Updated November 27, 2023
Difference Between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date
Ex-Dividend Date: The ex-Dividend date is two days before the record date. This is because trade gets settled in T + 2 days. The owner of the stock on the day before the ex-dividend date will receive the dividend. Ex-dividend date onward, the new stock buyer will not get a dividend. A stock price decreases on the ex-dividend date by an amount roughly equal to the dividend paid because a dividend decreases a company’s asset, which will reflect in the stock price.
Record Date: A record date is when whoever holds the share will receive the dividend. An investor must buy shares before the ex-dividend date to own them on the record date and be eligible for the dividend. Even though investors are holding shares for months and selling shares just before the ex-dividend date will disqualify investors from the dividend payment.
A dividend is a profit distributed to a shareholder by the company. One must understand four important dividend dates to understand the basics of dividends.
- Declaration Date
- The Ex-Dividend Date
- The Record Date
- The Payment Date
Declaration date: The date the company’s board of directors announces its approved dividend payment. On the declaration date, a board of directors announces the record date & the payment date.
Payment date: The payment date Is when the actual dividend is paid via bank account transfer or checks.
Example of the dividend important dates
|
Type |
Date |
Notes |
| Declaration Date | July 21, 2017 | Infosys announced a dividend |
| Ex-Dividend Date | Sep 14, 2017 | The date before you must buy the share to be eligible for dividend payment. |
| Record Date | Sep 16, 2017 | The date on which you must be on the books as a shareholder to receive the dividend |
| Payment date | Oct 2, 2017 | The date on which Infosys pays a dividend to its shareholders. Investors on the book as shareholders as of Sep 16, 2017, will get a dividend. |
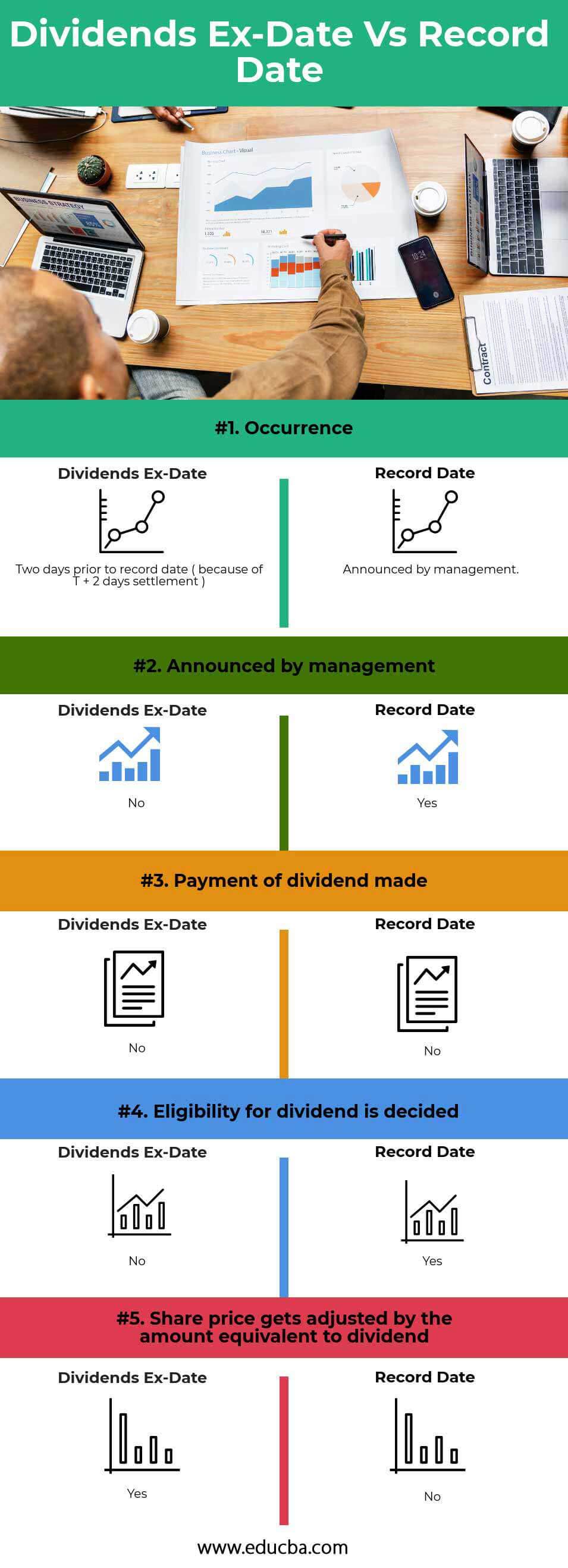
Head To Head Comparison Between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 difference between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date
Key Differences Between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date
Both Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date
The ex-dividend date is two days before the record date.
Stock price gets adjusted by the amount of dividend on the ex-dividend date.
The management announces the record date. A buyer on the ex-dividend date will not be eligible for the dividend, but the seller will be eligible for the dividend.
Comparison Table
Below is the 5 topmost comparison between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date
| Parameter | Ex-Dividend Date | Record Date |
| Occurrence | Two days before the record date ( because of T + 2 days settlement ) | Announced by management |
| Announced by management |
No |
Yes |
| Payment of dividend made |
No |
No |
| Eligibility for the dividend is decided |
No |
Yes |
| Share price gets adjusted by the amount equivalent to a dividend |
Yes |
No |
Conclusion
To be eligible for the dividend,
- You should buy shares before the ex-dividend date
- You should be on the book as a shareholder on the record date announced by the management at the time of declaration.
- Stock price gets adjusted almost equivalent to the dividend declared amount.
- If you purchase stock after the ex-dividend date or on the ex-dividend date, you will not be eligible for the dividend.
- If you are eligible for the dividend, you will receive a dividend on the payment date.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Dividends EX-Date vs Record Date. Here, we also discuss the key differences between infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.