What is Distribution Management?
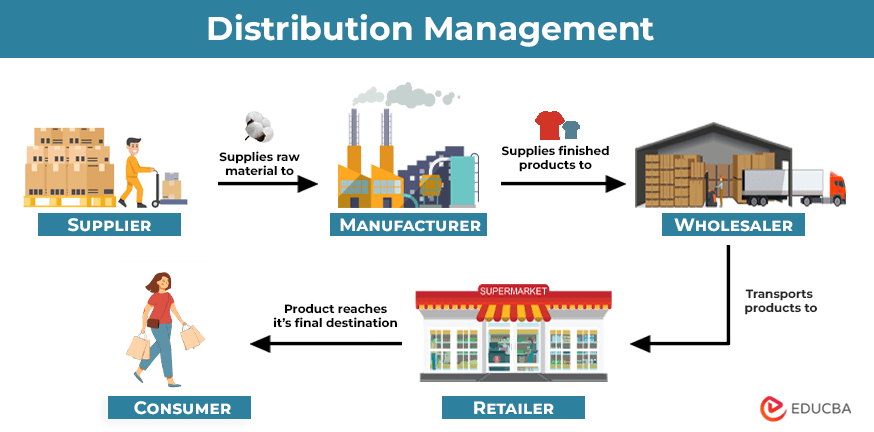
Distribution management refers to planning and transporting the products from the place of manufacturing to where they are sold. It involves transporting raw materials from suppliers to manufacturers, finished products from manufacturers to wholesalers or retailers, and lastly to customers.
It is an important step in supply chain and inventory management to ensure that manufacturer products reach their destinations in a timely and good condition to meet customer demands. Therefore, effective distribution management is necessary to maintain a competitive position in the market, minimize costs, improve profit margins and inventory turnover rate, and maximize customer satisfaction.
Table of Contents
- What is Distribution Management?
- Channels
- Process
- Strategies
- Challenges
- Advantages & Disadvantages
- Distribution vs. Logistics
Channels of Distribution Management
A distribution channel is a medium through which manufacturers distribute products or services to customers.
#1 Wholesaler
Wholesalers purchase bulk quantities of finished products from the manufacturer at a low price. They then send it to distributors or retailers. Some wholesalers also provide raw materials to manufacturers to make finished goods.
#2 Retailer
Retailers purchase products from wholesalers, suppliers, or directly from manufacturers. Retailers then sell those products to consumers through various sales vendors.
#3 Distributor
A distributor is an intermediate between a manufacturer and wholesalers/retailers. When manufacturers increase their product sales, they hire licensed distributors.
#4 E-commerce
The digital era has replaced traditional digital channels with e-commerce platforms and direct-to-customer (DTC) models. Here, the online e-commerce website displays the products, and once the customer places an order, items are picked from the inventory or warehouse and distributed directly to the consumer.
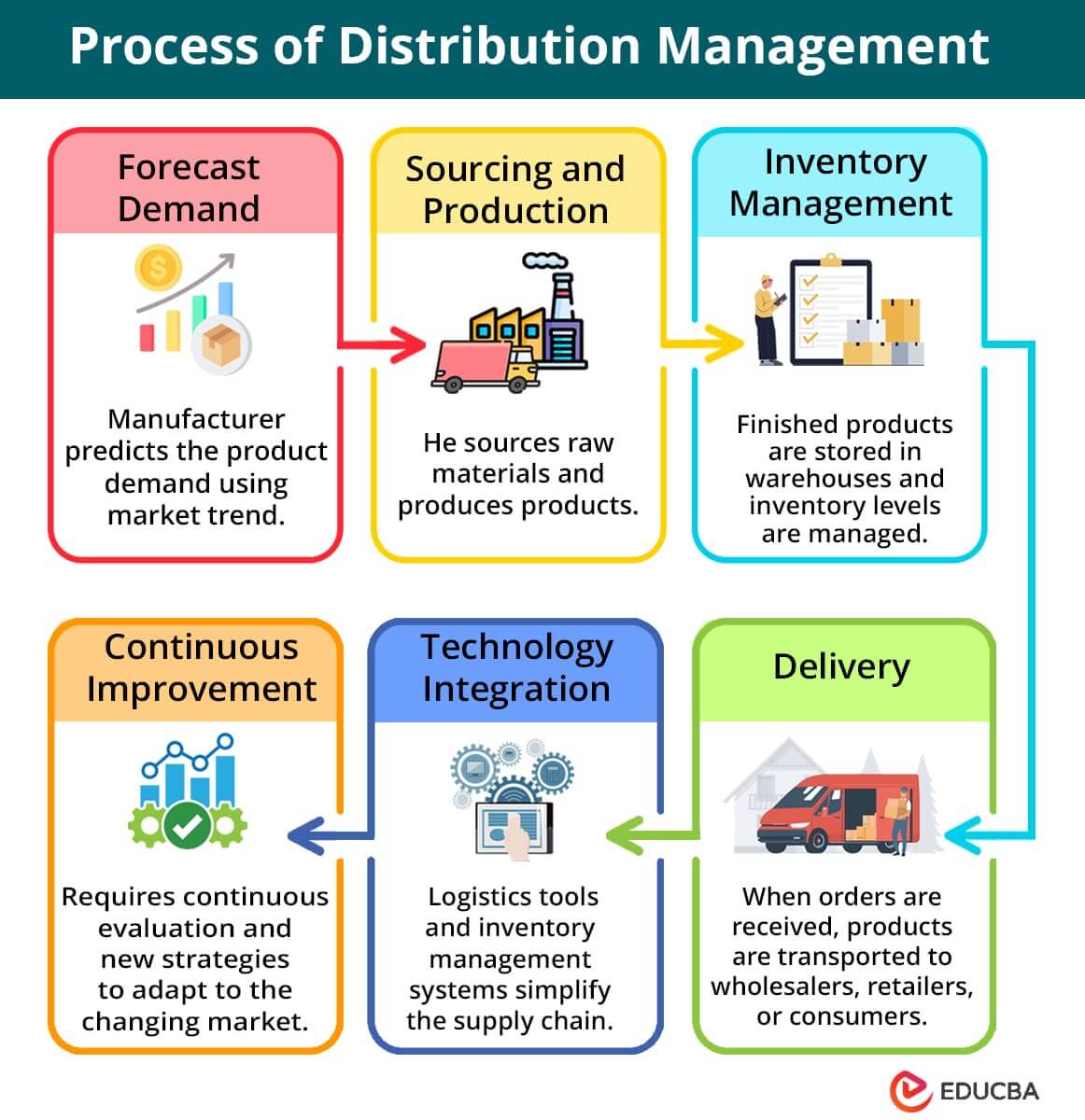
Process of Distribution Management
The process of distribution management is as follows.
Step #1: Forecast Demand
Manufacturers predict customer demand for products using sales patterns and market trends. They forecast the required quantity of products and plan distribution channels, inventory levels, and logistical strategies accordingly.
Step #2: Sourcing and Production
Manufacturers then buy raw materials and manufacture products and ensure they meet quality standards before distribution.
Step #3: Inventory Management
Now, finished products get stored in warehouses of manufacturing facilities or distribution centers. Here, inventory levels are managed for efficient distribution, maintaining supply and demand to prevent overstocking or shortages.
Step#4: Delivery
Once orders are received, manufacturers transport products from warehouses to distributors, retailers, or directly to consumers.
Step#5: Technology Integration
Technology like inventory management systems, logistics software, and tracking tools will help track products, streamline operations, improve efficiency, and simplify the supply chain.
Step#6: Continuous Improvement
Thus, distribution management requires continuous evaluation and implementation of new strategies to adapt to changing market conditions and optimize the distribution process.
Strategies of Distribution Management
Distribution management strategies are plans and approaches businesses use to move products to consumers efficiently. Some common distribution management strategies include:
1. Direct Distribution (DTC)
The direct distribution strategy involves selling products directly from manufacturers to consumers without intermediaries through company-owned stores, websites, or catalogs.
2. Indirect Distribution
The indirect distribution strategy involves using intermediaries like wholesalers, retailers, or distributors to sell products to consumers. This strategy helps to reach the target market and reduces the burden of sales efforts on the company.
3. Mass
The mass strategy helps distribute the products to a large number of customers. Manufacturers distribute their products through numerous channels and vendors to reach every market.
4. Selective
The selective strategy involves companies selling their products through only a limited number of suppliers. This strategy aims to distribute products to a selective or specific group of people and target markets to ensure better sales control.
5. Exclusive
The exclusive strategy is applied by companies who want to distribute their products to a highly limited group. It’s for premium and exclusive goods to control brand image and integrity. For example, Apple carefully sells its products to selected authorized retailers or carriers within specific regions or markets.
Challenges of Distribution Management
The following are some distribution management challenges companies face while managing product distribution.
1. Natural disruptions
Climate change or unpredictable weather conditions like floods and earthquakes can damage crops, leading to a shortage of raw materials. It affects inventory, leading to shortages in warehouses and disturbing supply chains.
2. Transportation Issues
Sometimes, natural disasters like earthquakes can damage transportation routes and cause delays in delivery services. Other challenges include traffic, lack of vehicles, accidents that cause an increase in maintenance cost, delays in flight carrying products, and disruption in the transportation system and overall delivery timeline.
3. Pandemics
Pandemics can severely disrupt global supply chains. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a shortage of raw materials and products, closures of many small-scale industries, shortages in labor or workers, and more.
4. Lack of Skilled Workers
It is challenging for companies to find and retain skilled workers for distribution operations. A lack of trained workers and specialized professionals can pressure companies to spend more on training and recruiting processes. A lack of skilled workers may lead to errors in handling goods or inventory management.
5. Economic Issues
Fluctuating currency exchange, market volatility, inflation, recessions, and trade policy changes can impact expenses, demand, pricing, and supply chains. Companies must adopt proper strategies to adapt to changing economic conditions in distribution management.
6. Inaccurate inventory management
Inaccuracies in inventory tracking and management can result in overstocking or stockouts. If goods are there in the warehouse for a longer time, they will get damaged, causing a loss to the company. It will increase storage costs and cause product delays, causing customer dissatisfaction and indirectly damaging the brand’s reputation.
7. Shipment issues or delays
Issues with shipments, such as damaged goods, customs clearance delays, or documentation errors, can disrupt the flow of products. Other challenges include issues in packaging, quality control problems, changes in shipment address, and returning damaged goods, which also cause a loss to the company.
8. Supply chain shortages
Disruptions in the supply chain due to raw material shortages, production delays, or supplier issues can lead to insufficient inventory levels and hinder timely deliveries.
9. Customer Expectations
Customer demands for faster deliveries, flexible shipping options, and real-time tracking can cause the implementation of new technologies, which leads to expenses and creates pressure on the distribution systems.
10. Globalization Challenges
Companies operating in global markets deal with diverse regulations, cultural differences, longer periods of supply chains, and varying consumer preferences, making it difficult to distribute products across borders.
Advantages and disadvantages of Distribution Management
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of distribution management.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It ensures that customers receive the finished products efficiently, at the right time, and at the right quality. | It may cause delays or disruptions in delivery due to many factors. |
| The intermediator acts as a medium to transport products. | The manufacturer may have to share profit with the intermediator, increasing product price. |
| It strengthens the relationships with distributors, retailers, or suppliers. | It may be challenging to coordinate and control multiple distribution channels. |
Distribution vs. Logistics
The following is the difference between distribution and logistics in the supply chain.
| Particulars | Distribution | Logistics |
| Definition | It is the process of transporting finished goods from manufacturers to consumers. | It is the complete process of organization, storing, and moving of products from the beginning stage to the end users. |
| Focus | To deliver products to end consumers. | To manage the supply chain. |
| Types | Retailers, wholesalers, e-commerce platforms, and distributors. | Reverse logistics, Inbound logistics, outbound logistics, etc. |
| Activities | Order fulfillment, packaging, storage, transportation, and customer service. | Supply management, inventory management, fleet management, delivery management, warehousing, and shipment tracking. |
| Challenges | Maintaining inventory levels, transportation costs, timely delivery, and market demand fluctuations. | Complexity in supply chain, high logistics management process cost, and advanced technology |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the factors that influence distribution management?
Answer: There are numerous factors impacting distribution management, including market demand, product characteristics, advancements in technology, and the role of intermediaries. These factors influence the decision process regarding distribution strategies, like efficiently moving goods to consumers by meeting market demands.
Q2. What is the importance of distribution management?
Answer: Distribution management is important as it ensures products get to the right place, at the right time, and in good shape. It helps meet customer demands, control product costs, and improve customer satisfaction by making quality goods available to them when and where needed.
Q3. How do you choose a distribution management system?
Answer: Selecting a distribution management system involves the following steps.
- Evaluate your business requirements, such as company size, product types, and target market.
- Conduct thorough research on the available distribution management systems, study their features, and check compatibility with existing infrastructure for easy implementation.
- Additionally, consider the overall costs, including the initial setup expenses and ongoing support provided by the system providers.
- Seek feedback from industry experts and select a system that meets business needs and provides adequate support for operation within your business.
Recommended Articles
We hope this information about “Distribution Management” was beneficial and informative. To learn more, check out the following articles.