Updated July 17, 2023
Definition of Deferred Annuity
A deferred annuity is a mechanism to supplement retirement income. It is a contract between the insurance company and the buyer. The buyer has to make a regular contribution towards the annuity plan and can receive the return as a monthly income or as a lump sum after retirement.
Explanation
It further bifurcates into two phases, i.e., the investment and income. The investment phase begins when the buyer makes a contribution or a lump sum contribution in the annuity plan and continues until their last contribution. And income phase begins after investors’ retirement, from when they start receiving the monthly income or lump sum, whichever option they have chosen.
The contribution to the deferred annuity is allowed for taxation purposes, but the IRS (internal revenue service) taxes the return. If the investors have to avoid the penalty of 10% on early withdrawal, they will have to wait 59.5 years before withdrawing anything. In case of the investor’s death, the beneficiary will get the remaining funds in the annuity.
How Does It Work?
Below is the step wise step explanation of how it works:
- Step 1 is the agreement between the insurance company and the buyer.
- Step 2: The buyer must make a regular or one-time lump sum contribution to the annuity.
- Step 3: After retirement, investors can receive regular monthly income and a lump sum benefit, or they can annuitize their annuity fund to receive periodic payments till death.
- Step 4: The contribution to the annuity fund is allowed for taxation purposes, but the income received after retirement is taxed by the IRS (Internal revenue service.)
- Step 5: The buyers use the annuity plan as a supplementary retirement income.
Formula
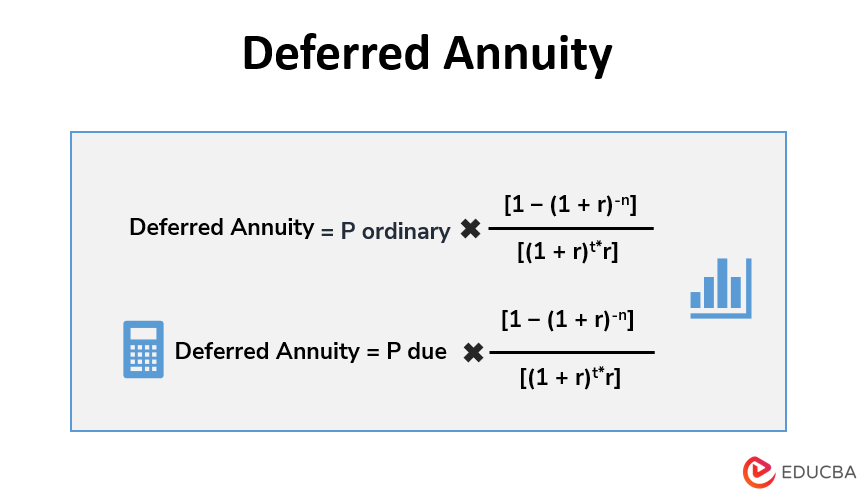
A deferred annuity based on an ordinary annuity, i.e., payment is made at the end of each period, is as follows:
Where,
- P ordinary = ordinary annuity payment
- r = Effective Interest rate
- n = No. of Periods
- t = Deferred Periods
Deferred annuity based on the annuity due, i.e., where the payment is made at the start of each period, is as follows:
Where,
P due = Annuity payment due
The rest is the same as above.
Example of Deferred Annuity
For example, an investor purchased a deferred annuity in which he has to invest $90,000 and will get 30 payments of $9,000 each annually post-retirement. The effective interest rate is 4.5%, and the no. of the period after which the annuity payment will start is 10.
Deferred Annuity = $9,000 * [1 – (1 + 4.5%)-30] / [(1 + 4.5%) 10 * 4.5%]
| Particular | Value |
| Payment in a year | 1 |
| P(ordinary) | 9,000 |
| The effective rate of interest (r) | 5% |
| No. Of deferred period (t) | 10 |
| no of the period (n) | 30 |
| Deferred Annuity | 94,399.80 |
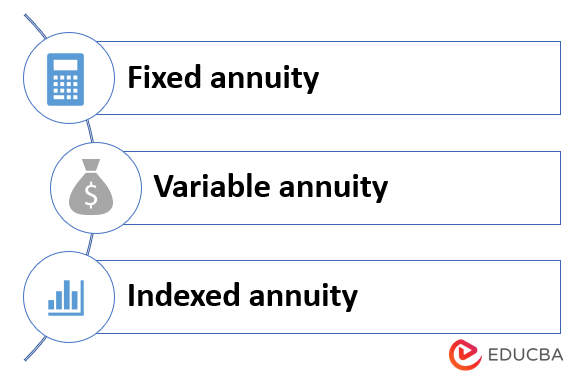
Types of Deferred Annuity
There are three types of it:
- Fixed annuity: The interest rate is fixed and never changes in this type. But it has a lower return rate than other types of annuities.
- Variable annuity: In this type of annuity, the funds are invested in various investment options like stocks, bonds, etc. It provides a potentially higher return rate and is also associated with increased risk.
- Indexed annuity: In this annuity, the minimum rate of return is guaranteed like in a fixed interest annuity, but the rate can go up, determined by the market index.
Uses
Some of the uses are below:
- It serves as a supplementary retirement income.
- The annuity can a buyer get tax benefits on the contribution payment on a deferred annuity.
- The buyer can enjoy the peace of regular monthly income if that is what they choose through the deferred annuity option.
Advantages
Some of the advantages are below:
- The contributions towards deferred annuity payments are allowable for tax benefit purposes.
- There is no annual contribution limit for price towards the deferred annuity.
- The buyer can receive a monthly steady income post-retirement or a lump sum after retirement.
- It helps buyers comfortably plan their retirement.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are below:
- The return of the deferred annuity post-retirement is taxable.
- If a person withdraws the money before a stipulated period, they must give a 10% penalty.
- The annuity providers charge hefty commissions when selling the funds to the investors.
- Some deferred annuities have high annual fees for their maintenance purpose.
Conclusion
The crux of the matter is that it is a perfect option to enhance retirement income and helps in planning life after retirement. Though it does have some minus points like every other thing in the world, its very purpose and benefits overshadow the impact of disadvantages or limitations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Deferred Annuity. Here we also discuss the definition and how it works, along with its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –