Introduction to Digital vs Physical Games
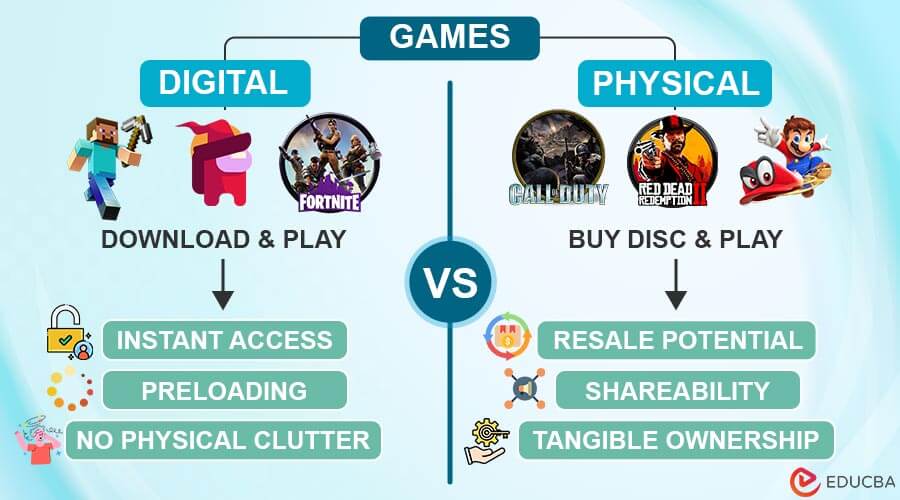
The gaming community is actively engaged in a fascinating debate regarding the merits of digital and physical game formats, which center on convenience and ownership. Digital games offer unparalleled ease of acquisition through online platforms and downloads, granting immediate access. On the other hand, physical games hold a certain nostalgic charm for some gamers, with tangible discs or cartridges fostering a sense of ownership and a unique interactive experience. These physical copies can also be resold, traded, or lent among friends, further enhancing the social aspects of gaming, but they lack the immediate accessibility of digital downloads.
Table of Contents
Digital vs Physical Games – Convenience
Digital Games
Pros:
- Instant Access: Digital games offer immediate access upon purchase, allowing players to download and start playing without any delays associated with physical delivery.
- No Physical Visits: Online platforms’ convenience enables gamers to access an extensive library of titles from their homes, eliminating the need to travel to physical stores.
- Multi-Device Access: Digital games are often associated with user accounts, enabling players to access their purchased games across various devices, including consoles, PCs, and mobile devices, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Preloading: Players can preload highly anticipated games before their official release dates, ensuring they’re ready to play when the game becomes available, minimizing wait times, and maximizing gaming time.
- No Physical Clutter: Unlike physical game discs or cartridges, which require storage space, digital games store themselves electronically, saving physical space and reducing clutter in gaming environments.
Cons:
- Internet Dependency: While digital downloads offer convenience, they require a stable internet connection for downloading and playing, rendering them inaccessible in areas with poor connectivity.
- Storage Space: Digital games can consume significant storage space on devices, especially with larger game files or extensive collections, necessitating regular management to free up space.
- Account Reliance: Digital games often tie to user accounts, which can pose risks such as potential loss of access if accounts are compromised or the platform ceases operation.
- Limited Resale Value: Digital games typically need more physical copies. Similarly, players cannot resell or trade them., reducing potential returns on investment.
- Licensing Issues: Ownership rights for digital copies may be subject to licensing agreements, potentially resulting in issues with access or ownership if agreements change or platforms close down.
Physical Games
Pro:
- Tangible Ownership: Holding physical copies provides a tactile sense of ownership and collection, appealing to collectors and enthusiasts who appreciate the physicality and nostalgia associated with physical media.
- Collectors’ Appeal: Physical game packaging often includes artwork, manuals, and other collectible items, enhancing the overall experience and appeal for collectors interested in preserving gaming history.
- Shareability: Physical games can be easily shared, traded, or lent to friends and family, fostering social interactions and community building among gamers.
- Resale Value: Physical copies retain resale value and can be sold or traded in the second-hand market, offering potential returns on investment compared to digital copies.
- No Internet Requirement: Once installed, physical games do not require an Internet connection, ensuring access even in offline environments, such as during Internet outages or traveling.
Cons:
- Time-Consuming Acquisition: Acquiring physical games often involves visits to physical stores or waiting for delivery, which can be time-consuming compared to the instant access provided by digital downloads.
- Risk of Damage: Physical discs or cartridges are susceptible to damage, scratches, or loss, potentially compromising gameplay or requiring replacements, which can be costly.
- Storage Space: Accumulating physical game cases can take up physical space in homes or storage units, especially for avid collectors with extensive game libraries.
- Limited Availability: Due to limited market availability, older or rare physical copies may become scarce or expensive, making them challenging for collectors or enthusiasts to obtain.
- Environmental Impact: The production of physical discs and packaging contributes to ecological waste, making physical games less environmentally friendly than digital downloads, which have minimal physical footprints.
Cost
Digital Games
Pros:
- Lower Production Costs: Digital games eliminate the need for physical production, distribution, and retail markup, often resulting in lower prices than physical copies.
- Frequent Sales and Discounts: Online platforms frequently offer sales, discounts, and bundle deals for digital games, allowing players to save money on purchases.
- Convenience of Pricing: Digital storefronts often provide transparent pricing and easy comparison options, making it simpler for players to find the best deals.
- No Additional Costs: Digital games eliminate additional expenses such as shipping fees or taxes typically associated with physical purchases, potentially saving players money in the long run.
- No Risk of Damage or Loss: Since digital games are stored electronically, there is no risk of damage, loss, or theft, protecting the player’s investment.
Cons:
- Diminished Resale Value: Digital games typically lack resale or trade-in options, preventing players from recovering their investment by selling used copies.
- Internet Expenses: Digital downloads require a reliable internet connection, potentially resulting in additional expenses from internet service providers or data usage charges.
- Storage Constraints: Digital games’ sizable file sizes can consume considerable device storage, prompting the need for supplementary storage solutions and potentially incurring extra costs.
- Platform-Specific Purchases: Players might be required to procure games separately for different platforms (e.g., PlayStation, Xbox, PC), potentially leading to duplicate purchases and heightened expenditures.
- Subscription Costs: Certain digital gaming platforms charge subscription fees for access to game libraries, multiplayer features, or additional content, which contributes to the overall cost of gaming.
Physical Games
Pros:
- Resale Potential: Physical copies enable resale, trading, or lending, allowing players to regain some of their expenditure.
- Collector’s Worth: Unique physical releases or scarce editions have the potential to increase in value over time, presenting investment opportunities for collectors.
- Independence from the Internet: Physical games operate without reliance on Internet connectivity, ensuring uninterrupted access, even in offline scenarios, without additional costs.
- Communal Use: Physical copies facilitate shared enjoyment among friends or family members, allowing multiple individuals to engage with the same game without incurring extra expenses.
- Possible Price Reductions: Though less frequent than digital sales, physical editions may undergo price reductions, particularly for older or less popular titles.
Cons:
- Higher Production Costs: Physical games incur production, distribution, and retail markup costs, which are often higher than those of their digital counterparts.
- Limited Discounts: Physical game sales and discounts may be less frequent or substantial compared to digital counterparts, limiting opportunities for savings.
- Risk of Damage or Loss: Physical discs or cartridges are susceptible to damage, loss, or theft, potentially requiring replacements or repairs at additional costs.
- Space Requirements: Accumulating physical game collections can require significant storage space, potentially necessitating additional storage solutions such as shelves or cabinets.
- Acquisition Inconvenience: Acquiring physical copies may involve trips to physical stores or waiting for delivery, which can be time-consuming and entail additional costs such as transportation or shipping fees.
Ownership & Sharing
Digital Games
- Ownership Model: Digital games are often subject to licensing agreements rather than traditional ownership, meaning players may have limited rights to the content they purchase.
- Sharing Mechanism: Some digital platforms allow for limited sharing through family sharing features or account logins on multiple devices, enabling sharing among a select group of individuals.
- Portability: Digital libraries can be accessed from any device with internet connectivity, offering gamers convenience.
- Resale Restrictions: Players generally cannot resell or trade digital games, limiting their ability to share or transfer ownership of their games.
Physical Games
- Ownership Model: Players typically acquire full ownership rights to the physical copy when purchasing physical games. In contrast, licensing agreements often govern digital games.
- Sharing Flexibility: Physical copies offer greater flexibility for sharing, trading, or lending among friends or family without the restrictions commonly imposed by digital platforms.
- Offline Access: Physical games offer the advantage of being playable without an internet connection, ensuring access even in offline settings and expanding sharing opportunities.
- Resale Opportunities: Players can maintain the resale value of physical games and sell or trade them in the second-hand market, enabling them to exchange or transfer ownership of their games.
Digital vs Physical Games – Storage and Resale
Digital Games:
- Storage Method: Digital games are stored digitally, residing on devices like computers, consoles, or mobile devices or within online accounts linked to digital storefronts. This storage method eliminates the necessity for physical discs or cartridges, streamlining the gaming process.
- Space Requirements: Although digital games save physical space by eliminating the need for tangible media, they can demand significant digital storage space on devices. Large titles or extensive game collections can swiftly consume hard drives or cloud storage, necessitating efficient management of digital libraries.
- Convenience: Digital games provide the convenience of immediate access and download, enabling players to purchase and commence gameplay without awaiting physical delivery or visiting physical stores. This aspect of convenience is particularly appealing to gamers seeking instant enjoyment.
- Account Integration: Digital games are frequently associated with user accounts, allowing players to access their game libraries across multiple devices. This integration facilitates seamless transitions between devices, ensuring game accessibility regardless of the player’s location.
- Security: Digital games, stored electronically, provide enhanced security against physical harm, loss, or theft. Concerns regarding damaged discs or misplaced cartridges that could impact the gaming experience are alleviated.
Physical Games:
- Storage Medium: Tangible discs or cartridges house physical games, requiring physical storage space like shelves, cabinets, or storage units. Enthusiasts often proudly showcase their physical game collections, contributing to the visual appeal of gaming setups.
- Tangible Ownership: Possessing physical game discs or cartridges grants players a palpable sense of ownership. This physical connection can enrich the gaming experience, particularly for collectors or enthusiasts.
- Collector’s Value: Certain editions of physical games, such as limited releases or special editions, may appreciate over time, rendering them sought-after collector’s items. Collectors may actively pursue rare or distinctive physical copies to augment their collections.
- Sharing and Trading: Physical games afford greater flexibility for sharing, trading, or lending among acquaintances or family members. Players can pass physical game discs or cartridges to others, enabling them to partake in the game without acquiring their copy.
- Resale Opportunities: Physical games retain value over time and can be resold or traded within the secondary market. This resale potential allows players to recoup a portion of their initial investment or finance future gaming acquisitions by selling or trading their physical game assortments.
Difference between- Digital vs Physical Games
| Environmental Impact | Digital Games | Physical Games |
| Waste Reduction | Eliminates physical production, distribution, and disposal of discs or cartridges, reducing environmental waste. | Physical games do not directly contribute to electronic waste; they do not rely on electronic devices for storage or distribution. |
| Energy Efficiency | It requires less energy than physical manufacturing and transportation processes, lowering carbon emissions and energy consumption. | It requires minimal energy consumption for distribution, not involving electronic downloads or online services. |
| Lifespan Extension | It has an indefinite lifespan because storing it electronically reduces the need for frequent replacements or upgrades, contributing to resource conservation. | They can become collectible items, extending their lifespan and reducing the likelihood of disposal. |
| Transportation Emissions | Users cannot resell or trade it, limiting the lifecycle and potential for reuse. | Users can resell or trade in the second-hand market, extending their lifecycle and reducing the need for new production. |
Conclusion
To weigh the merits of digital versus physical games, one must consider various factors: convenience, cost, ownership, environmental impact, and more. Digital games provide instant access and environmental benefits, while physical games offer tangible ownership and potential resale value. The choice between digital and physical gaming experiences depends on personal preferences, gaming habits, and environmental considerations. Nevertheless, both formats contribute to the gaming landscape, serving diverse player needs and preferences. As gaming continues to evolve, digital and physical games remain essential components, ensuring a vibrant and inclusive gaming community.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Which is cheaper, digital or physical games?
Answer: Digital games often offer lower prices due to reduced production and distribution costs. However, physical games may have resale value, potentially offsetting their initial cost.
Q2. Which format offers better long-term value?
Answer: This depends on individual preferences and circumstances. While digital games may offer convenience and lower initial costs, physical games can retain resale value and provide a sense of ownership.
Q3. Are physical games more reliable than digital ones?
Answer: Physical games aren’t reliant on internet connectivity and aren’t prone to potential digital rights management (DRM) complications. Nonetheless, they can be vulnerable to physical damage or loss.