What is Demand-Pull Inflation?
Demand-pull inflation refers to a rise in prices when the demand for products increases more than their supply.
For example, during the economic depression of 2008, banks started taking mortgage-backed securities, which increased the demand for and price of housing in the USA.
When there is a rise in demand for goods, the prices rise. It significantly impacts businesses, as it affects the cost of doing business. As the cost of goods and services rises, companies may have to raise their prices to remain profitable. It can cause prices to go up for consumers, hurting demand and slowing economic growth.
Key Highlights
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds the supply, leading to higher prices.
- Governments can increase taxes, reduce government spending, or raise interest rates to combat inflation.
- Proactive measures, such as diversification and hedging against inflation, can help businesses protect their bottom line from the adverse effects of inflation.
- Governments must work to ensure that policies are in place. These policies help to contain inflation while also promoting economic growth.
Examples
#1. Rise in Oil Prices
Inflation that happened due to the rise in global oil prices in 2022 has significantly impacted the cost of production for many businesses. Therefore, companies have to raise their prices to keep up with the rising costs of materials and labor, increasing overall consumer prices.
#2. CoronaVirus
After 2020, people began to receive corona vaccine, and countries began to reopen. It led to a sharp increase in the demand for goods. Despite this, the factories had an inventory shortage due to the global shutdown, because of which supply could not keep up with demand, which led to inflation.
#3. Global Events
The Russia-Ukraine war in 2022 increased the cost of essential resources like oil and gas because there aren’t as many around. It led to a rise in the prices of goods and raw materials. Thus, increasing costs, meaning consumers and businesses had to pay more.
#4. Government Policies
In 2019 Sri Lanka went through an economic crisis because of increased taxes. The government had put restrictions or taxes on certain products, increasing the prices—as a result, leading to higher levels of inflation. Poor government policies can also lead to inflation.
Demand-Pull vs. Cost-Push Inflation
|
Demand-Pull Inflation |
Cost-Push Inflation |
| Demand-pull inflation happens when the demand for goods & services outruns the supply. | Cost-push inflation happens when production costs increase, leading to an increase in prices. |
| It leads to an increase in prices as more people bid for the same goods & services. | An increase in wages, taxes, or the cost of raw materials can cause this. |
| It is more likely to affect consumer goods. | Cost-push inflation is more likely to affect businesses and industrial production. |
| This imbalance increases prices, as people are willing to pay more for the limited available goods. | This imbalance increases prices, as people are willing to pay more for the limited available goods. |
Effects
- In the general economy, it leads to higher prices, slower job growth, and decreased purchasing power.
- In specific markets, it can lead to shortages of certain goods and services and wage inflation as businesses compete for scarce resources.
- Ultimately, inflation can have a destabilizing effect on the economy, and governments need to keep a close eye on economic indicators so that they can take action when necessary.
- Inflation is an economic phenomenon that occurs when an imbalance exists between the demand and supply of a good or service.
- This imbalance causes the worth of the good or service to rise, increasing the overall price level in the economy.
- The effects of inflation can be both positive and negative.
- On the one side, it can lead to increased economic activity, higher salaries, and greater job security.
- It can lead to higher prices, reduced purchasing power, and increased inequality. In addition, inflation can cause currency devaluation and lead to higher interest rates.
- Thus, while inflation can have some positive effects, its adverse effects should be considered when making economic policy decisions.
Causes
Increased Money Supply
- One fundamental cause of inflation is an increased money supply faster than the economy’s growth.
- When the value of a currency weakens against that of another, it makes imports more expensive and increases the cost of producing goods in an economy.
- It can increase prices as producers pass these additional costs to consumers.
Speculation
- Investors who speculate on an asset, such as stocks or commodities, often bid up their prices due to increased demand.
- It can raise prices in the broader economy as producers pass on these higher costs to consumers.
Demand-Pull Inflation Graph
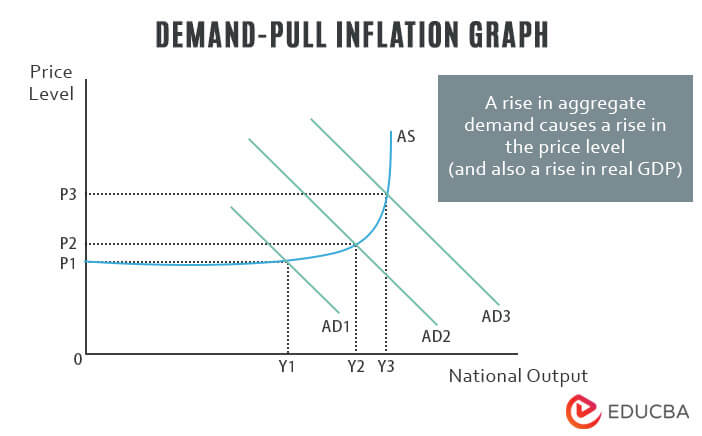
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when total demand increases faster than aggregate supply.
- This graph illustrates how it works.
- The green line represents aggregate demand, and the blue line represents aggregate supply.
- As you can see, when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, prices rise due to increased competition among consumers for scarce resources.
Advantages of Demand-Pull Inflation
- It can offer significant advantages to businesses looking for sustained economic growth.
- Inflation creates a healthy environment for businesses to thrive by stimulating aggregate demand through increased spending.
- Inflation allows businesses to invest and expand without fear of deflation, as the economy will always have a strong level of demand. It encourages companies to innovate, as they can expect their products and services to sell well.
- Moreover, with increased wages due to higher prices for goods & services, businesses can benefit from an influx of consumer spending.
- Overall, inflation helps create a favorable economic climate for businesses, leading to increased profits and sustained economic growth.
- Additionally, inflation helps reduce unemployment levels by creating more jobs. With a higher level of aggregate demand in the economy, businesses are more pressured to hire additional employees, thus providing more people with jobs and a source of income.
Disadvantages of Demand-Pull Inflation
- Higher Prices – When there is an increase in overall demand, prices tend to rise, which can strain businesses’ budgets and reduce their potential profits.
- Increased Interest Rates – Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation, making it more difficult for businesses to borrow money and finance their operations.
- Lower Purchasing Power – With prices increasing, customers have less purchasing power, decreasing demand for products and services and reducing business sales.
- Uneven Distribution of Wealth – Inflation tends to disproportionately benefit those with higher incomes, while those with lower incomes struggle more to cope with the rising prices. It can lead to an uneven distribution of wealth, damaging businesses and the economy as a whole.
- Reduced Savings – With prices rising more quickly than wages, it can be difficult for people to save money, leading to reduced consumer spending and decreased revenue for businesses.
- Decreased Investment – Inflation can also lead to decreased investment in businesses due to uncertainty and higher interest rates, reducing their ability to grow and expand.
Final Thoughts
Demand-pull inflation is a crucial concept to understand regarding economic trends. Businesses must be aware of this trend and how it can affect their bottom line. For a business to stay competitive and make money, it is essential to take proactive measures such as adjusting prices or changing production methods. These measures can help a company keep going during inflation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is demand-pull inflation?
Answer: Demand-pull inflation is an economic phenomenon that happens when an imbalance exists between the demand and supply of a good or service.
Q2. Why does demand-pull inflation occur?
Answer: This type of inflation happens due to factors like increased consumer spending, increased money supply, or government spending. Global factors can also cause demand-pull inflation, like a drop in the number of imported goods or a rise in the price of raw materials. Demand-pull inflation always happens when there aren’t enough goods and services to meet the higher demand.
Q3. What is demand-pull inflation also called?
Answer: Demand-pull inflation is also known as price inflation. It happens when the total demand exceeds the total supply. It is the most common cause of inflation.
Q4. How is demand-pull inflation controlled?
Answer: The government uses monetary and fiscal policy to reduce demand-pull inflation. On the economic side, a central bank can raise interest rates or reduce the money supply to reduce demand. On the fiscal side, the government can raise taxes or reduce government spending to reduce the need.
Government policies that boost productivity and supply can also help ease inflation pressure. For example, infrastructure, education, and technology investments can help improve the economy’s ability to produce goods and services while reducing the stress of inflation.
Recommended Articles
We hope that you found this EDUCBA information on Demand-Pull Inflation very helpful. For further guidance on inflation-related topics, EDUCBA recommends these articles.


