Updated July 14, 2023

Definition of Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue (also known as “unearned revenue”) is that part of the revenue against which the customer already receives advance. Still, the service provision is yet not completed, or the risk & rewards in the ownership of goods are not yet transferred to the customer.
They are presented as a company liability in its balance sheet. In this topic, we will see different examples of deferred revenue.
Explanation
- “To defer” means “postp””e”. So, the” term deferred revenue refers to the revenue that does not belong to the current year under consideration but to future years.
- Since the company is yet to perform its obligation (of sale of goods or provision of service), it is treated as a liability in its balance sheet.
- Books are maintained on are accrual basis of accounting. Hence, receipt of advance is not to be treated as revenue. Instead, it is advance revenue, which the company has not yet earned. Thus, it is also known as unearned revenue.
- We can also say that if the company fails to perform its obligations in the near future, it can refund the advance received earlier without impacting its profits.
- As and when the company delivers its goods or renders its services, the unearned revenue is treated as earned revenue and shown as revenue of the entity.
- Let’s havLet’sook at how accounting entries are routed for the treatment of deferred revenue:
Step 1: Receipt of advance
| Bank Account (Debit) | $ 400,000 |
| Deferred Revenue Account (Credit) | $ 400,000 |
Step 2: Transfer of advance to Deferred revenue account
| Customer Account (Debit) | $ 400,000 |
| Deferred Revenue Account (Credit) | $ 400,000 |
Step 3: After completion of performance obligations, the revenue is recognized
| Deferred Revenue Account (Debit) | $ 400,000 |
| Revenue Account (Credit) | $ 400,000 |
In step 3, the revenue is recognized.
Examples of Deferred Revenue
We will use different examples of deferred revenue to deal with the different aspects each time.
Example #1
Let’s conLet’s the following extract of the balance sheet of a company:
| Liabilities | December 2018 ($) | December 2019 ($) |
| Deferred Revenue | 12,50,000 | 17,15,000 |
Explanation
The deferred revenue above has a “net” inc”eas” of $ 465000. The net increase means the net impact of an increase on receipt of more advances during the year & a decrease on account of the recording of revenue from the deferred revenue account.
The net amount of increase signifies the following:
- Receipt of advance from the customer
- Confirmation of sales order
- Least chance of sales return
- Lower risk in the realization of revenue
- No hurdles in the booking of the revenue as soon as performance obligations are performed
- The increased liquidity position of the company
- Reduction in the finance cost of the company shortly.
- Good corporate image since it reflects the customer’s confidence in the company’s procompany’sred revenue incocompany’sxt year.
Example #2
Say a company manufactures water filters. The production capacities are as follows:
| The capacity of production (in a month) – in units | 15,000 |
| Already occupied capacity as of 21st December 2019 – in units | 14,200 |
| Price per unit | $225 |
| Discounted Price for orders above 50 | $200 |
Say another company order 25000 units for its plants all over the country. It needs the supply in lots of 800 units & is ready to wait until all orders are delivered. It has made full payment at a discounted rate.
The company closes its books on December 31, 2020.
Solution:
| Units to be supplied in December 2020 | 800 |
| Balance to be supplied in January 2020 | 24200 |
| Revenue for 800 units (since max capacity reached for December 2020) | $ 1,60,000 |
| Deferred Revenue (24200* $ 200) | $ 48,40,000 |
On the date of receipt of the order (22nd December 2020)
| Bank Account (Debit) | $ 50,00,000 |
| Deferred Revenue (Credit) | $ 50,00,000 |
On the delivery of 800 units (31st December 2020)
| Deferred Revenue Account (Debit) | $ 1,60,000 |
| Revenue (Credit) | $ 1,60,000 |
| The net amount of Deferred Revenue is to be shown as a liability | $ 48,40,000 |
Explanation
- The amount of $ 4840000 is shown as deferred revenue (current liability) in its balance sheet as of 31st December 2020.
- As soon as the company delivers the next lot of water filters, it will make an invoice for the same & will adjust the deferred revenue account accordingly to reflect the revenue earned by the company.
- Say the company sold 9 lots in January 2020 and will record the sale of 800*9 = 7200 units at $ 200 each. This will adjust the deferred revenue account by $ 14,40,000.
- This goes so and forth till all orders are delivered.
Example #3
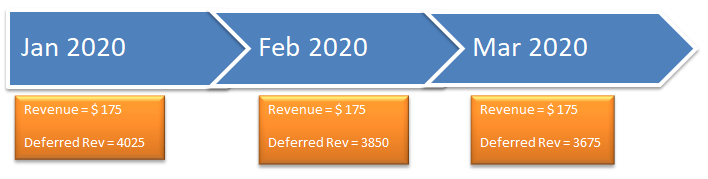
We can consider a classic example of the subscription business of magazines. In this business, the amount is the receipt in advance usually. Most readers pay the full amount at the start of the year.
The monthly subscription cost of the magazine is $ 225. Say a customer subscribes to a 2-year plan of the magazines for $ 4200. The Price is discounted for a long-term plan. The magazine seller will start providing the magazines as soon as the payment is received and the balance of 23 magazines as and when the same is published.
Thus, it will record monthly revenue of 4200/24 = $ 175 each.
On the date of receipt of the money
| Bank Account (Debit) | $4,200 |
| Deferred Revenue (Credit) | $4,200 |
On the sale of each magazine
| Deferred Revenue (Credit) | $175 |
| Revenue (Credit) | $175 |
Explanation
- We can pictorially present the data as follows:
- As and when the magazines are sold, the revenue is recorded, and the deferred revenue (liability) decreases.
- In the end, the deferred revenue becomes NIL, and the whole revenue is recorded, ensuring the sale of all magazines.
Example #4
Say a company provides services on a contract basis & it takes the full amount in advance. The company also assures its services through a refund mechanism wherein it will refund the amount for that month in case services are not provided.
Say the rate of a one-year contract is $10500. On January 1, 2020, the company records a receipt of $ 10500. As and when services are performed, it raises invoices to the party & adjusts the deferred revenue account.
On January 1, 2020
| Bank Account (Debit) | $ 10,500 |
| Deferred Revenue (Credit) | $ 10,500 |
At the end of each month
| Deferred Revenue (Credit) | $875 |
| Revenue (Credit) | $875 |
Explanation
- We can see the change recording of revenue through each month based on the following:
| Months | Revenue ($) | Cumulative Revenue ($) | Deferred Revenue ($) |
| 0 | – | – | 10,500 |
| 1 | 875 | 875 | 9,625 |
| 2 | 875 | 1,750 | 8,750 |
| 3 | 875 | 2,625 | 7,875 |
| 4 | 875 | 3,500 | 7,000 |
| 5 | 875 | 4,375 | 6,125 |
| 6 | 875 | 5,250 | 5,250 |
| 7 | 875 | 6,125 | 4,375 |
| 8 | 875 | 7,000 | 3,500 |
| 9 | 875 | 7,875 | 2,625 |
| 10 | 875 | 8,750 | 1,750 |
| 11 | 875 | 9,625 | 875 |
| 12 | 875 | 10,500 | – |
- So, it is clear that as soon as the risk & rewards are transferred, the revenue is recognized in completeness.
Conclusion
The theme line is that
“How can you own something which “you have not earned!”
This is the logic behind “reati “g such advances as deferred revenue instead o” real revenue. The realization of money is different from the accrual of the same. The books are maintained on an accrual basis & hence, you can only realize something accrued. This is important for companies that are engaged in the recurring supply of goods or recurring provision of services. As soon as the deliveries are completed, a company can recognize the revenue already received.
On the other hand, advance receipt of revenue improves the company’s liquidity position. A company can also manage its payables in a good manner & it can stay unexposed to the risk of doubtful debts. It will also help a company to reduce its financing costs to a greater extent.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Deferred Revenue Examples. Here we also discuss the definition and different examples of deferred revenue along with an explanation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –