What is Descriptive Research?
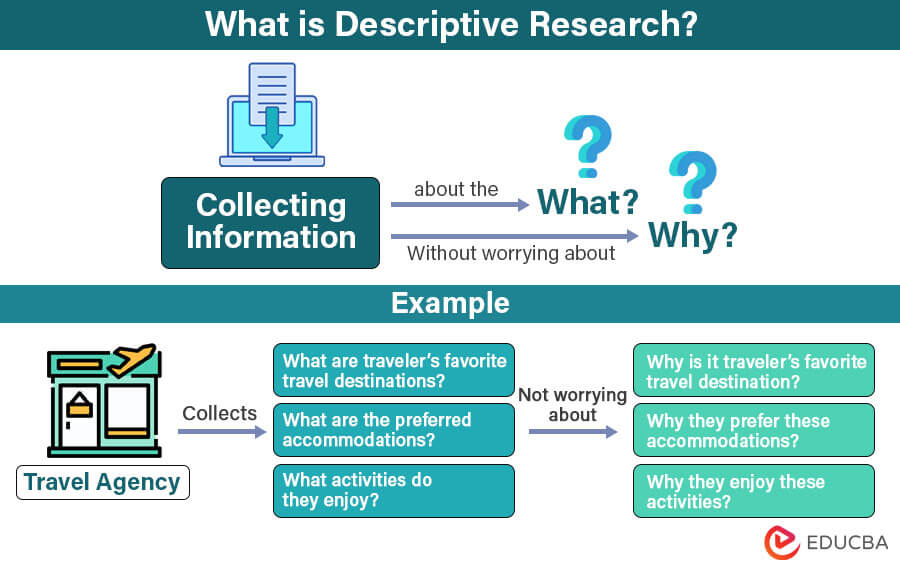
Descriptive research is a methodology that focuses on explaining “what” is happening in a given situation, problem, or phenomenon. It only describes and understands a specific topic without explaining the reasons behind whatever is happening. It provides information about the characteristics and behaviors but doesn’t give in-depth knowledge of the causes or reasons for those behaviors.
For example, a travel agency wants to gain information about the travel preferences of its customers. They interview a sample of customers and only collect the “what” part of the data, like what are their favorite travel destinations, what accommodations they prefer, and what activities they enjoy. The agency does not collect any information about why the customers prefer those destinations, accommodations, and activities.
Table of Contents
Purpose – Why Perform Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a type of research methodology that only collects data related to “what,” then why do researchers use this research? Here are some of the key purposes of this research:
- Describing Characteristics: It helps in providing a detailed and objective description of a group, event, or object, giving a clear picture of the topic.
- Finding Relationships: Although it doesn’t explain any causes or reasons, it can help make connections or find relationships between different factors.
- Identifying Trends: Researchers can use it to spot patterns or changes over time, helping them understand shifts in a particular area of interest.
- Foundation for Analytical Research: It gathers foundational data before more in-depth research or experiments, helping analytical researchers.
- Creating Profiles: This research helps create profiles of individuals or groups, capturing their characteristics, which is useful in understanding specific populations.
- Market Research and Decision Making: It aids businesses in analyzing consumer behavior, market trends, and customer preferences using AI marketing tools. This helps them to make informed decisions, especially when it comes to small business ideas
- Guiding Policies: Policymakers and organizations use it to do planning and make decisions based on objective data and evidence.
If you need research paper help for your descriptive research projects, experts at All Essay Writer can assist you with comprehensive and detailed writing support.
#3: Sleep Habits and Technology Use
Sleep researchers may conduct surveys or studies to describe how technology usage before bedtime affects people’s sleep quality and duration. This research is particularly relevant in the context of modern technology’s impact on sleep patterns.
Data Collection Methods of Descriptive Research
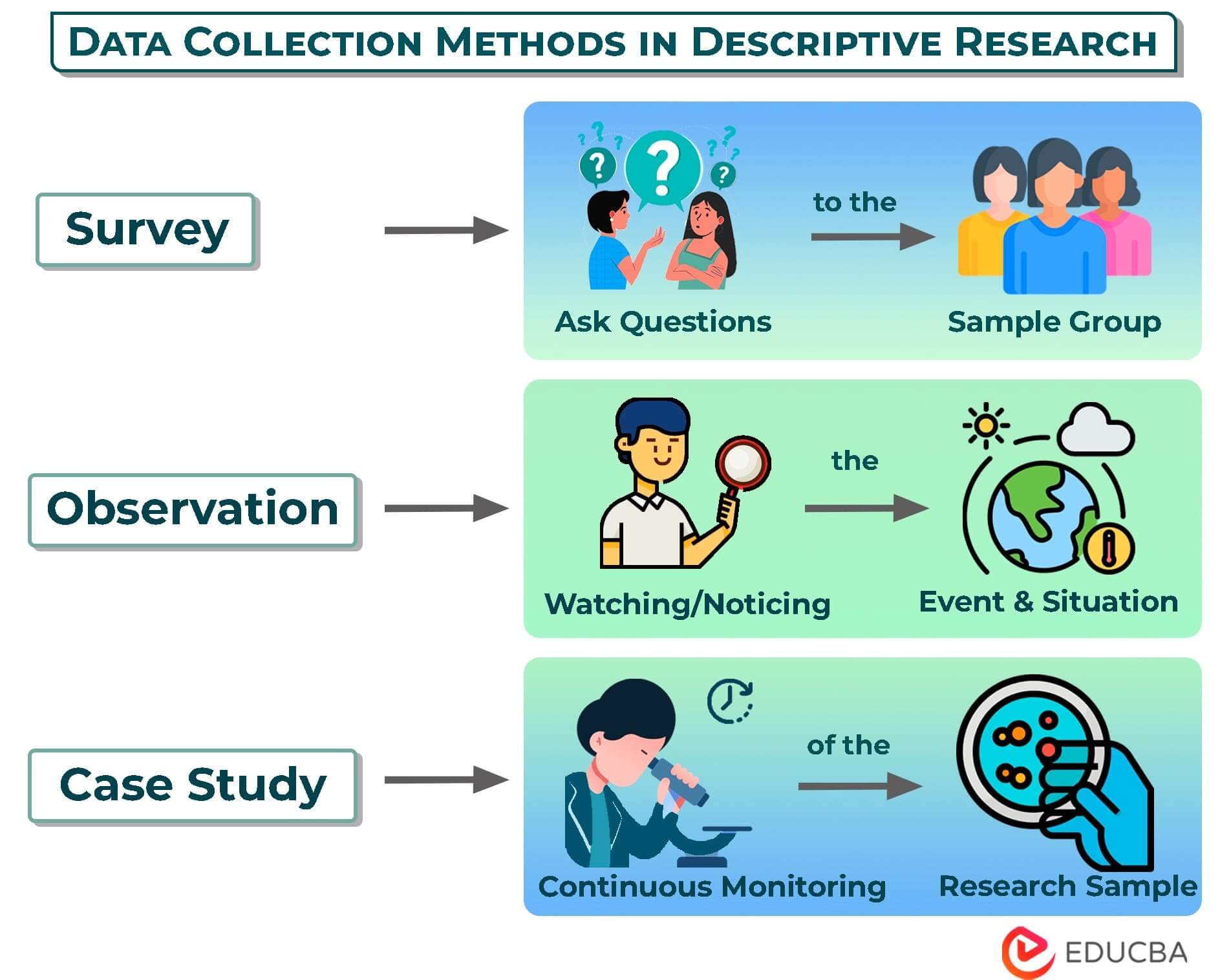
1. Survey Method
- Surveys involve gathering data from a sample of individuals or groups through structured questionnaires or interviews.
- They help collect information on opinions, attitudes, behaviors, and demographics.
- Researchers can use surveys in various formats, such as online surveys, face-to-face interviews, telephone interviews, or mailed questionnaires.
2. Observation Method
- Observation involves simply looking at the behavior and characteristics of individuals or groups and recording the observations.
- Researchers may be unobtrusive observers, meaning they can remain hidden and not interact, or participant observers, meaning they engage with the subjects.
- Observations can provide valuable insights into real-life behaviors and contexts.
3. Case Study Method
- In a case study, the researcher studies a single individual, group, or organization over a period.
- Researchers gather data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, to comprehensively understand the case.
- Case studies are beneficial when investigating unique or rare phenomena and providing in-depth insights into complex situations.
How to Conduct Descriptive Research?
Step 1: Choose your Research Topic
Pick a subject you want to study and define what you want to learn about it. Make sure it’s something you can realistically investigate and relevant to your field of interest.
Step 2: Read Existing Studies
Look at what others have already researched about your topic. It will help you understand the subject better, find gaps in knowledge, and refine your research questions.
Step 3: Decide how to Collect Information
Decide how you will gather information. You can use surveys, questionnaires, interviews, observations, case studies, or analyze existing data. Choose the method that suits your topic best.
Step 4: Choose Your Sample
Pick a group representing the larger population, so your findings can apply to more people. Also, make sure to use random or stratified sampling to avoid bias.
Step 5: Gather and Organize the Data
Collect information following your chosen method. Be careful and accurate in recording the data. You can collect data in person, online, or through other appropriate ways. Finally, arrange your data in an organized manner.
Step 6: Draw Conclusions
Look at what you found in your data analysis. Explain the key findings and what they mean. Based on your findings, come to conclusions that answer your research questions. Relate your results to what others have found in previous studies.
Step 7: Share Your Results
Write a detailed report with an introduction, what others have studied before, your methods, findings, and conclusion. Use tables, graphs, and visuals to make it easier to understand.
Dr. Richard selects the volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands as the subject of his study. He aims to find out why these volcanoes erupt and what makes them different from other volcanoes.
Step 2: Finding and Studying Existing Research
Dr. Richard seeks research paper help and reads many books and research papers about the volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands. He looks at old records and talks to other experts to learn more about these volcanoes.
Step 3: Deciding which Methods to Use
He decides to use the observation method to collect data. He also carries several measuring tools to assist with the data collection.
Step 4: Selecting a Sample
Dr. Richard wants to study different types of volcanoes to understand them better. So, he picks a few different volcanoes to study in the Hawaiian Islands.
Step 5: Collecting the Required Data
Dr. Richard goes to the Hawaiian Islands to study the volcanoes and observes them closely. He also uses tools to measure shaking on the ground caused by volcanic activity.
Step 6: Arriving at Conclusions
After studying the data, Dr. Richard records all the information collected about the volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands and explains their behavior.
Step 7: Sharing the Research Findings
Dr. Richard writes a report with all the information he finds. He shares this report with other scientists, government agencies, and environmentalists.
Advantages
- Provides a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the subject
- Suitable for exploring new topics
- Doesn’t invade people’s privacy
- Findings can often apply to a larger group
- Time and cost-effectiveness compared to other research types.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a hypothesis in descriptive research?
Answer: In descriptive research, a hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables. For example, a hypothesis could be “People who post more than three times a day on social media have 20% more followers than those who post less frequently.” This hypothesis describes the connection between posting frequency on social media and the number of followers.
Q2. Is descriptive research design qualitative or quantitative?
Answer: The nature of a descriptive research design can be either qualitative or quantitative. In qualitative research, researchers collect non-numerical data to gain in-depth insights. On the other hand, in quantitative research, researchers collect numerical data to summarize and describe the subject of study.
Q3. What is descriptive research also known as?
Answer: Descriptive research is also known as hypothesis-generating research. Here, researchers observe and describe a phenomenon without changing any variables. It helps them gather important information and acts as a starting point for more in-depth studies.
Recommended Articles
This article was a comprehensive guide to the descriptive research methodology. We discussed its characteristics, examples, advantages and disadvantages, and more. You may read some similar articles given below: