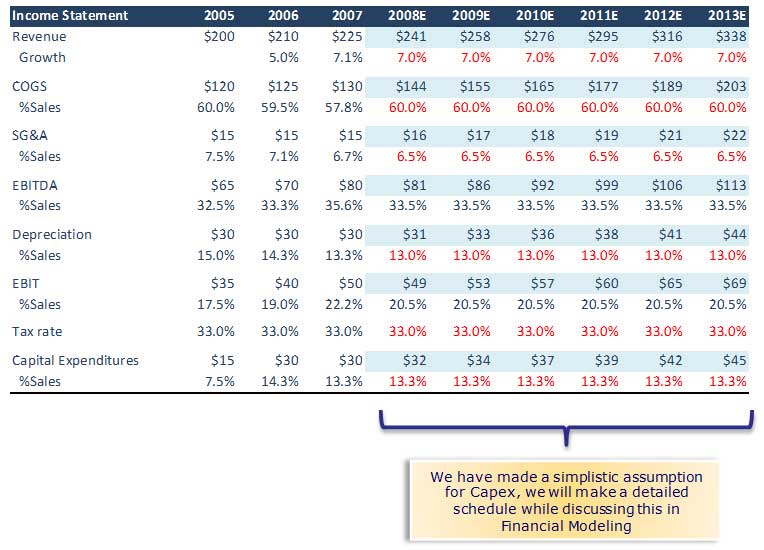
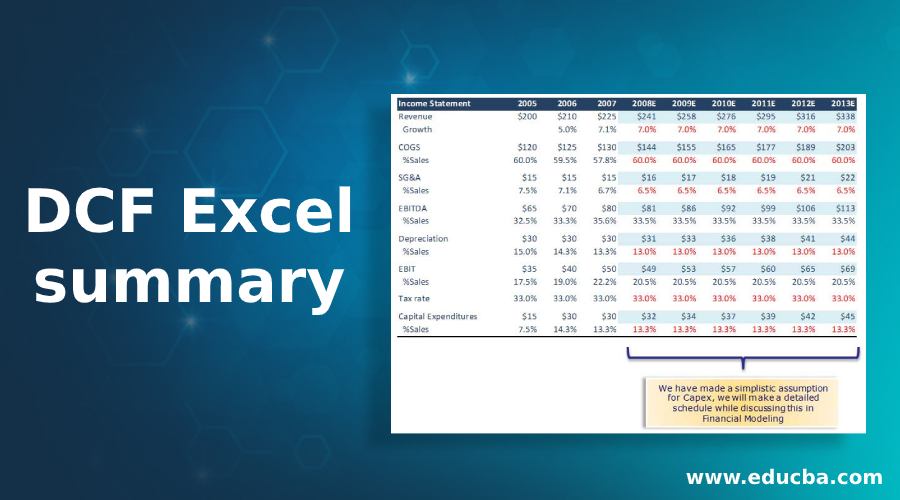
Step 1 – Forecast the Income Statement and other FCFF drivers for the Explicit Period
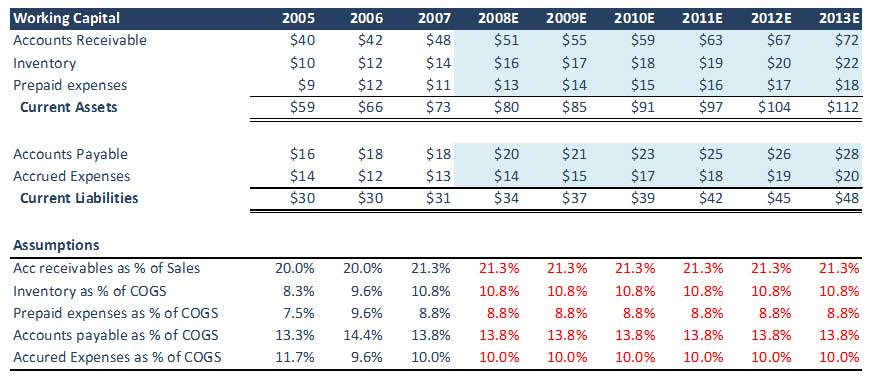
Step 2 – Forecast Working Capital
Here is the table:
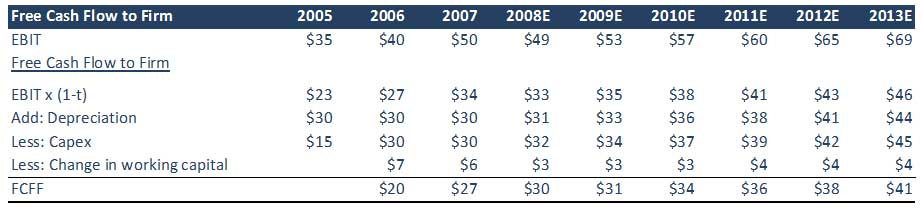
Step 3: Calculate FCFF using EBIT formula
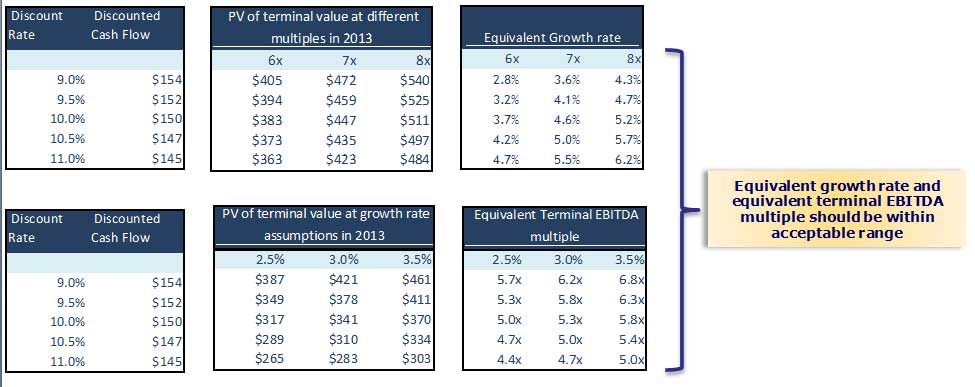
Step 4: Calculate Terminal Value
Method 1 – Perpetuity Growth Method
When WACC = 10% & Growth rate = 4.5%,
Method 2 – Exit Multiple Method
When the EBITDA transaction multiple is 7x,
Step 5: Terminal Value Reality Check of Assumptions
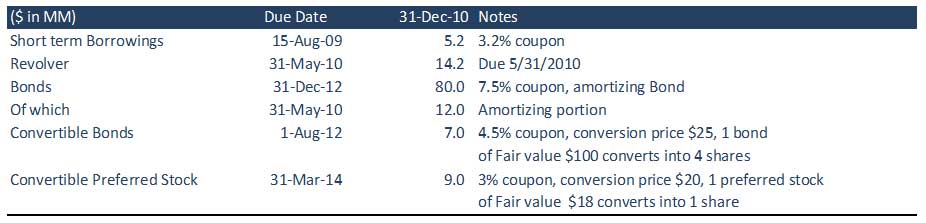
Step 6: Extract the Capital Structure
Please refer to the below image:
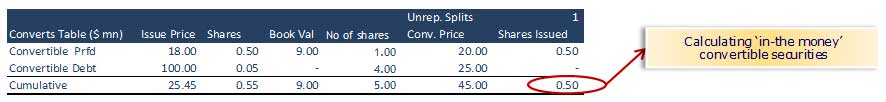
Step 7 – Understanding the Convertible Features: Calculate ‘in the money’ convertible securities
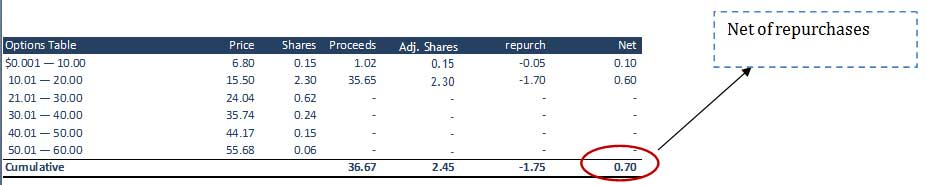
Step 8: Calculate ‘in the money’ stock options
Please refer to the below table:
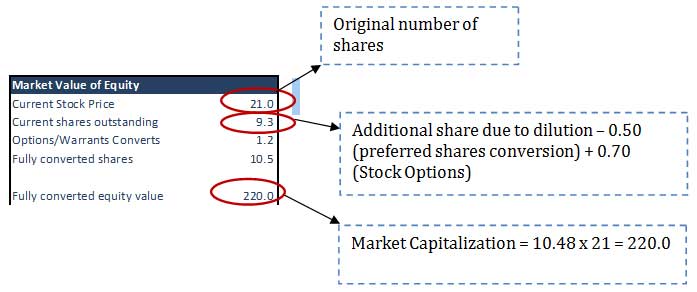
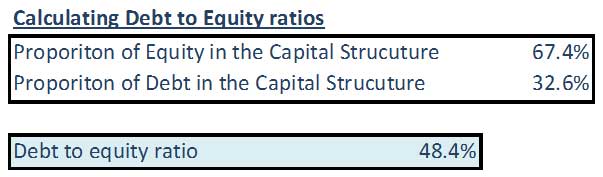
Step 9: Calculate the Value of Debt / Proportion of Equity & Debt in the Capital Structure
Debt
Total Capital = Debt + Equity
Total Capital = 220.0 + 106.4 = 326.4
The above proportions will be used to calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC).
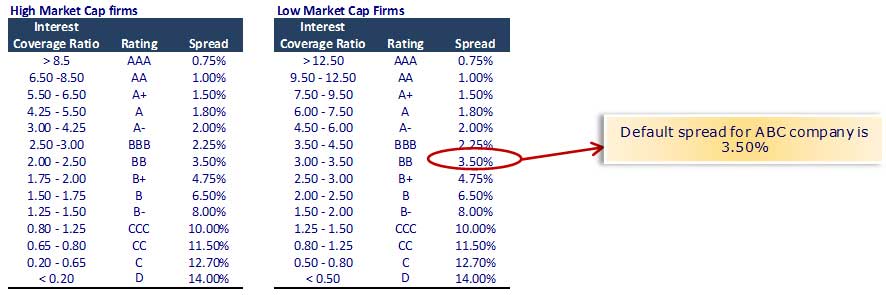
Step 10 – WACC: Cost Of Debt
Using the synthetic rating method, we have Interest coverage ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense
Interest Expense for ABC company (small cap $257million) is 15; Interest coverage ratio = 50/15 = 3.33
Pre-tax Cost of Debt = Risk-free rate + default spread = 5.0% + 3.50% = 8.50%
Post-tax cost of debt = 8.50% × (1-33%) = 5.70%
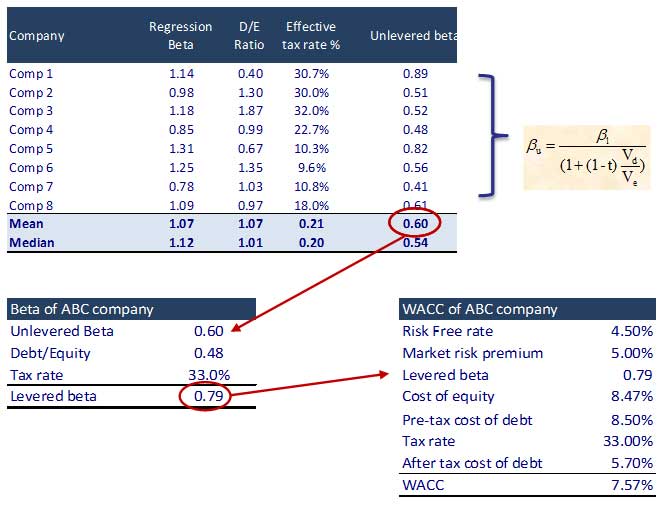
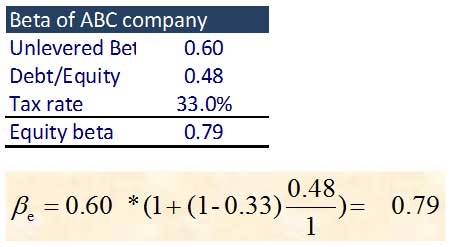
Step 11 – Calculate Cost of Equity & WACC
Identify the listed comparables and their Beta. Also, find the Unlevered Beta for comparables
Step 12: Present Value of the FCFF for the projected years
Calculate the Present Value of the Explicit Cash Flows using WACC derived above
Step 13: Calculate the Present Value of the Terminal Value using WACC
(A) Terminal Value using Perpetuity Growth Method
(B) Terminal Value using Exit Multiple Method
Please note that the Terminal Values from both approaches are not in sync. We may have to double-check our assumptions on EBITDA Exit Multiples or the WACC/growth rate assumptions applied. Both approaches should ideally give similar answers.
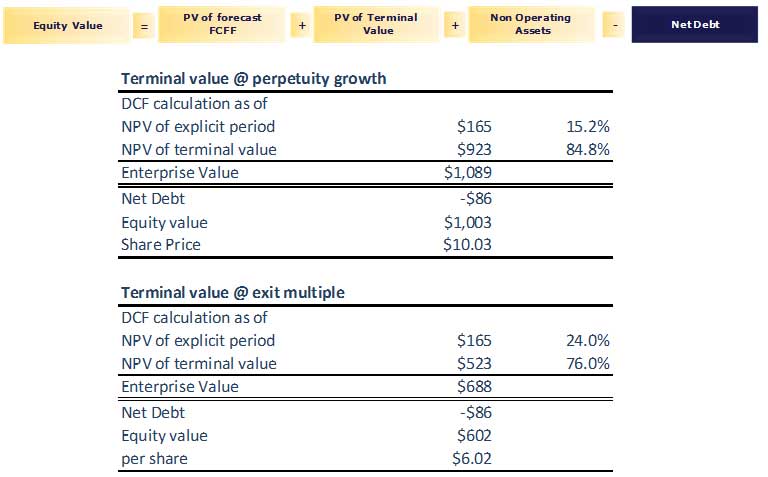
Step 14: Calculate the Enterprise value of the firm
By summing the (adjusted) present value of the projected free cash flows and the (adjusted) present value of the terminal value (whether calculated using the perpetuity method or multiple method), the result is the Enterprise Value of the modeled business.
Step 15 – Arrive at the Equity Value of the firm post Adjustments
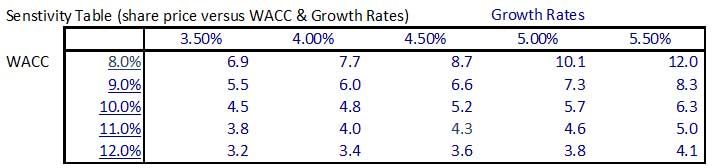
Step 16: Sensitivity Analysis of Key Inputs
The data table function is especially useful for conducting Share Price Sensitivity Analysis
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles that will help you to get more details about the DCF Excel summary: