Updated March 14, 2023
Difference between Debian and Arch
In this topic, we will learn about the difference between Debian vs Arch with the introduction, key differences and head-to-head comparison table, which is provided below.
Debian
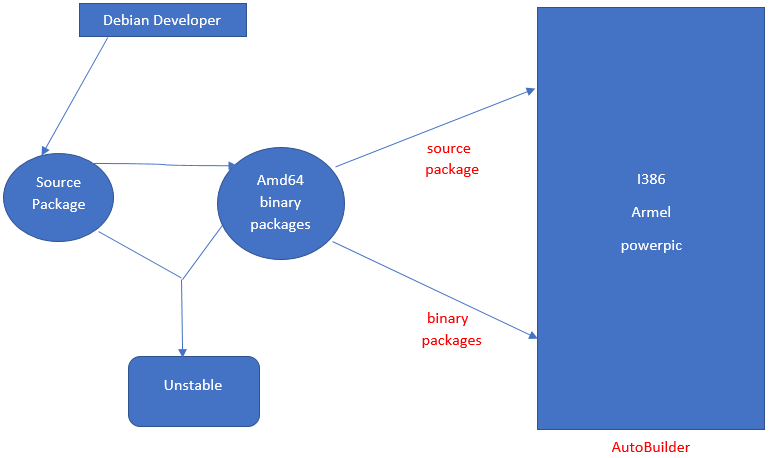
Debian is a GNU/Linux distribution, open-source and is a Linux kernel-based operating system. It was released in August 1993. Debian can access online repositories containing more than 50000 packages; you can also download free or not free software and install them to Debian. APT is the front-end package manager, and the kernel type is monolithic. The Debian installer is modular and generic. The developers’ community provides proper support for bug fixing, and there is a proper channel from fixing to uploading the patch.
The figure below shows the approach followed –
Arch
Arch Linux is an x86-64 general-purpose GNU/Linux distribution. It is simple and doesn’t add unnecessary modifications or additions; the patches that are not supported by upstream are avoided. Packages are split only when compelling advantages exist. GUI configuration utilities are not encouraged, and users have to perform system configuration from the shell editor. Arch maintains stable release versions until no package break is recorded. Arch includes the init system, modern file systems, LVM2, udev support, and initcpio.
Head to Head Comparison between Debian and Arch (Infographics)
Below is the Top 12 Comparison between Debian vs Arch
Key Differences between Debian and Arch
Below are the lists of points, describe the key differences between Debian vs Arch:
- Debian is simpler than the arch, and for a novice, its easy and favourable to stick forward with Debian than an arch.
- Debian installation steps are as follows –
- Boot and start the installer via means of any CD/DVD; you can choose for install or graphic install or for Intel or AMD processor-based machines; the message will appear like 64-bit install or 64-bit graphics install.
- Then select the language.
- Select the country
- Select the keyboard layout
- Then the installer would do the hardware detection, and it loads modules to various hardware components.
- Hardware network detection, this is also an automated step where the hardware network card gets recognized, and modules are loaded into it.
- Network configuration is done then via DHCP; this also is an automatic process.
- Administrator password, root-password is asked by the system.
- Then the user can be configured.
- Then partitioning, RAID, etc., tasks are to be done.
- Then base installation happens in which the apt tools and dpkg tools are installed; then the apt package manager has to be configured.
- Then the installation of the GRUB bootloader is done.
- Then it finishes up, and after rebooting, you have your Debian setup.
It would help if you visited https://www.debian.org/releases/ to have installation manuals for detailed info; they are present in multiple languages.
For more details, please visit –
3. Arch installation steps are as follows –
- Download the ISO from the official site
- Create USB of Arch
- Boot from that USB
- Then disk partitioning and clock setting is the next step.
- The keyboard layout is set then.
- Boot mode is to be verified.
- Connect to the internet to check for network interface and configure the network connection
- Format the partitions and mount the file systems.
- Select mirrors for installation
- Install base packages then.
- Configure fstab, Chroot, Time zone, Localization, network configuration, initramfs, root password, boot loader.
For scripts, please refer to the official website.
- Arch is a pragmatic distribution.
- In the arch, the user is offered the ability to build a custom system by choosing among thousands of high-quality packages
- Debian releases live install images for CDs, DVDs, and USBs with a choice of desktop environments
- In the arch, the following repositories are there –
- Core
- Extra
- Community
- Multilib
- Testing
- Community-testing
- Gnome-unstable
Debian vs Arch Comparison Table
below is the topmost comparison between Debian vs Arch:
| S.No |
Debian |
Arch |
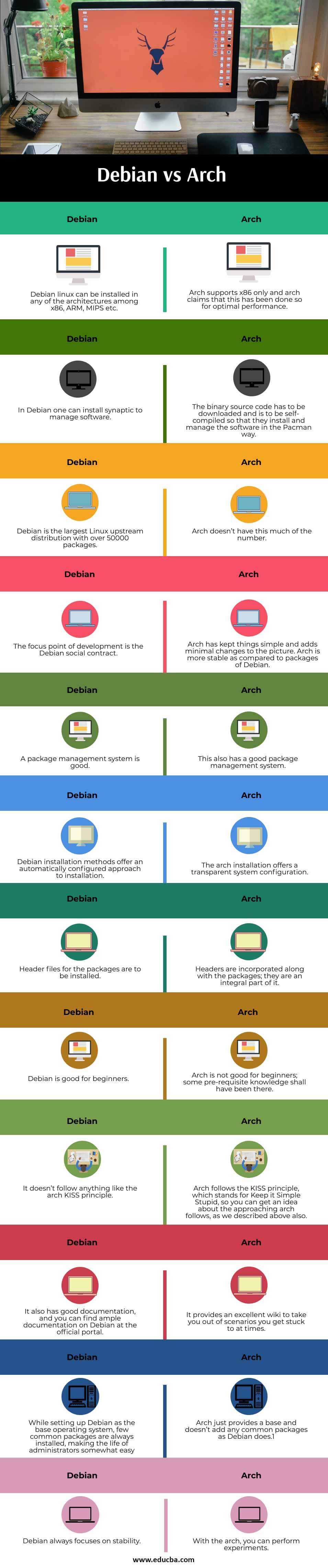
| 1. | Debian Linux can be installed in any of the architectures among x86, ARM, MIPS, etc. | Arch supports x86 only, and arch claims that this has been done so for optimal performance. |
| 2. | In Debian, one can install synaptic to manage software. | The binary source code has to be downloaded and is to be self-compiled so that they install and manage the software in the Pacman way. |
| 3. | Debian is the largest Linux upstream distribution with over 50000 packages. | Arch doesn’t have this much of the number. |
| 4. | The focus point of development is the Debian social contract. | Arch has kept things simple and adds minimal changes to the picture. Arch is more stable as compared to packages of Debian. |
| 5. | A package management system is good. | This also has a good package management system. |
| 6. | Debian installation methods offer an automatically configured approach to installation. | The arch installation offers a transparent system configuration. |
| 7. | Header files for the packages are to be installed. | Headers are incorporated along with the packages; they are an integral part of it. |
| 8. | Debian is good for beginners. | Arch is not good for beginners; some pre-requisite knowledge shall have been there. |
| 9. | It doesn’t follow anything like the arch KISS principle. | Arch follows the KISS principle, which stands for Keep it Simple Stupid, so you can get an idea about the approaching arch follows, as we described above also |
| 10. | It also has good documentation, and you can find ample documentation on Debian at the official portal. | It provides an excellent wiki to take you out of scenarios you get stuck to at times. |
| 11. | While setting up Debian as the base operating system, few common packages are always installed, making the life of administrators somewhat easy | Arch just provides a base and doesn’t add any common packages as Debian does.1 |
| 12. | Debian always focuses on stability. | With the arch, you can perform experiments. |
Conclusion
We analyzed the key differences between the Debian vs arch systems, and the mentioned points above could give enough idea on which system you can look forward to adapting with, based on the expertise you have.
Although novice can head with Debian and after years of experience in Linux, you can head with the arch as it offers options for customization is multiple ways.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Debian vs Arch. Here we also discussed the key differences with infographics. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-