Updated May 20, 2023
Introduction to Django HttpResponseRedirect
The procedure may assign the final results as a reaction. This reaction can be any formulated object that you expect to position as an output to the webpage. From that point on, we assign the response item to a variable. You will use this variable to set up the responses. The reaction techniques and attributes are, in large part, useful. They are useful in putting in place the attributes and values for the attributes which might be used.
Syntax:
response = Httpresponseredirect(response item)According to the above syntax, you encapsulate the intended response item within an Httpresponseredirect method. After formulating this output, you can further encapsulate it using an Httpresponseredirect approach to generate the reaction item. Once you generate the reaction item, you assign it to a variable and dispatch it as output.
Django HttpResponseRedirect Methods
| Httpresponse attribute | Description |
| HttpResponse_redirect.__init__(content=”, content_type=None, status=200, reason=None, charset=None) | The content page and content type are associated with the response object |
| HttpResponse_redirect.__setitem__(header, value) | The value is associated with the header name |
| HttpResponse_redirect.__delitem__(header) | Deletes a specific header |
| HttpResponse_redirect.__getitem__(header) | Returns a value for the specific header name |
| HttpResponse_redirect.has_header(header) | It returns True or False based on a case-insensitive check for a header with the provided name. |
| HttpResponse_redirect.setdefault(header, value) | Allows to formulate a default header value |
| HttpResponse_redirect.write(content) | The response for file-like objects is created using this. |
| HttpResponse_redirect.flush() | Allows the response object to get flushed |
| HttpResponse_redirect.tell() | A file-like object will be created in the response |
| HttpResponse_redirect.getvalue() | It is used to get the value of HttpResponse_redirect.content. |
| HttpResponse_redirect.readable() | A stream-like object will be created in the response |
| HttpResponse_redirect.seekable() | It makes the response object reachable |
Changes in Models.py file:
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# Model variables
# Create your models here.
class Object(models.Model):
Django_response_redirect__Example_name = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_thegai = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_State = models.CharField(max_length=50,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_District = models.CharField(max_length=50,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Address = models.TextField(null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Phone = models.BigInteger_Example_Field(null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_profession = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_salary = models.BigInteger_Example_Field(null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Under_Graduation_Degree = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Under_Graduation_college = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Post_Graduation_Degree = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Post_Graduation_college = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Rasi = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Nakshatra = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Post_Graduation_Degree = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Post_Graduation_college = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
Django_response_redirect__Example_Rasi = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.nameCreate a view for the form:
The shop technique will take location with the shape.shop() method. Next, you fetch and save the current logged-in user information onto the form. This is how the shape garage will take location. Once you successfully save the shape, you can render it directly to the browser using a render method.
def Main_page(request):
Post_keys = []
Object_id_str_list = []
Objects = Object.objects.all()
# Object_Image = Objects.Image
# context2['Image'] = Object_Image
context = {'Objects':Objects}
if request.method == 'GET':
State = request.GET.get('state', '')
District = request.GET.get('district', '')
thegai = request.GET.get('thegai', '')
Rasi = request.GET.get('Rasi', '')
print(len(State),len(District),District, Rasi)
if len(State) > 0:
Filter_context = {}
Object = Object.objects.filter(State=str(State))
Filter_context = {'Objects':Object}
return render(request,'Mainpage.html',Filter_context)
if len(District) > 0:
Filter_context = {}
Object = Object.objects.filter(District=str(District))
print(Object)
Filter_context = {'Objects':Object}
return render(request,'Mainpage.html',Filter_context)
if len(thegai) > 0:
Filter_context = {}
Object = Object.objects.filter(thegai=str(thegai))
print(Object)
Filter_context = {'Objects':Object}
return render(request,'Mainpage.html',Filter_context)
if len(Rasi) > 0:
Filter_context = {}
Object = Object.objects.filter(Rasi=str(Rasi))
print(Object)
Filter_context = {'Objects':Object}
return render(request,'Mainpage.html',Filter_context)
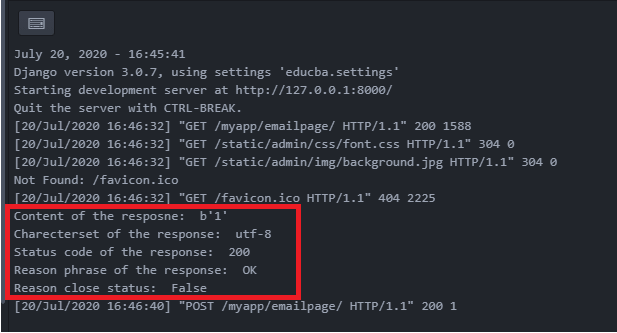
print("Content of the resposne: ",responseredirect.content)
print("Charecterset of the response: ",responseredirect.charset)
print("Status code of the response: ",responseredirect.status_code)
print("Reason phrase of the response: ",responseredirect.reason_phrase)
print("Reason close status: ",responseredirect.closed)
return render(request,'Mainpage.html',context)
@login_required
def profile_reg_user(request):
Filter_context = {}
current_user = request.user
Object = Object.objects.filter(Creator=current_user)
Filter_context = {'Objects':Object}
print("Content of the resposne: ",responseredirect.content)
print("Charecterset of the response: ",responseredirect.charset)
print("Status code of the response: ",responseredirect.status_code)
print("Reason phrase of the response: ",responseredirect.reason_phrase)
print("Reason close status: ",responseredirect.closed)
return render(request,'Profiles_reg_user.html',Filter_context)
@login_required
def form_update(request,pk):
update_profile = Object.objects.get(id=pk)
form = Valueform(instance=update_profile)
context = {'form':form}
if request.method == 'POST':
form = Valueform(request.POST,instance=update_profile,files=request.FILES)
print(form)
if form.is_valid():
post = form.save()
post.Creator = request.user
print('Creator user stored',request.user)
post.save()
obj = form.instance
return render(request,'form.html', {"obj": obj,"form": form})
print("Content of the resposne: ",responseredirect.content)
print("Charecterset of the response: ",responseredirect.charset)
print("Status code of the response: ",responseredirect.status_code)
print("Reason phrase of the response: ",responseredirect.reason_phrase)
print("Reason close status: ",responseredirect.closed)
return render(request,'form.html', {"form": form})url.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.conf.urls import url
from matrimony_pages import views
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
urlpatterns = [
url(r'Jsoncheck/',views.Json_Response,name='Json_Response'),
url(r'^$',views.Welcome_page,name='Welcome_page'),
url(r'Mainpage/',views.Main_page,name='Main_page'),
url(r'all/',views.All_users,name='all'),
url(r'form/',views.form_view,name='form_view'),
url(r"signup/", views.Sign_up_request, name="register"),
url(r"login/", views.login_request, name="login"),
path(r'profile//',views.profile_page,name='profile'),
url(r'logout/',views.logout_request,name='logout'),
url(r'reg/',views.profile_reg_user,name='reg'),
path(r'update//',views.form_update,name='update'),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]+ static(settings.MEDIA_URL,document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)Form.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Django App1</title>
{% load static %}
<link href="{% static 'admin/css/font.css' %}" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body {
background-image: url("{% static 'admin/img/background.jpg' %}");
background-color: #acccbb;
}
.myDiv {
border: 5px outset red;
background-color: lightblue;
text-align: center;
font-family: "Comic Sans MS", cursive, sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
letter-spacing: 2px;
word-spacing: 1.8px;
text-align: left;
color: #02071C;
font-weight: 200;
text-decoration: none;
font-style: normal;
font-variant: normal;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> <u> DJANGO HANDELING EMAILS </u> </h1>
<nav class='navbar'>
<div class='navbar_div'>
<a class="navbar" onclick="redirect2()" >Home! </a>
<a class="navbar" onclick="redirect2()" >Contact</a>
</div>
</nav>
<div class="tablediv">
<script>
function form1() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/form";
}
function redirect1() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/Mainpage";
}
function redirect2() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/";
}
function redirect3() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/login";
}
function redirect4() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/signup";
}
function redirect5() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/";
}
function redirect6() {
window.location.href = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/logout";
}
/* Open when someone clicks on the span element */
function openNav() {
document.getElementById("myNav").style.width = "100%";
}
/* Close when someone clicks on the "x" symbol inside the overlay */
function closeNav() {
document.getElementById("myNav").style.width = "0%";
}
</script>
<div class="body">
<br>
{% block content %}
<form method="PUT" class='formarea' enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div class='formdiv'>
{{ form.as_p }}
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" class='button' value="Update">
</div>
</form>
{% endblock content %}
<div class="myDiv" style = "max-width:470px;">
<form method = 'POST' ">
{{ email.as_p }}
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="submit" style="text-align:center">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Conclusion
In the Django framework, the article mentions the creation of the HTTPResponseRedirect object. Furthermore, the thing explains the method of printing the reaction cost again withinside the console. The values are displayed withinside the console.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Django HttpResponseRedirect” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.