Updated June 8, 2023
Difference Between DOS and Windows
- DOS or Disk Operating Systems are the very initial operating systems of the computer world. This was an era when computers were not advanced graphically. There used to be a plain screen with a black/blue background and white textual commands written on it. This was the Disk Operating System.
- Windows Operating System is the most advanced and modern version. It has all the fancy graphics to make the visuals more appealing. The textual commands have been replaced with colorful interactive icons that respond to mouse clicks, human touch, and voice commands.
Head to Head Comparison between DOS and Windows
Below are the top 11 differences between DOS vs Windows:
Key Differences between DOS and Windows
Let us discuss some of the significant differences between DOS vs Windows.
- The major difference between DOS and Windows is the interface. As stated above, DOS is a simple interface where you give text commands for everything. This is similar to the command prompt terminal in modern-day Windows OS.
- Windows uses graphics to provide a more visually appealing interface. The introduction of the mouse made it easy to use. There was no longer any need to remember commands. All you had to do was click the mouse. Graphics also made it possible to play movies, images, and games on the computer.
- Of course, there were many other enhancements regarding storage systems, security, networking, etc. Windows was an advanced version of computing technology, and advancements in integrated circuits and compact memory chips supported this.
Fun Fact
- After reviewing the complete article, did it make you wonder, “Why the name Disk Operating System”? The nomenclature was so because it was considered a considerable achievement to transfer commands from an external disk (floppy drive, hard disk, etc.) to computer memory (RAM) for execution. This was a radical advancement to its predecessor Tape Operating System (TOS), which involved magnetic tapes. Thus, the name DOS came into being. Today, any modern operating system is implicitly a disk operating system but isn’t explicitly named.
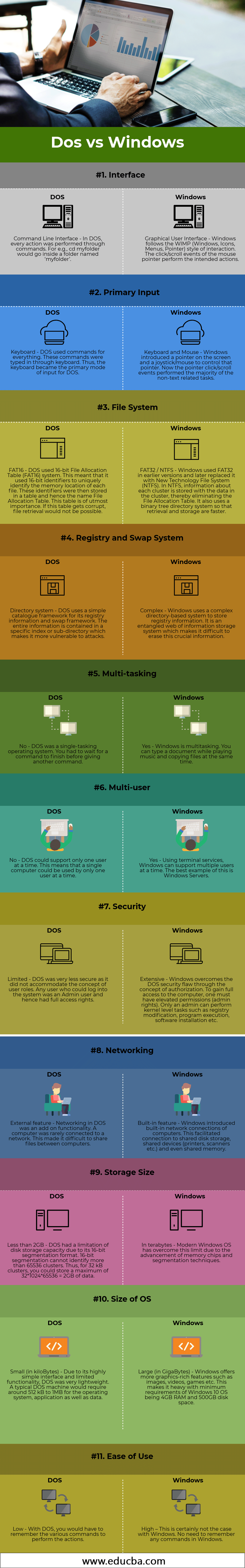
DOS vs Windows Comparison Table
Let us discuss the top 11 differences between DOS vs Windows:
| Basis of Comparison | DOS | Windows |
| Interface | Command Line Interface – In DOS, every action was performed through commands. E.g., cd my folder would go inside a folder named ‘myfolder’. | Graphical User Interface – Windows follows the WIMP (Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointer) interaction style. The click/scroll events of the mouse pointer perform the intended actions. |
| Primary Input | Keyboard – DOS used commands for everything. These commands were typed in through the keyboard. Thus, the keyboard became the primary mode of input for DOS. | Keyboard and Mouse – Windows introduced a pointer on the screen and a joystick/mouse to control that pointer. Now the pointer clicks/scroll events performed most of the non-text related tasks. |
| File System | FAT16 – DOS used a 16-bit File Allocation Table (FAT16) system. This meant that it used 16-bit identifiers to identify the memory location of each file uniquely. These identifiers were then stored in a table and hence the name File Allocation Table. This table is of utmost importance. If this table gets corrupted, file retrieval will not be possible. | FAT32 / NTFS – Windows used FAT32 in earlier versions and later replaced it with New Technology File System (NTFS). In NTFS, information about each cluster is stored with the data in the cluster, thereby eliminating the File Allocation Table. It also uses a binary tree directory system so that retrieval and storage are faster. |
| Registry and Swap System | Directory system – DOS uses a simple catalog framework for its registry information and swap framework. The entire information is contained in a specific index or sub-directory, which makes it more vulnerable to attacks. | Complex – Windows uses a complex directory-based system to store registry information. It is an entangled web of information storage system, which makes it difficult to erase this crucial information. |
| Multitasking | No – DOS was a single-tasking operating system. You had to wait for a command to finish before giving another command. | Yes – Windows is multitasking. You can type a document while playing music and copying files simultaneously. |
| Multi-user | No – DOS could support only one user at a time. This means that only one user could use a single computer at a time. | Yes – Using terminal services, Windows can support multiple users simultaneously. The best example of this is Windows Servers. |
| Security | Limited – DOS was very less secure as it did not accommodate the concept of user roles. Any user who could log into the system was an Admin user and had full access rights. | Extensive – Windows overcomes the DOS security flaw through the concept of authorization. To gain full access to the computer, one must have elevated permissions (admin rights). Only an admin can perform kernel-level tasks such as registry modification, program execution, software installation, etc. |
| Networking | External Feature – Networking in DOS was an add-on functionality. A computer was rarely connected to a network. This made it difficult to share files between computers. | Built-in Feature – Windows introduced built-in network connections of computers. This facilitated connection to shared disk storage shared devices (printers, scanners, etc.), and even shared memory. |
| Storage Size | Less than 2GB – DOS had a limitation of disk storage capacity due to its 16-bit segmentation format. 16-bit segmentation cannot identify more than 65536 clusters. Thus, for 32 kB clusters, you could store a maximum of 32*1024*65536 = 2GB of data. | In terabytes – Modern Windows OS has overcome this limit due to the advancement of memory chips and segmentation techniques. |
| Size of OS | Small (in kilobytes) – DOS was very lightweight due to its highly simple interface and limited functionality. A typical DOS machine would require around 512 kB to 1MB for the operating system, application, and data. | Large (in GigaBytes) – Windows offers more graphics-rich features such as images, videos, games, etc. This makes it heavy, with the minimum requirements of Windows 10 OS being 4GB RAM and 500GB disk space. |
| Ease of Use | Low – With DOS, you must remember the various commands to perform the actions. | High – This is certainly not the case with Windows. No need to remember any commands in Windows. |
Conclusion
DOS is no longer used in personal computing. Windows has a majority of the market share. However, even the breakthrough concept of WIMP faces challenges from newer advancements like touch-based OS, voice-based interfaces, gesture commands, and so on. As technology advances, so does human-computer interaction.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to DOS vs Windows. Here we also discuss the critical differences with infographics and comparison tables. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –