What is Downstream?
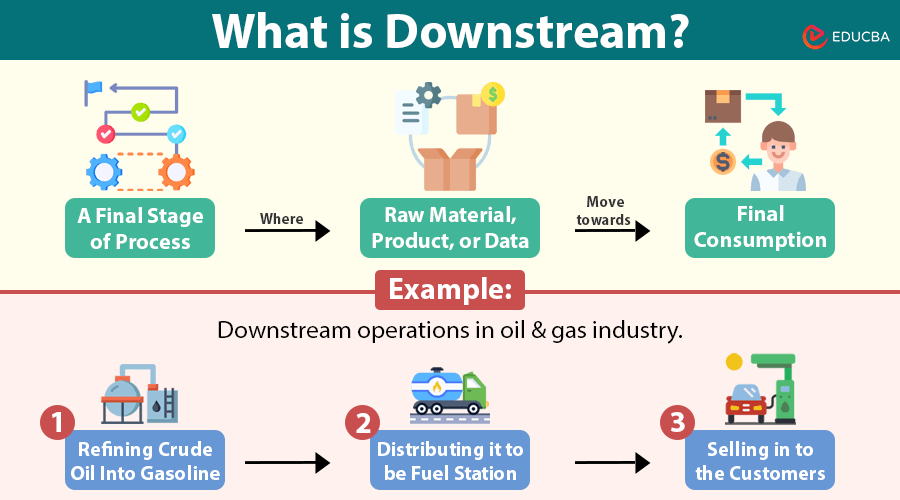
The term “downstream” refers to the latter stages of a process, where raw materials, products, or data move toward the final consumer or output. It is commonly used in industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, supply chain, and even data processing.
For example, downstream operations in the oil and gas industry include refining crude oil into gasoline, distributing it to fuel stations, and eventually selling it to consumers. Similarly, in a supply chain, downstream activities involve delivering finished products from warehouses to retailers or customers.
These processes are critical because they ensure the smooth movement of products and services from production to consumption. These activities directly impact quality, efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability. Without effective management, even the best-produced goods may fail to reach the intended market in the right condition and time.
Downstream in Different Industries
1. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, it refers to activities that occur after the extraction and production of crude oil or natural gas. It includes:
- Refining crude oil into usable products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
- Distributing refined products to wholesalers, retailers, and end-users.
- Marketing and selling fuels and other petroleum-based products.
2. Manufacturing Industry
In manufacturing, it include packaging, branding, and distributing products to consumers. For instance, after a car is assembled, the downstream phase covers quality checks, marketing, dealership distribution, and customer sales.
3. Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, its segment focuses on delivering products from warehouses to retail stores or directly to customers. It also involves customer service, after-sales support, and returns management.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceuticals, it refers to the purification and packaging of drugs after their synthesis. It includes filtration, drying, and quality testing before the drugs are distributed to hospitals and pharmacies.
5. Data Processing and IT
In data processing, it refers to the use of processed data to derive insights, make business decisions, or provide services. For example, after raw data is analyzed, the downstream phase includes report generation, dashboard visualization, and data-driven decision-making.
Challenges in Downstream Operations
Managing these activities comes with various challenges, including:
- Logistics and Distribution Issues: Ensuring timely delivery and maintaining product quality.
- Market Fluctuations: Changes in demand can affect inventory management and pricing.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industries like oil, pharmaceuticals, and food must meet strict legal requirements.
- Customer Satisfaction: Effective processes help retain customers through timely and quality service.
Strategies for Effective Downstream Management
To improve efficiency, businesses can implement the following strategies:
- Optimized Supply Chain Management: Using technology like AI and IoT for better logistics tracking.
- Quality Control Measures: Ensuring products meet industry standards before reaching customers.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Providing good after-sales support and seamless delivery services.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Using analytics to predict demand and manage inventory accordingly.
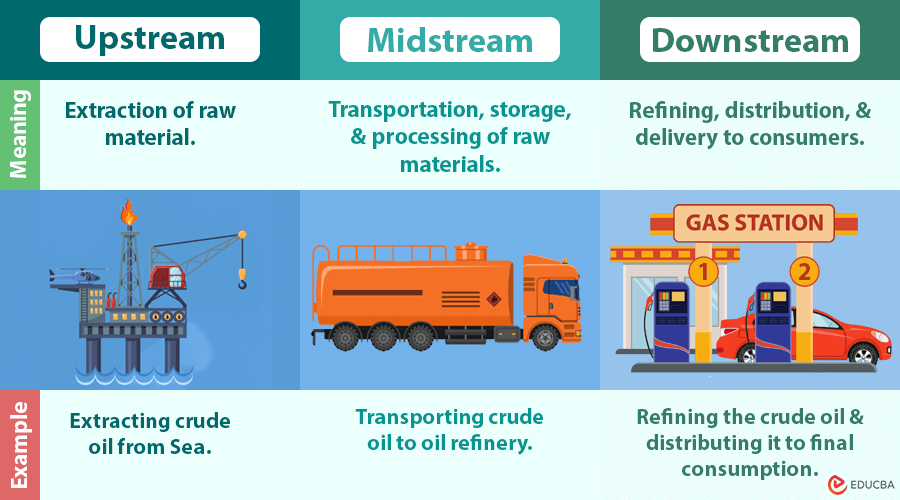
Downstream vs. Midstream vs. Upstream
| Aspect | Upstream | Midstream | Downstream |
| Definition | Initial stages of production, focusing on resource extraction or raw material acquisition. | Transportation, storage, and processing of raw materials between upstream and downstream. | Final stages of processing, refining, distribution, and delivery to consumers. |
| Industry Role | Involves exploration, drilling, and extraction of raw materials. | Focuses on moving raw materials efficiently through pipelines, shipping, or storage. | Involves refining, manufacturing, packaging, marketing, and sales. |
| Example (Oil & Gas) | Extracting crude oil from wells and transporting it to refineries. | Storing and transporting crude oil via pipelines, tankers, or terminals. | Refining crude oil into gasoline and selling it at fuel stations. |
| Example (Manufacturing) | Sourcing raw materials and assembling product components. | Transporting and storing semi-finished goods between factories or distribution centers. | Packaging, branding, and distributing finished products to customers. |
| Example (Supply Chain) | Procuring raw materials and managing initial logistics. | Moving goods through warehouses, distribution centers, and regional hubs. | Warehousing, order fulfillment, and last-mile delivery. |
| Example (Data Processing) | Collecting and storing raw data from various sources. | Transferring, structuring, and cleaning data for further analysis. | Analyzing data, generating reports, and using insights for decision-making. |
Final Thoughts
Downstream processes are key in many industries, helping products and services reach consumers efficiently. Managing these processes, from oil refining to manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and supply chains, improves business performance, customer satisfaction, and profits. Companies can enhance their operations by overcoming challenges and using modern strategies for lasting success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is technology impacting downstream operations?
Answer: AI, automation, IoT, and data analytics advancements help optimize processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
Q2. How does downstream impact pricing?
Answer: Downstream costs, such as refining, distribution, and marketing, contribute to the final price of goods. Market demand, competition, and global economic factors also influence pricing strategies.
Q3. How does the downstream affect consumers?
Answer: It ensures the availability, affordability, and quality of products. Efficient operations lead to faster deliveries, better prices, and improved customer experiences.
Q4. How does the downstream impact the economy?
Answer: Downstream industries contribute to GDP, employment, and trade. They drive consumption, create jobs, and generate revenue through taxation and investments.
Q5. How do downstream operations adapt to market changes?
Answer: Companies use demand forecasting, flexible supply chains, and digital transformation to stay competitive. They also adopt just-in-time inventory and dynamic pricing strategies to manage fluctuations.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on downstream has been helpful. Check out these recommended articles for more insights on supply chain management, logistics optimization, and industry best practices.