Updated April 5, 2023
Difference Between Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list
- The singly linked list and doubly linked list is a type of linked list to arrange memory and information.
- The singly linked list and doubly linked list is part of dynamic data structure to avoid memory wastage and traverse using element in the list.
- The doubly linked list is a function that contains data, next node, and previous node simultaneously.
- The singly linked list is a function that contains data and the next node only.
- The singly linked list is a simple linked list to traverse one way from the first node to the next node.
- The doubly linked list is a complex linked list to traverse both ways from one node to another and vice versa.
- The singly linked list contains two parts, such as memory and pointer, but the last pointer becomes null.
- The doubly linked list contains three parts such as a previous pointer, memory node, and next pointer but the initial and last pointer becomes null.
Head to Head Comparison Between Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list
Key differences between Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list
Some of the key differences between Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list are given below:
- The doubly linked list is bidirectional because of two address pointer. Therefore, a singly linked list is unidirectional because of the one address pointer.
- The doubly linked list has occurred more memory space than the singly linked list.
- The singly linked list simple, whereas the doubly linked list, is a complex dynamic data structure of the list.
- The doubly linked list provides an empty head and tail pointer. Hence, a singly linked list provides an empty tail only.
- The doubly linked list more efficient than the singly list.
- The doubly linked list contains three parameters, and the singly linked list contains two parameters.
- The singly linked list image is given below.
- The doubly linked list image is given below.
- The doubly linked list gives time complexity O(1), whereas the singly linked list gives time complexity O(n).
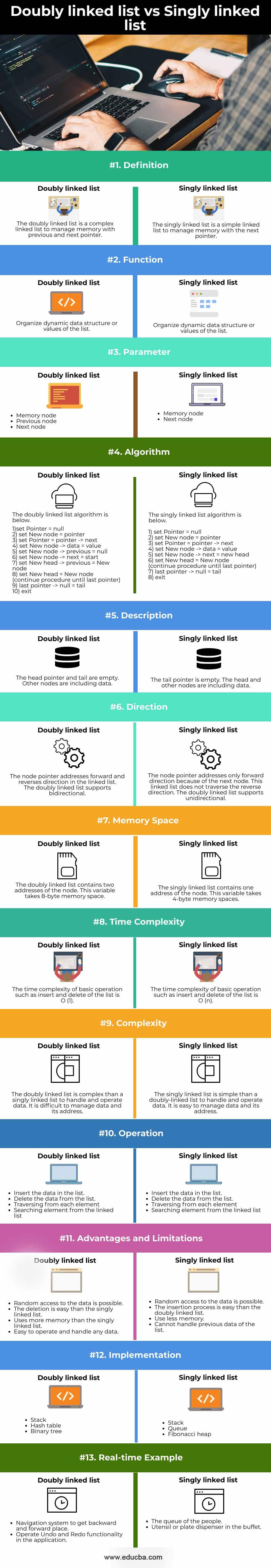
Comparison table
- The doubly linked list is a complex function, and the singly linked list is a simple data structure.
- The comparison table is displayed features and descriptions of the singly linked list and doubly linked list.
- The below table is showing similarities and differences of the type of the linked list.
| Features | doubly linked list | singly linked list |
| Definition | The doubly linked list is a complex linked list to manage memory with previous and next pointer. | The singly linked list is a simple linked list to manage memory with the next pointer. |
| Function | Organize dynamic data structure or values of the list. | Organize dynamic data structure or values of the list. |
| Parameter |
|
|
| Algorithm | The doubly linked list algorithm is below.
1) set Pointer = null 2) set New node = pointer 3) set Pointer = pointer -> next 4) set New node -> data = value 5) set New node -> previous = null 6) set New node -> next = start 7) set New head -> previous = New node 8) set New head = New node (continue procedure until last pointer) 9) last pointer -> null = tail 10) exit |
The singly linked list algorithm is below.
1) set Pointer = null 2) set New node = pointer 3) set Pointer = pointer -> next 4) set New node -> data = value 5) set New node -> next = new head 6) set New head = New node (continue procedure until last pointer) 7) last pointer -> null = tail 8) exit |
| Description | The head pointer and tail are empty. Other nodes are including data. | The tail pointer is empty. The head and other nodes are including data. |
| direction | The node pointer addresses forward and reverses direction in the linked list. The doubly linked list supports bidirectional. | The node pointer addresses only the forward direction because of the next node. This linked list does not traverse the reverse direction. The doubly linked list supports unidirectional. |
| Memory space | The doubly linked list contains two addresses of the node. This variable takes 8-byte memory space. | The singly linked list contains one address of the node. This variable takes 4-byte memory spaces. |
| Time complexity | The time complexity of basic operation such as insert and delete of the list is
O (1). |
The time complexity of basic operation such as insert and delete of the list is
O (n). |
| complexity | The doubly linked list is complex than a singly linked list to handle and operate data. It is difficult to manage data and its address. | The singly linked list is simple than a doubly-linked list to handle and operate data. It is easy to manage data and its address. |
| Operation |
|
|
| Advantages and limitations |
|
|
| Implementation |
|
|
| Real-time Example |
|
|
Conclusion
- The singly linked list and doubly linked list make the application usable, handy, and manageable.
- The singly linked list and doubly linked list helps to manage and operate a list of data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list. Here we discuss the Doubly linked list vs Singly linked list key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –