Updated November 27, 2023

Difference Between Dividend vs Growth
The difference between Dividend vs Growth stock arises due to the decisions made by the management. When the company makes a profit, it has two options: either return it to the investors as a dividend, and the second is to invest it back in the company.
The company that believes it will generate higher returns by investing in the company than it might have in other investments does not pay dividends. Some companies have just started and have the scope for further expansion and opportunities. On the other hand, dividend-paying companies are mature and stable and believe that future growth is limited, so they would rather pay the investors and find better investment opportunities.
Because of these differences, both companies attract different types of investors with different investment objectives. Investors are differentiated based on risk capabilities, Risk seeking, Risk-neutral, and Risk aversion. Risk-seeking investors opt for growth companies, while risk-averse investors opt for a Dividend stock. Risk-neutral investors may have a portfolio combining both or comprising only dividend or growth stock.
Head To Head Comparison Between Dividend vs Growth (Infographics)
Below is the top 9 difference between Dividend vs Growth
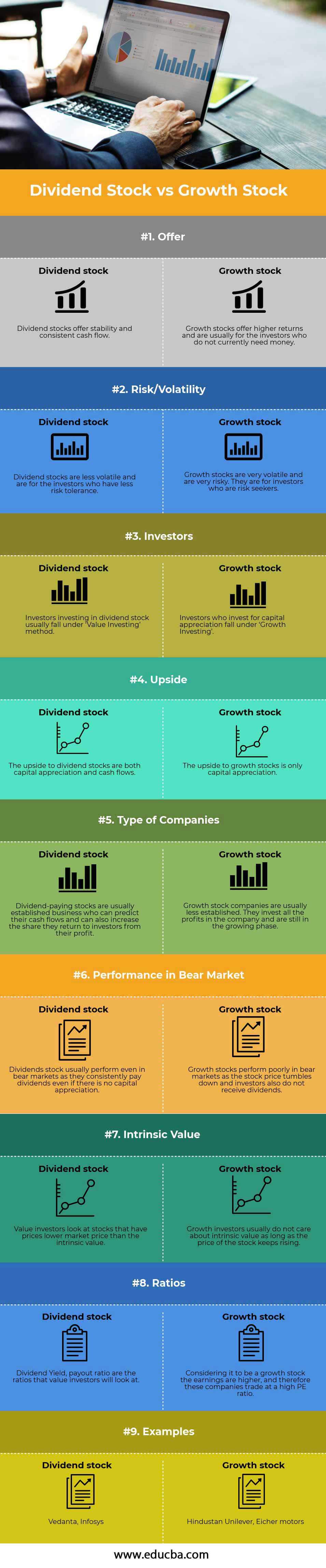
Key Differences Between Dividend vs Growth
Both Dividends vs Growth are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences between Dividend vs Growth
- The classification of a company is dividend or growth, as it is determined by how it treats profits. Companies that invest the profit back in their operations or expansion are considered growth companies. On the other hand, companies that pay dividends to their investors rather than invest in their operations are considered dividend-paying companies.
- Dividend stocks offer stability and consistent cash flows, while growth stocks give higher returns and are meant for young investors and investors who do not need money immediately.
- Risk-seeking investors usually opt for growth stocks as there is high volatility involved and are prone to market cycles; on the other hand, risk-averse investors opt for dividend-paying stocks as the risk involved with these stocks is limited.
- Dividend-paying stocks are usually established businesses that can predict their cash flows and increase the share they return to investors from their profit. Growth stock companies are usually less established. They invest all the profits in the company and are still in the growing phase.
- Investors investing in dividend stock usually fall under the ‘Value Investing’ method, while Investors who invest for capital appreciation fall under ‘Growth Investing’
- Dividend stocks provide both capital appreciation as well as dividends. Growth stocks usually never pay a dividend and only have capital appreciation.
- Dividend stock usually performs even in bear markets as they consistently pay dividends even if there is no capital appreciation. Growth stocks perform poorly in bear markets as the stock price tumbles and investors do not receive dividends.
- Value investors look at stocks with lower market prices than the intrinsic value. Growth investors usually do not care about intrinsic value as long as the stock price keeps rising.
- Dividend yield, the payout ratio, is the ratio that dividend investors usually look at before investing. Growth investors look at PE ratios, EBITDA growth, and PAT growth before investing; both these ratios, however, look at the company’s performance to peers.
- Examples of high dividend-paying companies in the Indian market are Vedanta and Infosys, while growth companies are Eicher Motors, Hindustan Unilever, etc.
Dividend vs Growth Comparison Table
Below is the 9 topmost comparison between Dividend vs Growth
| Basis of Comparison | Dividend stock | Growth stock |
| Offer | Dividend stocks offer stability and consistent cash flow | Growth stocks offer higher returns and are usually for investors who do not currently need money |
| Risk/Volatility | Dividend stocks are less volatile and are for investors with less risk tolerance. | Growth stocks are very volatile and are very risky. They are for investors who are risk-seekers |
| Investors | Investors investing in dividend stock usually fall under the ‘Value Investing’ method. | The Investors who invest for capital appreciation fall under ‘Growth Investing’ |
| Upside | The upside to dividend stocks is both capital appreciation and cash flows | The upside to growth stocks is only capital appreciation |
| Type of Companies | Established businesses, capable of predicting their cash flows and increasing the shares returned to investors from their profits, typically pay dividends. | Growth stock companies are usually less established. They invest all the profits in the company and are still in the growing phase. |
| Performance in Bear Market | Dividend stocks usually perform even in bear markets as they consistently pay dividends without capital appreciation. | Growth stocks perform poorly in bear markets as the stock price tumbles and investors do not receive dividends. |
| Intrinsic Value | Value investors look at stocks with lower market prices than the intrinsic value. | Growth investors usually do not care about intrinsic value as long as the stock price keeps rising. |
| Ratios | Dividend Yield and payout ratio are the ratios that value investors will look at | Considering it to be a growth stock, the earnings are higher; therefore, these companies trade at a high PE ratio. |
| Examples | Vedanta, Infosys | Hindustan Unilever, Eicher motors |
Conclusion
Selecting the type of stock depends on the investment style, age group, goals, and income. A young investor can invest most of his money in high-growth stocks because a young investor has a long career and a long time to recover from market fluctuations.
If the investor develops a good portfolio at the beginning of his career, it will exponentially affect the portfolio size when he is old. As the investor ages, he can transfer the growth portfolio to a stable dividend portfolio to reduce the blow in a market turmoil.
However, these are not the fixed mantra for investing. An investor may have a combination of both Dividends vs Growth stocks even when he is young, or an investor at very old age may have a portfolio comprising only growth stocks. This type of portfolio depends on the type of investor and his objectives and income.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Dividends vs Growth. Here, we also discuss the key differences between the Dividend Stock vs Growth Stock with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.


